10 Medical Treatments from History That Actually Worked
Many historical medical treatments were dismissed as folklore or superstition but proved to have real therapeutic value. Their effectiveness laid the groundwork for modern medical discoveries.
- Tricia Quitales
- 4 min read
Throughout history, medicine has seen a mix of trial, error, and surprising successes. Some ancient and historical treatments were remarkably effective despite the lack of modern scientific understanding. These methods ranged from herbal remedies to surgical techniques and have influenced modern medicine.
1. 1. Willow Bark for Pain Relief

Scampz on wikimedia
Willow bark was used in ancient Egypt and Greece to reduce pain and fever. The bark contains salicin, which the body converts into a compound similar to aspirin. Patients reported relief from headaches, inflammation, and fevers. Modern research confirms its effectiveness as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic. This natural remedy became the basis for one of the most widely used drugs today.
2. 2. Honey for Wound Healing

Scott Bauer, USDA ARS on wikimedia
Honey has been applied to wounds since ancient times due to its antibacterial properties. Its high sugar content inhibits bacterial growth and promotes tissue healing. Studies confirm that honey accelerates the recovery of minor cuts and burns. Ancient physicians observed faster healing and reduced infections in treated wounds. Honey remains a complementary treatment in modern wound care.
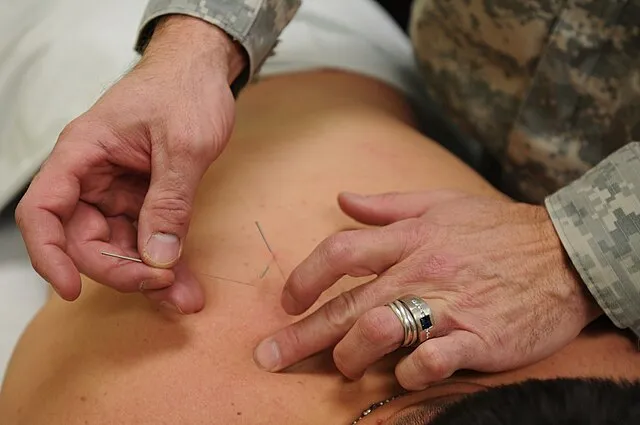
3. 3. Acupuncture for Pain Management
Pfc. Jennifer Kennemer, 16th MPAD on wikimedia
Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. It was traditionally used to balance energy and relieve pain. Modern studies show acupuncture can effectively reduce chronic pain, migraines, and osteoarthritis symptoms. The technique stimulates the nervous system and releases endorphins. Its continued use demonstrates the practical benefits of ancient knowledge.
4. 4. Mercury for Skin Diseases

A on wikimedia
Mercury compounds were used in ancient medicine to treat skin infections and syphilis. While toxic in large doses, controlled applications helped reduce bacterial infections. Historical reports indicate noticeable improvement in symptoms. Today, derivatives of mercury have been replaced by safer antibiotics. The treatment illustrates early recognition of chemical antimicrobial properties.
5. 5. Aloe Vera for Burns and Skin Care
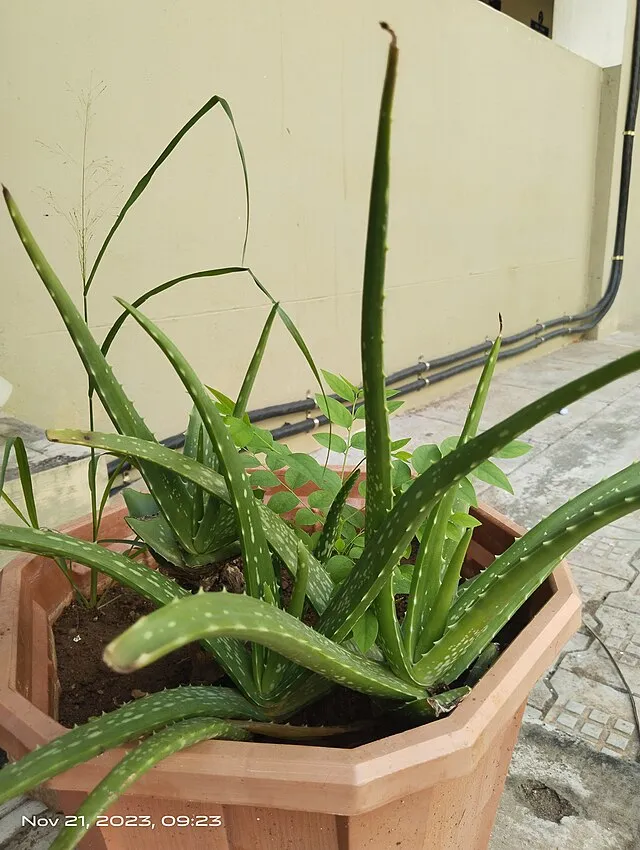

Shewagramji on wikimedia
Aloe vera has been applied for thousands of years to soothe burns and skin irritations. Ancient Egyptians referred to it as the “plant of immortality” for its healing abilities. Modern research confirms that aloe accelerates skin repair and reduces inflammation. Its gel contains vitamins, enzymes, and antioxidants that support recovery. Aloe remains a staple in dermatology and skincare products.
6. 6. Bloodletting for Certain Fevers
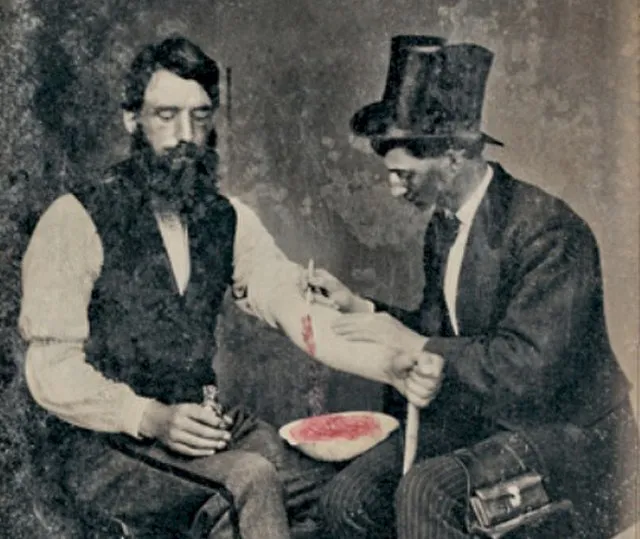

Burns Archive on wikimedia
Although often overused, bloodletting was effective in some cases of polycythemia and high blood pressure. Ancient physicians observed symptom relief in specific conditions. It helped regulate blood volume and reduce complications in extreme cases. Modern medicine replaced bloodletting with safer methods. Historical use shows observation sometimes led to valid interventions.
7. 7. Opium for Pain Relief

Public domain on wikimedia
Opium, derived from poppies, was used in ancient Greece and Egypt for severe pain. It contains morphine and codeine, which are powerful analgesics still in use today. Physicians documented relief from injuries, surgeries, and chronic pain. Modern medicine has developed safer dosing and administration methods. Its effectiveness highlights natural compounds with lasting medical impact.
8. 8. Castor Oil for Digestive Issues

Jengod on wikimedia
Castor oil was used for centuries as a laxative and to treat constipation. Ancient civilizations observed its strong effect on the digestive tract. Modern studies confirm its active compound, ricinoleic acid, stimulates intestinal movement. It remains a natural remedy for short-term constipation relief. Historical use emphasizes empirical understanding of plant-based treatments.
9. 9. Garlic for Infection Prevention

Fumikas Sagisavas on wikimedia
Garlic has been used since antiquity to combat infections and improve immune function. Its sulfur-containing compounds, such as allicin, exhibit antibacterial and antiviral properties. Historical records describe its use for wounds, respiratory infections, and digestive ailments. Modern research supports garlic’s efficacy as a natural antimicrobial agent. Its long history reflects practical experimentation and observation.
10. 10. Trepanation for Head Injuries
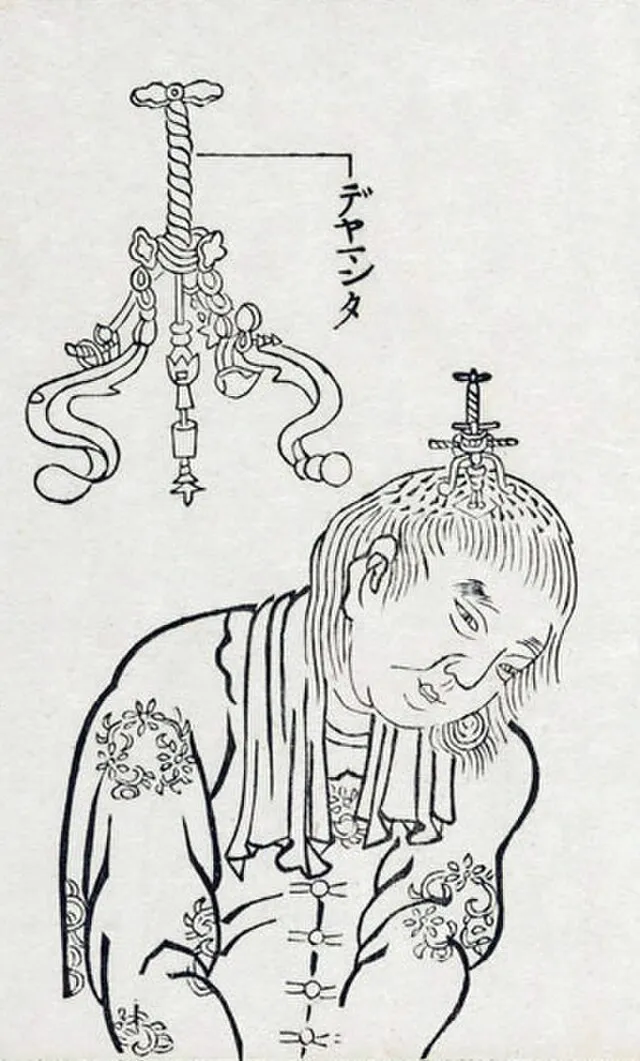

WolfgangMichel on wikimedia
Trepanation involved drilling a small hole in the skull to relieve pressure or treat injuries. Evidence from ancient civilizations shows patients often survived the procedure. Modern neurosurgery confirms that relieving intracranial pressure is life-saving in certain cases. The practice demonstrates early understanding of brain pressure and surgical intervention.