10 Scientific Questions That Still Don’t Have Definitive Answers
Curiosity has always driven human progress, especially in fields where firm answers remain out of reach. Even with advancing technology and new discoveries, some scientific mysteries continue to resist complete explanation.
- Tricia Quitales
- 6 min read

Unanswered questions remind people that science is a journey shaped by evolving insights. Researchers often uncover new layers of complexity while searching for solutions. These open questions motivate exploration across physics, biology, astronomy, and cognitive science. Many theories attempt to solve these puzzles, yet none have achieved universal acceptance. Their uncertainty leaves room for further breakthroughs. Some mysteries may take decades to resolve. Others might never receive a single definitive explanation. Each unanswered question adds depth to our understanding of the world. They inspire scientists to look beyond established knowledge in pursuit of clarity.
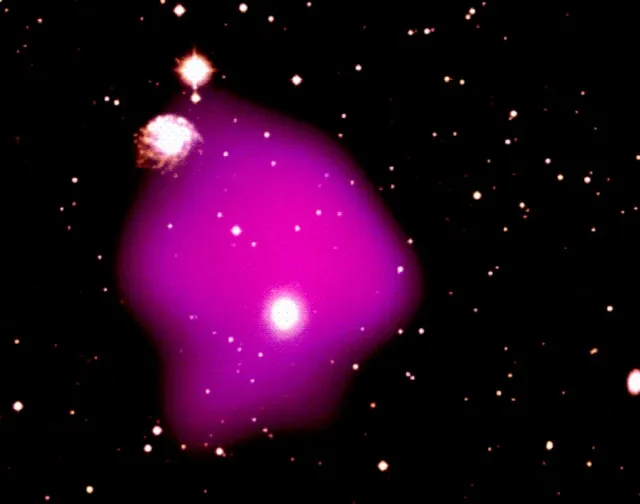
1. 1. What Exactly Is Dark Matter

NASA on wikimedia
Dark matter remains one of the greatest puzzles in modern astrophysics. Scientists observe its influence through gravitational effects on galaxies. The substance does not emit or absorb light. Its invisible nature makes direct detection extremely difficult. Many experiments have attempted to capture its particles without success. Theories include exotic particles that have never been observed. Dark matter appears essential for explaining cosmic structure. Without it, galaxies would not hold together as they do. The mystery continues to challenge current scientific models. Researchers persist in their search for definitive proof.
2. 2. How Life First Emerged on Earth

Pixabay on pexels
The origin of life presents a complex scientific question that lacks a single explanation. Researchers study chemical reactions in early Earth conditions. Some theories suggest life began in deep-sea vents. Others point to shallow pools exposed to changing temperatures. Experiments attempt to recreate early molecular processes. No model fully explains how simple molecules formed self-replicating systems. The environment billions of years ago remains partially unknown. Life’s emergence may have required rare conditions. Scientists continue to investigate how chemistry transformed into biology. The question remains open to new discoveries.
3. 3. Why We Sleep

Ivan Oboleninov on pexels
Sleep is essential for survival, yet its full purpose remains only partially understood. Researchers have identified numerous benefits, including memory consolidation and cognitive restoration. However, no single theory fully explains all aspects of sleep. Different species require widely varying amounts of rest, adding complexity to its study. Some animals sleep in unusual or fragmented ways, further complicating understanding. During sleep cycles, the brain undergoes complex changes that support mental and physical health. Many studies focus on how sleep restores energy, repairs tissues, and regulates body systems. Despite advanced tools and research, the exact reason humans must sleep remains partly unknown. The process continues to hold mysteries that challenge scientists.
4. 4. What Consciousness Truly Is

Mikhail Nilov on pexels
Consciousness remains one of the most challenging scientific questions. Researchers attempt to understand how subjective experience forms. Brain activity correlates with awareness but does not fully explain it. Philosophers contribute different interpretations. Neuroscientists use imaging tools to study conscious states. None of the findings offers a complete definition. The question spans multiple disciplines. Consciousness may involve processes the human mind cannot yet measure. Studies continue to explore perception and identity. Many believe the answer will require a new scientific framework.
5. 5. Why the Universe Is Expanding Faster

Pixabay on pexels
The universe’s expansion rate continues to puzzle scientists across multiple fields. Observations indicate that this expansion is accelerating faster than previously predicted. Dark energy is commonly invoked to explain this unexpected behavior. However, the true nature of dark energy remains completely unknown. Measurements from distant galaxies add further complexity and deepen the cosmic mystery. Conflicting data challenge existing models and assumptions about the universe. Researchers continually refine equations and simulations to better match observations. The accelerating expansion forces a reevaluation of theories about cosmic evolution.
6. 6. How Plate Tectonics First Began
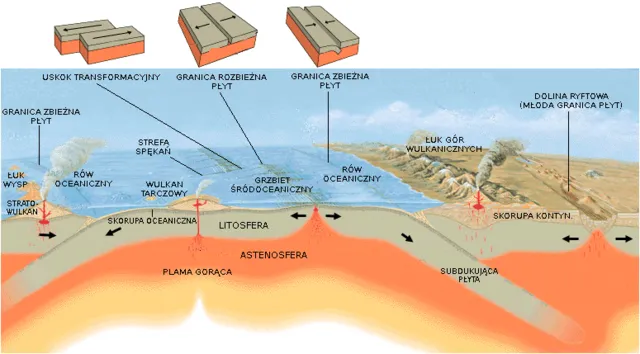
Jose F. Vigil. USGS, translated by Szczureq on wikimedia
Plate tectonics continuously shapes Earth’s surface, yet its origins remain uncertain. Scientists study ancient rocks and geological formations to understand early tectonic activity. Some evidence suggests the process may have begun as Earth’s surface cooled. Other theories propose that massive collisions triggered the initial movement of plates. Rising heat and pressure from the mantle may have also contributed to tectonic activity. Evidence from the planet’s earliest years remains scarce and difficult to interpret.
Plate tectonics plays a crucial role in the formation of volcanoes, earthquakes, and mountain ranges. Understanding how they began could reveal important insights into Earth’s overall evolution. The question continues to drive research in geology and Earth sciences.
7. 7. Why We Experience Emotions

Andrea Piacquadio on pexels
Emotions play a central role in guiding human behavior, yet their scientific basis is not fully understood. Some theories emphasize the survival advantages of emotions in responding to danger or opportunity. Others focus on neurological responses and the ways the brain processes emotional stimuli. Brain chemistry influences feelings but cannot fully explain their complexity. Cultural norms and social context also shape how emotions are expressed. Individual differences create unpredictable variations in emotional experience.
This complexity makes it difficult to arrive at definitive answers. Researchers study how emotions arise from interconnected brain networks and psychological processes. The science of emotions continues to evolve, uncovering new insights while leaving many mysteries unresolved.
8. 8. What Causes Ball Lightning

Public domain on wikimedia
Ball lightning is a rare and poorly understood atmospheric phenomenon. Witnesses often describe glowing, spherical lights appearing during thunderstorms. Scientists have struggled to reproduce it consistently in laboratory settings. Theories about its origin range from plasma formations to unusual chemical reactions. Observations are limited because ball lightning occurs unpredictably and briefly. Some experiments have produced similar effects, but never exact replicas of natural events.
The phenomenon continues to challenge and intrigue atmospheric researchers. Its behavior can vary widely between sightings, defying simple explanation. Studies aim to clarify its composition, energy source, and formation process. Despite ongoing research, the exact cause of ball lightning remains unknown.
9. 9. How Many Species Actually Exist

Valdemaras D. on pexels
Scientists continue to debate the total number of species on Earth. Many organisms inhabit remote or inaccessible regions, making study difficult. Some species remain undiscovered in the deep oceans, far from human observation. Others live in microhabitats that are rarely explored or sampled. Advances in genetics continually revise classifications and reveal previously hidden differences. Countless species go extinct before they can be documented by science. Estimates of global biodiversity vary widely between research groups. The sheer diversity of life complicates efforts to determine an accurate total. Large-scale projects aim to map and catalog biodiversity more comprehensively. Despite these efforts, the true number of species on Earth remains uncertain.
10. 10. Why Time Moves Forward

Andrey Grushnikov on pexels
The direction of time raises questions that physics cannot fully resolve. The forward flow of time feels intuitive to human experience. Thermodynamics suggests that entropy increases over time, giving a statistical sense of direction. However, this does not fully explain the subjective experience of time passing. Many fundamental physics equations are symmetrical, working equally well in both directions. The concept of the arrow of time remains only partly understood. Some theories link its origin to the conditions of the cosmos at the Big Bang. Others investigate quantum processes to explore time’s behavior at microscopic scales.