10 Medical Discoveries Made by Mistake
Some of the most important medical breakthroughs came from unexpected errors or surprising findings. These discoveries reshaped medicine in ways that scientists had never anticipated.
- Tricia Quitales
- 4 min read

Many groundbreaking medical discoveries were the result of unexpected errors or accidental observations. These fortunate mistakes have saved countless lives and transformed healthcare forever. Often, curiosity and careful observation turned these accidents into vital advancements. Exploring these moments highlights the unpredictable nature of scientific progress and the power of chance.
1. 1. Penicillin

United States Department of Agriculture on wikimedia
In 1928, Alexander Fleming noticed that a mold called Penicillium notatum had killed bacteria growing in one of his petri dishes. He realized this mold produced a substance that could fight bacterial infections. This accidental discovery led to the development of penicillin, the world’s first true antibiotic. It revolutionized medicine by providing an effective treatment for many deadly infections.
2. 2. X-rays
Wikibantu on wikimedia
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen discovered X-rays while experimenting with cathode rays in 1895. He noticed a glowing effect on a nearby screen, indicating an invisible type of radiation passing through objects. His accidental observation led to the creation of medical imaging, allowing doctors to see inside the body without surgery. The discovery quickly became an essential diagnostic tool.
3. 3. Insulin

MallardTV on wikimedia
In 1921, Frederick Banting and Charles Best isolated insulin while experimenting with pancreatic extracts. They initially struggled to produce a substance that lowered blood sugar in diabetic dogs. Their unexpected success gave hope for treating diabetes, a previously fatal disease. Insulin therapy transformed diabetes management and saved millions of lives.
4. 4. Pacemaker
Richardelainechambers on wikimedia
The invention of the cardiac pacemaker was partly accidental when electrical engineers were testing the stimulation of heart muscles. They realized that small electrical pulses could regulate irregular heartbeats. This led to the development of the first implantable pacemaker in the 1950s. The device has since saved countless patients from heart failure and sudden cardiac arrest.
5. 5. Warfarin
Alisa Machalek, NIGMS/NIH on wikimedia
Originally developed as a rat poison in the 1940s, warfarin was later found to be an effective blood thinner for humans. Doctors observed that patients exposed to the compound had a reduced risk of blood clots. Warfarin became a widely prescribed anticoagulant, preventing strokes and heart attacks. This accidental discovery dramatically improved cardiovascular treatment.
6. 6. Smallpox Vaccine
Tech. Sgt. Jim Varhegyi on wikimedia
Edward Jenner discovered the smallpox vaccine in 1796 after noticing milkmaids who contracted cowpox did not catch smallpox. His hypothesis was based on an observation linking cowpox exposure to immunity. Jenner’s experiment involved inoculating a boy with cowpox to protect him from smallpox. This accidental insight laid the foundation for modern immunology. The vaccine eventually led to the global eradication of smallpox.
7. 7. Botox

D. Schwarzburg on wikimedia
Botulinum toxin was originally studied as a dangerous poison causing paralysis. Researchers accidentally found that small doses could relax muscles and reduce wrinkles. This led to the cosmetic and therapeutic use of Botox for conditions like muscle spasms and migraines. What began as a feared toxin became a valuable medical tool.
8. 8. Anesthesia

National Museum of American History on wikimedia
Early attempts at anesthesia involved inhaling ether or nitrous oxide to reduce pain during surgery. The discovery that these substances could cause unconsciousness was unintentional but transformative. It allowed surgeons to perform more complex and longer procedures without causing pain to patients. Anesthesia revolutionized surgery and patient care.
9. 9. Lithium for Bipolar Disorder

Tomihahndorf on wikimedia
In the mid-20th century, lithium was initially used for gout treatment. Researchers noticed patients treated with lithium showed mood-stabilizing effects. This accidental observation led to its use in managing bipolar disorder. Lithium remains one of the most effective mood stabilizers available. It has improved the lives of millions struggling with mental illness.
10. 10. Helicobacter pylori and Ulcers
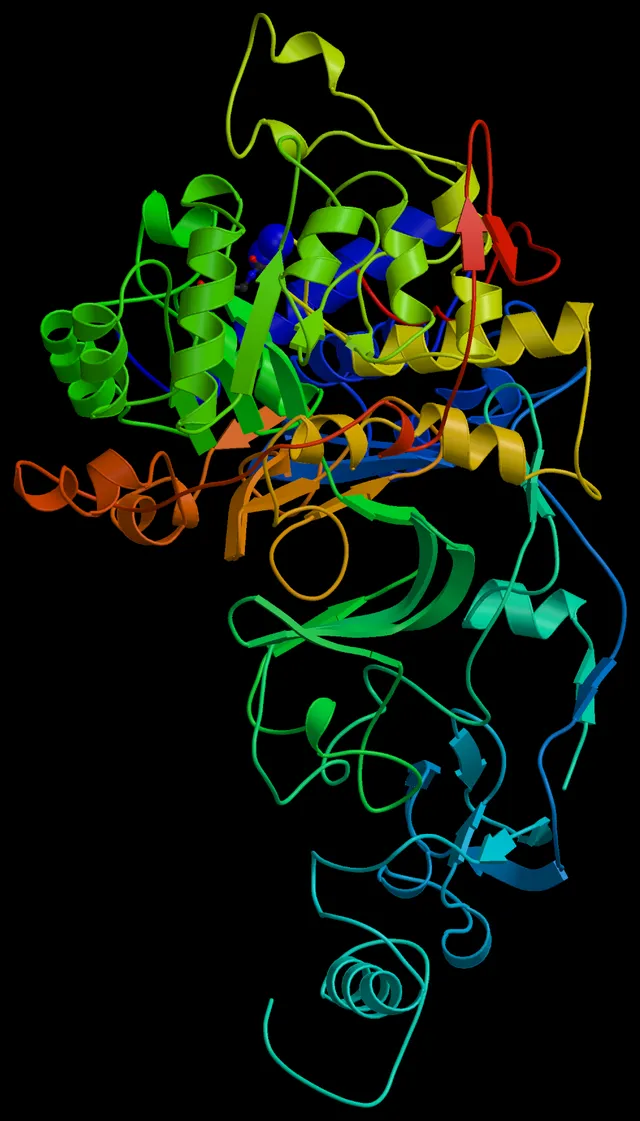
Jacobolus on wikimedia
Barry Marshall and Robin Warren discovered that a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori caused stomach ulcers. They made this breakthrough after noticing bacteria in stomach biopsies, which was previously thought impossible due to stomach acidity. Marshall famously drank the bacteria to prove it caused illness. This accidental discovery changed ulcer treatment from surgery to antibiotics.