10 Moments in History That Happened by Accident
Several important discoveries and events in history happened completely by accident.
- Sophia Zapanta
- 4 min read

History is full of unexpected turns, where accidents led to breakthroughs or turning points. These events were not planned, yet they shaped medicine, science, technology, and culture. Each moment shows how chance can influence the world in lasting ways.
1. 1. The Discovery of Penicillin

Ministry of Information Photo Division Photographer on Wikimedia Commons
In 1928, Alexander Fleming left a petri dish of Staphylococcus bacteria uncovered in his lab. Mold began to grow, and he noticed that the bacteria around it had been destroyed. This accident led to the discovery of penicillin. It became the first widely used antibiotic and transformed medical treatment.
2. 2. The Invention of the Microwave Oven

Wrightmt on Wikimedia Commons
Percy Spencer was working with radar equipment in 1945 when he noticed that a chocolate bar in his pocket had melted. He tested popcorn kernels and then an egg, which also reacted to the microwaves. From this accident, the microwave oven was developed. It changed food preparation in both homes and industries.
3. 3. The Discovery of X-Rays
ESO on Wikimedia Commons
In 1895, Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen was experimenting with cathode rays when he observed a fluorescent screen glowing. He realized that invisible rays were passing through solid objects and producing images. This discovery became known as X-rays. It allowed doctors to see inside the human body without surgery.
4. 4. The Creation of Coca-Cola

Cadythechill on Wikimedia Commons
In 1886, pharmacist John Pemberton was trying to make a medicinal syrup for headaches. When the syrup was mixed with carbonated water by accident, the result was a new type of drink. That drink became the first version of Coca-Cola. It grew into one of the most popular beverages in the world.
5. 5. The Arrival of Columbus in the Americas

USCapitol on Wikimedia Commons
Christopher Columbus set sail in 1492 with the goal of reaching Asia by crossing the Atlantic. Instead, he landed in the Caribbean islands. This unintended arrival connected Europe and the Americas for the first time in recorded history. It marked the beginning of major global exchanges in goods, culture, and people.
6. 6. The Invention of Velcro

Taylor 49 on Wikimedia Commons
In 1941, Swiss engineer George de Mestral went on a hunting trip and noticed burrs clinging to his clothing and his dog’s fur. He studied them under a microscope and saw how their hooks attached to fabric. This observation led him to design Velcro. It became widely used in clothing, gear, and technology.
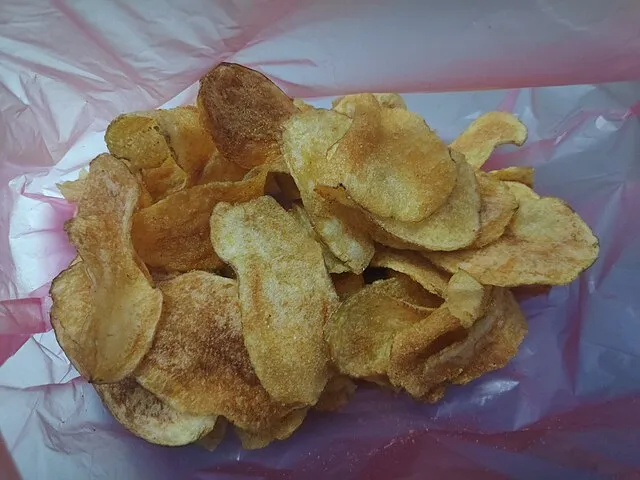
7. 7. The Creation of Potato Chips

Gaurav Dhwaj Khadka on Wikimedia Commons
In 1853, a customer at a restaurant in Saratoga Springs kept sending back his fried potatoes, asking for them to be thinner. Chef George Crum sliced them extremely thin and fried them until crisp. The customer approved, and potato chips were born. They quickly became a popular snack across the United States.
8. 8. The Discovery of Plastic

Deeneris on Wikimedia Commons
In 1869, John Wesley Hyatt was experimenting with materials to replace ivory in billiard balls. During the process, he created a new substance called celluloid. This was the first form of plastic. It opened the way to many applications in manufacturing and daily life.
9. 9. The Invention of Matches

Yann SEGALEN on Wikimedia Commons
In 1826, chemist John Walker was mixing chemicals when he accidentally scraped a coated stick against a surface. The stick ignited immediately. This accident became the basis for friction matches. It gave people a simple and reliable way to produce fire.
10. 10. The Use of Quinine for Malaria

Rothstein, Arthur on Wikimedia Commons
Indigenous people in South America discovered that cinchona bark helped reduce fever when brewed into a drink. Later, Europeans learned it could treat malaria. Quinine, the active substance in the bark, became the first effective medicine against the disease. It helped save countless lives in tropical regions.