12 Things That Were Supposed to Be Dangerous But Weren’t
Some things that seem dangerous at first turn out to be surprisingly safe.
- Sophia Zapanta
- 4 min read

Many objects, foods, or activities carry a reputation for being dangerous, but science and experience show otherwise. Misconceptions often arise from myths, overcautious warnings, or rare incidents. Learning the truth helps people enjoy life without unnecessary fear.
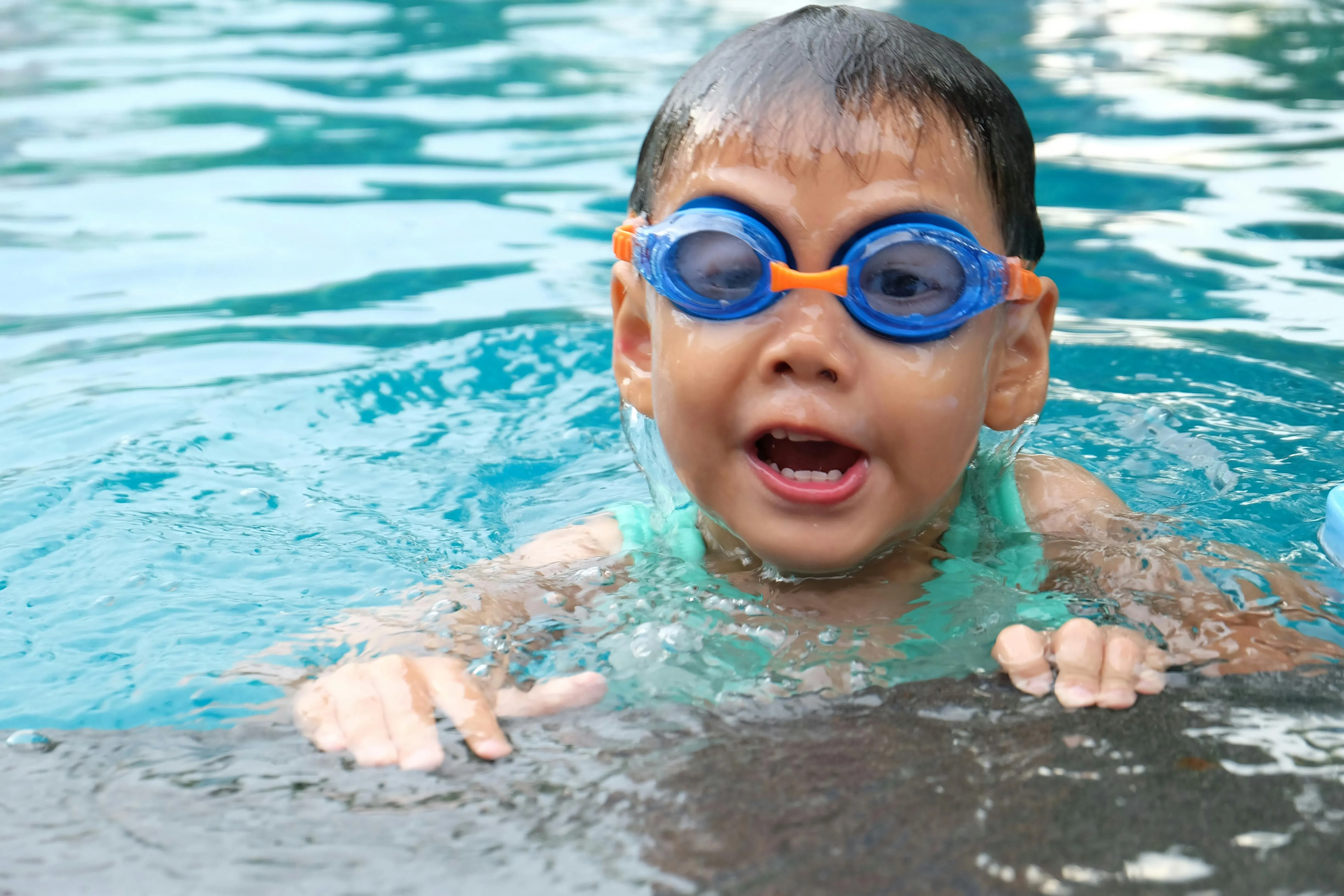
1. Swimming Right After Eating
 Porapak Apichodilok on Pexels
Porapak Apichodilok on Pexels
The idea that eating before swimming causes cramps and drowning is a long-standing myth. Studies show there is no evidence to support this belief. Moderate swimming after a meal is safe for most people. The real key is listening to your body and avoiding overexertion.
2. Spicy Food Causing Ulcers
 Nadin Sh on Pexels
Nadin Sh on Pexels
For decades, people thought spicy food created stomach ulcers. Research has shown that most ulcers are caused by H. pylori bacteria or certain medications. Spicy meals may cause discomfort for some, but they don’t create ulcers. This myth has been firmly debunked by medical science.
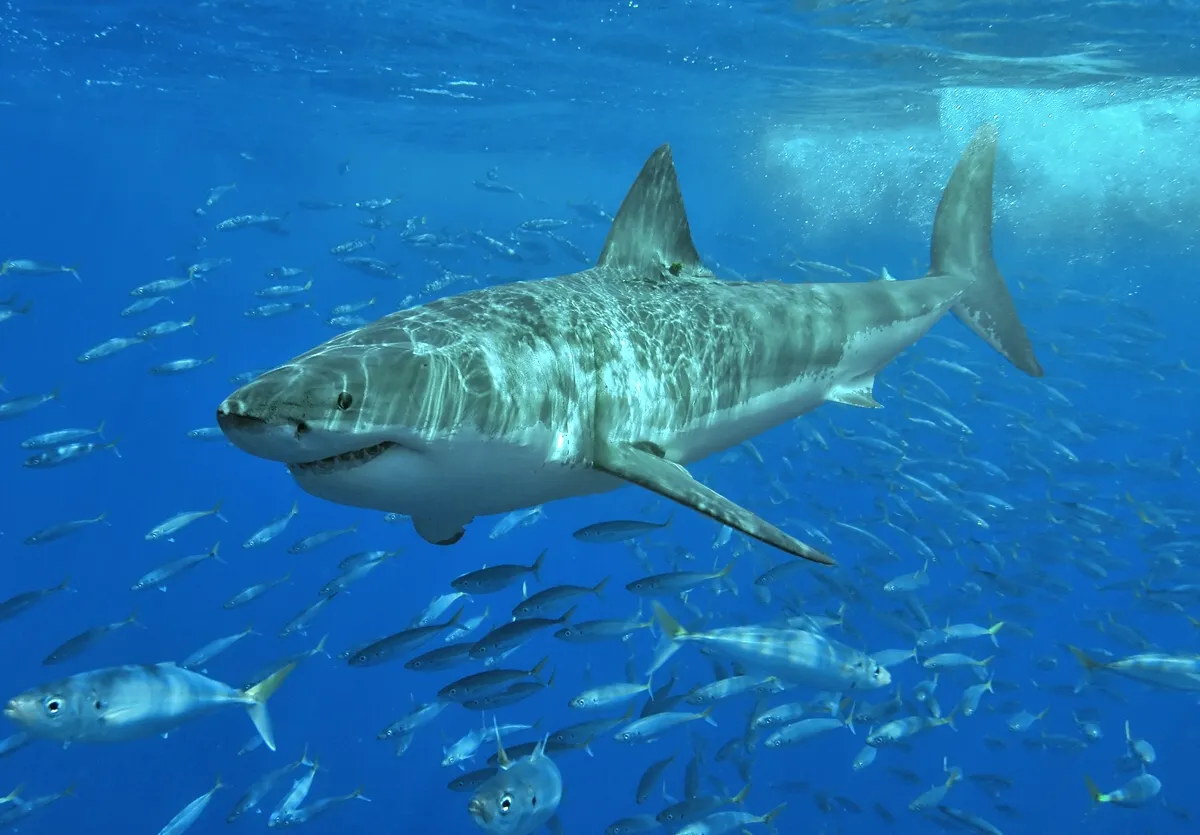
3. Sharks at the Beach
 Mariomassone on Wikimedia Commons
Mariomassone on Wikimedia Commons
Many fear shark attacks when swimming in the ocean. Statistically, the chance of being attacked by a shark is extremely low. Beaches with lifeguards and safety measures make it even safer. Sunburn and drowning are far more common risks than sharks.
4. Flying on Airplanes
 epSos.de on Wikimedia Commons
epSos.de on Wikimedia Commons
Fear of flying is common, but planes are among the safest forms of travel. Aviation has strict safety checks, trained crews, and advanced technology. The odds of a plane crash are much lower than those of a car accident. Air travel remains one of the safest ways to move long distances.
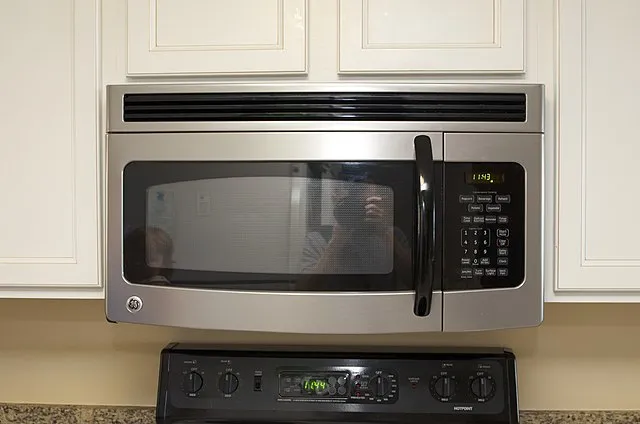
5. Microwave Radiation
 Brent Schmidt on Wikimedia Commons
Brent Schmidt on Wikimedia Commons
Some believe microwaves leak harmful radiation. In reality, microwaves use non-ionizing radiation, which cannot damage DNA like X-rays or gamma rays. Properly maintained microwaves are safe to use daily. Cooking food in them is no more dangerous than using an oven or stove.
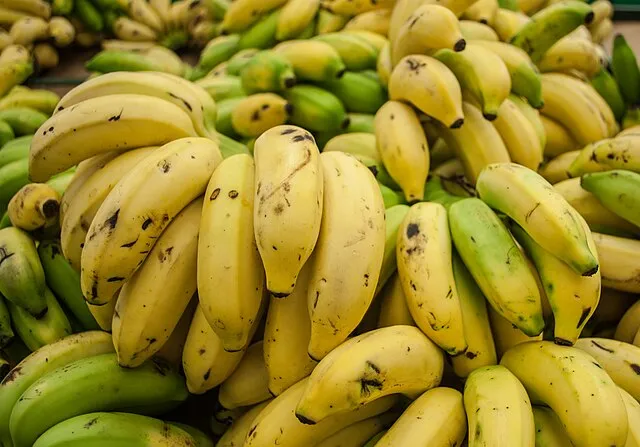
6. Bananas and Potassium
 Wilfredor on Wikimedia Commons
Wilfredor on Wikimedia Commons
Rumors spread that bananas are dangerous due to their potassium levels. While potassium is important for the body, you would need to eat an unrealistically large amount of bananas for it to be harmful. Bananas are safe, nutritious, and widely enjoyed. The “banana danger” myth is false.
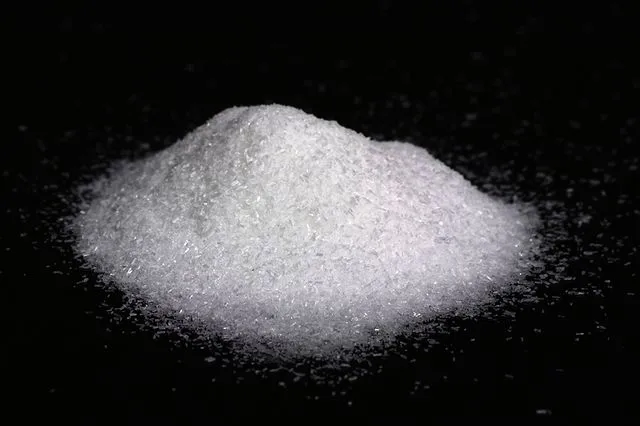
7. MSG in Food
 Ragesoss on Wikimedia Commons
Ragesoss on Wikimedia Commons
Monosodium glutamate (MSG) has long been blamed for headaches and illness. Modern scientific studies show it is safe for the general population. MSG is simply a flavor enhancer found naturally in foods like tomatoes and cheese. The fear around MSG is based on outdated misconceptions.
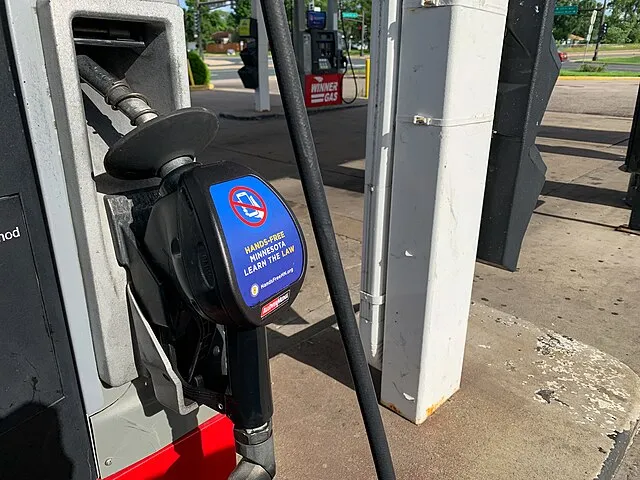
8. Cell Phones at Gas Stations
 Tony Webster on Wikimedia Commons
Tony Webster on Wikimedia Commons
Warnings about using cell phones while pumping gas have circulated for years. Research has found no cases of phones causing gas station fires. Static electricity and open flames are the real dangers, not cell phones. Most bans are precautionary rather than based on evidence.
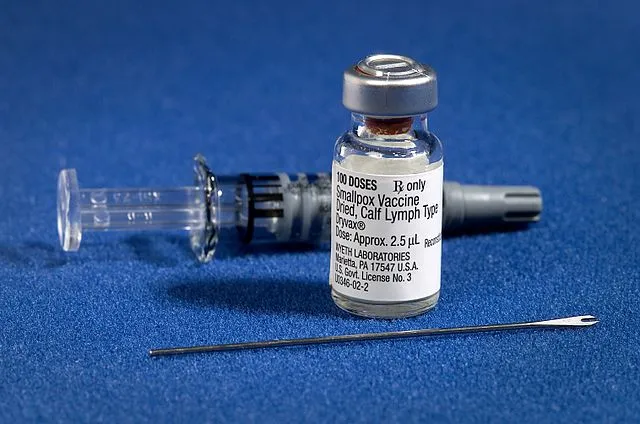
9. Vaccines Causing Autism
 James Gathany on Wikimedia Commons
James Gathany on Wikimedia Commons
A false link between vaccines and autism spread after a flawed study in the 1990s. That study has been fully discredited and withdrawn. Vaccines are safe and protect against serious diseases. The autism claim is one of the most damaging medical myths in history.
10. MSG in Chinese Food
 Slyronit on Wikimedia Commons
Slyronit on Wikimedia Commons
Chinese restaurant syndrome was once blamed on MSG in food. Science shows no reliable link between MSG consumption and illness. The symptoms reported were more likely caused by other factors. Today, MSG is recognized as safe by global health authorities.
11. Standing Too Close to TVs
 Ali Karimiboroujeni on Pexels
Ali Karimiboroujeni on Pexels
Parents once warned children that sitting near the television could harm their eyesight. Modern flat-screen TVs emit no harmful radiation. Sitting close may cause eye strain, but it doesn’t cause permanent damage. This warning is an outdated leftover from older television sets.
12. Air Conditioning Making You Sick
 Airam Dato-on on Pexels
Airam Dato-on on Pexels
Some believe cold air from air conditioners causes colds. In reality, colds come from viruses, not cold temperatures. Air conditioning can dry out the air and cause mild discomfort but doesn’t create illness. Proper maintenance makes air conditioners safe to use.