12 Forgotten AI Projects From the Early 20th Century
Early AI projects often involved mechanical computers or symbolic reasoning systems. While most failed or remained obscure, they laid the groundwork for modern artificial intelligence.
- Tricia Quitales
- 4 min read
Long before modern computers, inventors and mathematicians experimented with artificial intelligence concepts. Many projects were abandoned, underfunded, or lost to history despite showing remarkable ingenuity. These early AI experiments explored machine learning, automation, and logical reasoning.
1. 1. The Logical Machine of Ramon Llull

Francesc Ribalta on wikimedia
Ramon Llull created a mechanical device in the early 20th century designed to combine logic with automated decision-making. It used rotating disks to generate different combinations of concepts. The machine aimed to solve philosophical and theological problems through structured reasoning. Although primitive, it represented one of the first attempts to mechanize thought.
2. 2. The Automaton Chess Player
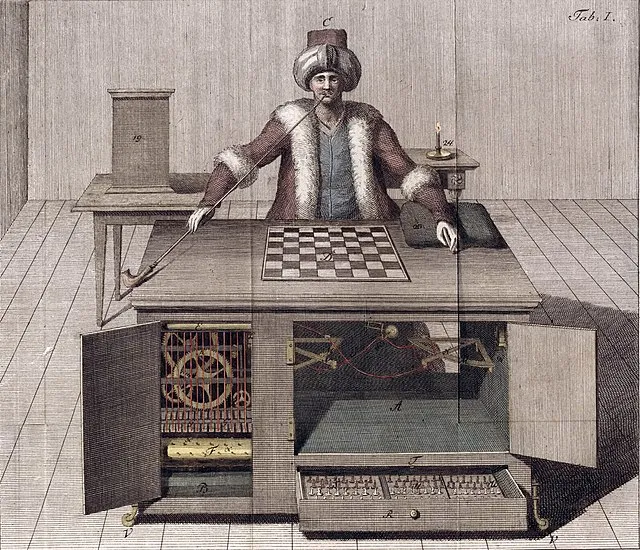
Joseph Racknitz on wikimedia
Inventors in the 1910s attempted to build chess-playing automatons using gears and levers. The goal was to simulate strategic thinking mechanically. Early tests showed limited success but captured public imagination. These devices often required hidden human operators to function fully. The project demonstrated the desire to replicate intelligence in machines.
3. 3. The Analytical Engine Simulation

NASA on wikimedia
Inspired by Charles Babbage, engineers developed small-scale simulations of his Analytical Engine. The machines aimed to perform basic computations automatically. Early attempts included punched-card inputs and mechanical calculators. They were limited by technology but proved programmable automation was possible. The work foreshadowed modern computer algorithms.
4. 4. The Logic Theorist Prototype
George Shelton on wikimedia
An early mechanical prototype of the Logic Theorist was built using electromechanical relays. It could solve symbolic logic problems step by step. Researchers experimented with applying rules of deduction mechanically. The project never reached wide implementation. Its design influenced later electronic AI systems in the 1950s.
5. 5. Mechanical Neural Network

Deviationsz1 on wikimedia
Some inventors tried building mechanical analogues of neural networks. These devices used levers, springs, and weights to simulate neurons and connections. They aimed to perform pattern recognition tasks. The machines were slow and prone to error. Nevertheless, they foreshadowed modern artificial neural networks.
6. 6. The Automated Theorem Prover

Daniel beardsmore on wikimedia
A few projects attempted to automate mathematical theorem proving using mechanical computers. Researchers coded basic rules of logic into rotating and sliding components. Results were limited to simple theorems. The project failed to scale due to mechanical constraints. It was a crucial early exploration of symbolic AI.
7. 7. The Mechanical Perceptron
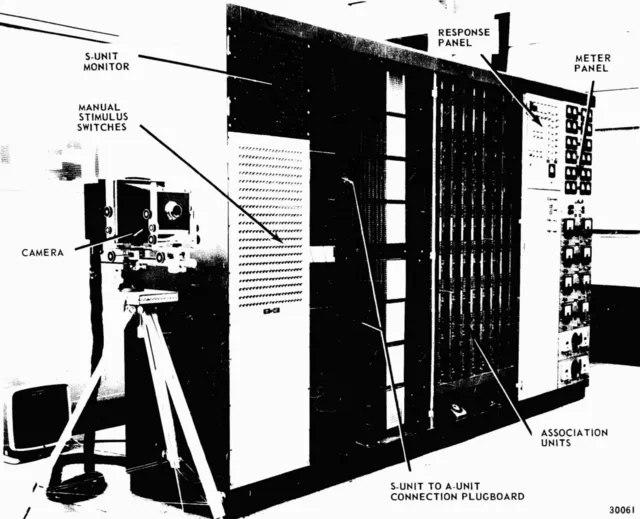
John C. Hay, Albert E. Murray on wikimedia
Engineers experimented with early versions of perceptrons using gears and electrical contacts. The device attempted to classify simple visual patterns. Success was limited, and the machine could only handle tiny datasets. Despite its constraints, it demonstrated pattern recognition principles mechanically. The idea anticipated future electronic perceptrons in the 1950s.
8. 8. The Automated Language Translator

Daderot on wikimedia
In the 1920s, a small team developed a mechanical device designed to translate words between languages. It used punched cards with preprogrammed vocabulary and rules. The machine could produce basic translations but lacked nuance. It was never commercially viable. The concept influenced later computational linguistics projects.
9. 9. The Predictive Weather Machine

Airman 1st Class Alexxis Pons Abascal on wikimedia
Inventors attempted to create a mechanical forecasting machine using mathematical equations and rotating components. It was designed to predict short-term weather patterns. Accuracy was poor due to incomplete data and primitive mechanics. The project was abandoned after repeated failures. Its ambition anticipated modern AI weather models.
10. 10. The Mechanical Music Composer

Public domain on wikimedia
An early attempt at automating music composition involved gears, punched rolls, and levers. The machine could generate simple melodies based on programmed rules. Results were repetitive but demonstrated algorithmic creativity. The project was mostly experimental and never widely used. It foreshadowed later computer-generated music research.
11. 11. The Cybernetic Automaton

National Institute of Standards and Technology on wikimedia
Some early 20th-century engineers experimented with self-regulating mechanical systems inspired by emerging cybernetics theories. These automatons could adjust movements based on mechanical feedback. They were limited in complexity and often fragile. However, they demonstrated early principles of adaptive behavior. These systems influenced later AI control and robotics research.
12. 12. The Early Decision Tree Machine

Public domain on wikimedia
A small number of researchers designed mechanical decision-making devices resembling decision trees. They could process inputs and follow branching rules to reach conclusions. The machines were limited to very narrow problems. They highlighted the potential for logical problem-solving automation. Modern decision tree algorithms can trace their conceptual roots to these experiments.