15 Computer Viruses That Caused Absolute Chaos
Computer viruses have caused a lot of trouble in the digital world throughout history. They have caused people and businesses to lose data, experience major interruptions, and even go bankrupt.
- Tricia Quitales
- 5 min read

Viruses in computers are bad programs that are made to damage, steal, or mess up data. They often spread without being noticed and do a lot of damage. From the first virus outbreaks that affected home computers to the latest ransomware attacks that hurt businesses, viruses cause a lot of trouble. This article discusses 15 of the most famous viruses in history, including how they spread, what happened as a result, and what we can learn from each one.
1. The Morris Worm
 Markus Spiske on Pexels
Markus Spiske on Pexels
The Morris Worm caused a lot of trouble on the early Internet. It took advantage of flaws in Unix systems and quickly spread to thousands of computers. The worm was one of the first big cyberattacks. It slowed down the Internet and caused many businesses to close for long periods.
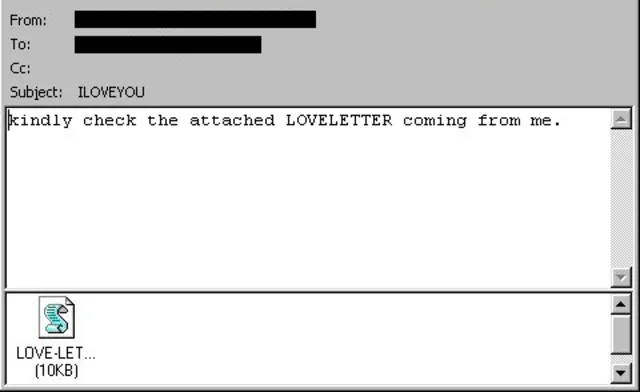
2. ILOVEYOU
 Mario23 on Wikimedia
Mario23 on Wikimedia
It was called the ILOVEYOU bug and spread through emails with the subject line “I love you.” Once the users opened the file, it would send itself to everyone in the victim’s address book, deleting many files in the process. This virus did about ten billion dollars worth of damage around the world, showing how powerful social engineering can be in spreading viruses.
3. MyDoom
 Darling on Wikimedia
Darling on Wikimedia
MyDoom was a virus that spread quickly through email files. At the time, it was one of the worms that spread the fastest. Websites and email systems were greatly slowed down, and search engines like Google were overloaded. Because it spread so quickly, it cost businesses billions of dollars and made people more aware of how dangerous email-based malware can be.
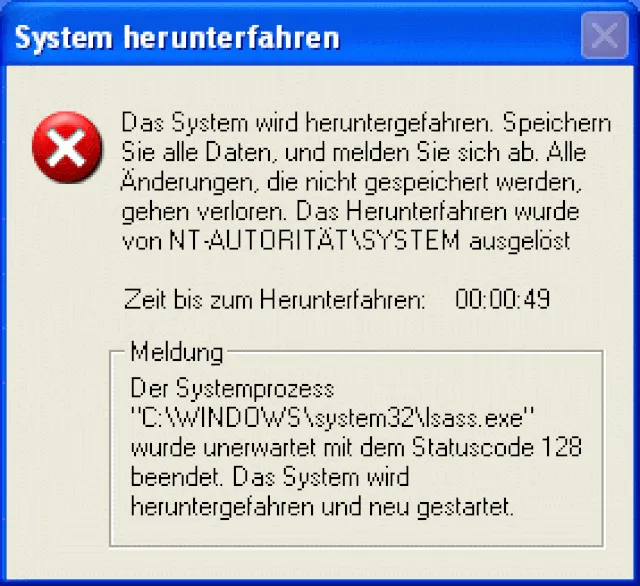
4. Sasser
 keiner, da keine SH on Wikimedia
keiner, da keine SH on Wikimedia
Sasser was a computer virus that attacked Microsoft’s LSASS service. Computers all over the world crashed because of it, messing up business processes and critical infrastructure. The speedy spread of the virus without any human intervention made it clear how important it is to apply security patches on time.
5. Conficker
 Markus Spiske on Pexels
Markus Spiske on Pexels
Conficker affected millions of computers around the world, making a huge network of computers called a “botnet” that hackers could use to do bad things. It used a flaw in Windows to spread, and even though people tried to stop it, the virus kept getting worse for months. Because it was so destructive and kept coming back, it was one of the most dangerous viruses of its time.
6. Blaster
 admin on Wikimedia
admin on Wikimedia
This worm called Blaster spread through a flaw in Microsoft’s Windows operating system. It would start a denial-of-service attack on Microsoft’s update systems as soon as it got into a computer. The Blaster worm messed up a lot of networks and made people more aware of how important it is to keep systems updated regularly.
7. CryptoLocker
 Pixabay on Pexels
Pixabay on Pexels
One of the first big ransomware bugs that got a lot of attention was the CryptoLocker. It locked people’s files and demanded a ransom for the key to unlock them. This cost companies and people a lot of money. This bug spread the idea of ransomware around the world and led to a lot of other similar attacks.
8. Zeus
 Tima Miroshnichenko on Pexels
Tima Miroshnichenko on Pexels
Zeus was a Trojan horse made to steal personal and banking information from computers it attacked. It mostly spread through scam emails and fake websites, which cost businesses billions of dollars. Zeus showed how hackers could use malware to steal people’s identities and money.
9. Stuxnet
 Tima Miroshnichenko on Pexels
Tima Miroshnichenko on Pexels
Steuxnet was a very smart worm that attacked Iranian nuclear sites and damaged equipment. The attack was very specific and meant to damage important facilities. People and businesses have learned from Stuxnet that hacks on industrial control systems can be dangerous.
10. Melissa
 Nemuel Sereti on Pexels
Nemuel Sereti on Pexels
Melissa was one of the first email viruses that spread by infecting Word files. It would send itself to the first 50 people in the user’s address book once it was opened. The virus greatly messed up business networks, especially in the U.S., and made people more aware of threats in email.
11. WannaCry
 Markus Spiske on Pexels
Markus Spiske on Pexels
WannaCry was a ransomware that quickly spread worldwide and hit over 150 countries, affecting one hundred thousand computers. It took advantage of a flaw in Windows systems to secure users’ files and demand Bitcoin as payment. WannaCry’s wide reach showed how important it is to keep security patches up to date and how vulnerable old systems are.
12. Klez
 Markus Spiske on Pexels
Markus Spiske on Pexels
Klez was a worm that spread through email attachments. It looked like a real file, and fake sender names were often used. It messed up email systems, causing them to run slowly and lose data. Klez was one of the most popular email viruses at the time, and it changed how people protected their emails in the future.
13. Android.Troj.Dropper
 Godfrey Atima on Pexels
Godfrey Atima on Pexels
This virus was one of the most well-known types of software that attacked Android devices. It looked like a real app, but it actually installed more harmful software on the device. This virus was especially dangerous because many people use smartphones. This shows how important it is to protect mobile devices.
14. Ramnit
 Danny Meneses on Pexels
Danny Meneses on Pexels
Ramnit was a Trojan horse virus that attacked Windows computers and stole private information like login information for banks. It spread through websites and files that were already affected, making a huge botnet. Ramnit was one of the most persistent and hard-to-get-rid-of malware strains because it could change and adapt to different settings.
15. Nimda
 hitesh choudhary on Pexels
hitesh choudhary on Pexels
Nimda was a complicated worm that spread quickly through email, websites, and file-sharing services. Once it entered a system, it could interfere with network traffic and file access. The speed with which Nimda spread caused many problems and showed that personal and business security was not as strong as it should have been.
- Tags:
- Virus
- Computer
- chaos
- damage
- Technology