15 Space Discoveries That Changed Everything We Know About the Universe
There have been times when human curiosity and science clashed to expose revolutionary findings. From the first observation of far-off galaxies to the discovery of gravitational waves, every discovery has influenced our perspective of the universe.
- Tricia Quitales
- 5 min read

People have been interested in the vast, mysterious universe for thousands of years. Amazing findings made possible by the development of technology and space exploration have changed the way we think about space and time forever. This article talks about some of the most important space finds that have changed the way we think about the world, from figuring out what black holes are to finding planets in faraway solar systems.
1. The Discovery of the Expanding Universe (1929)
 Johan Hagemeyer on Wikimedia
Johan Hagemeyer on Wikimedia
In 1929, Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe was expanding. By tracking the redshift of light coming from far-off galaxies, he discovered that galaxies were separating. This discovery led to the development of Hubble’s Law, which altered our knowledge of the universe’s beginnings.
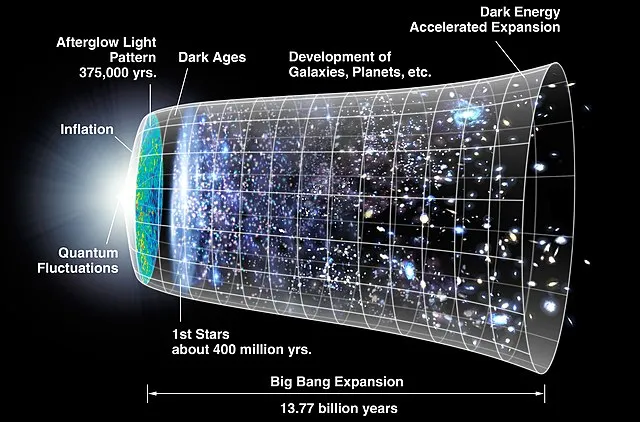
2. The Big Bang Theory
 NASA/WMAP Science Team on Wikimedia
NASA/WMAP Science Team on Wikimedia
People who believe in the Big Bang Theory say that the universe grew from a single point about 13.8 billion years ago. Other discoveries, like the cosmic microwave background radiation, helped back up this idea. We could think about how the world began and how it has changed since then.
3. The Discovery of Black Holes
 Iceberg San on Pexels
Iceberg San on Pexels
Astronomers found objects in the 1960s with such intense gravitational forces that nothing—not even light—could flee. These invisible giants were called black holes. Though prior theories had been developed, observational data verified their veracity.
4. The First Exoplanet Discovery (1992)
 Trent Schindler on Wikimedia
Trent Schindler on Wikimedia
In 1992, astronomers found the first planet that was orbiting a pulsar. At first, this planet was called PSR B1257+12, and it changed our ideas about where planets might be. This showed that many planets are orbiting stars outside our solar system, not just Earth.
5. The Hubble Space Telescope’s Deep Field Image (1995)
 NASA on Wikimedia
NASA on Wikimedia
In 1995, the Hubble Space Telescope produced an amazing picture of the deep universe, showing galaxies well beyond our own. The photograph, sometimes referred to as the Hubble Deep Field, showed thousands of galaxies, offering a glimpse into the far-off past of the universe.
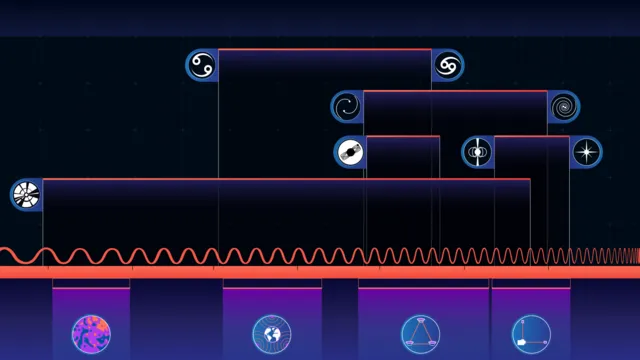
6. The Detection of Gravitational Waves (2015)
 NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio - University of Maryland College Park/Jeanette Kazmierczak, KBR Wyle Services, LLC/Scott Wiessinger, KBR Wyle Services, LLC/Krystofer Kim on Wikimedia
NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio - University of Maryland College Park/Jeanette Kazmierczak, KBR Wyle Services, LLC/Scott Wiessinger, KBR Wyle Services, LLC/Krystofer Kim on Wikimedia
It was a big deal for scientists when they found gravitational waves when two black holes collided in 2015. This discovery by LIGO proved Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity. It gave a new look at the universe through the lens of spacetime waves.
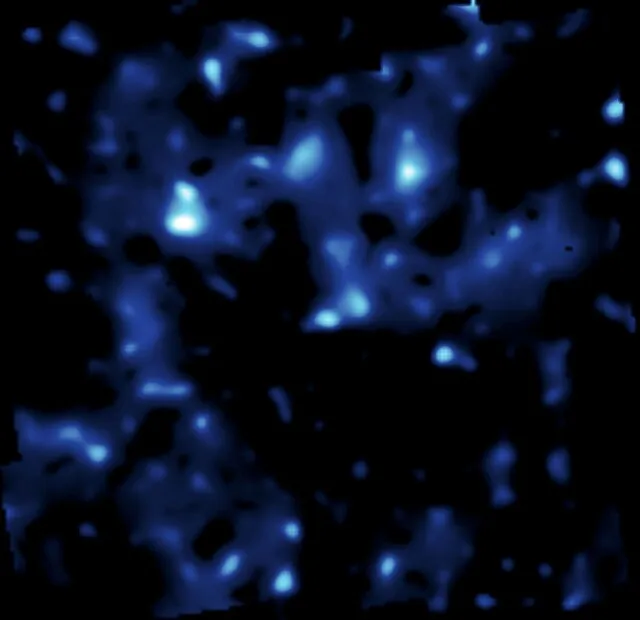
7. Dark Matter and Its Impact on the Universe
 NASA, ESA, and R. Massey (California Institute of Technology) on Wikimedia
NASA, ESA, and R. Massey (California Institute of Technology) on Wikimedia
Dark matter makes up about 27% of the universe. This was first figured out by looking at how its gravity pulls on things that can be seen. It can’t be found with standard methods because it doesn’t give off light. Its discovery has completely changed what we know about how the universe works.
8. The First Image of a Black Hole (2019)
 NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio - Caltech-IPAC/Robert Hurt, Caltech-IPAC/Keith Miller, NASA/JPL/Chelsea Gohd, Global Science and Technology, Inc./Ella Kaplan, NASA/GSFC/Mark SubbaRao on Wikimedia
NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio - Caltech-IPAC/Robert Hurt, Caltech-IPAC/Keith Miller, NASA/JPL/Chelsea Gohd, Global Science and Technology, Inc./Ella Kaplan, NASA/GSFC/Mark SubbaRao on Wikimedia
Released in 2019, the first-ever black hole image from the Event Horizon Telescope comes from the galaxy M87. In science, this was an enormous turning point. The picture displayed the event horizon of the black hole, with a dark center surrounded by brilliant gas.
9. The Discovery of Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Daniel Cid on Pexels
Daniel Cid on Pexels
Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson identified cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation in 1965. Spread over the universe, this faint glow is the residual heat from the Big Bang. Finding CMB gave vital proof in favor of the Big Bang idea.
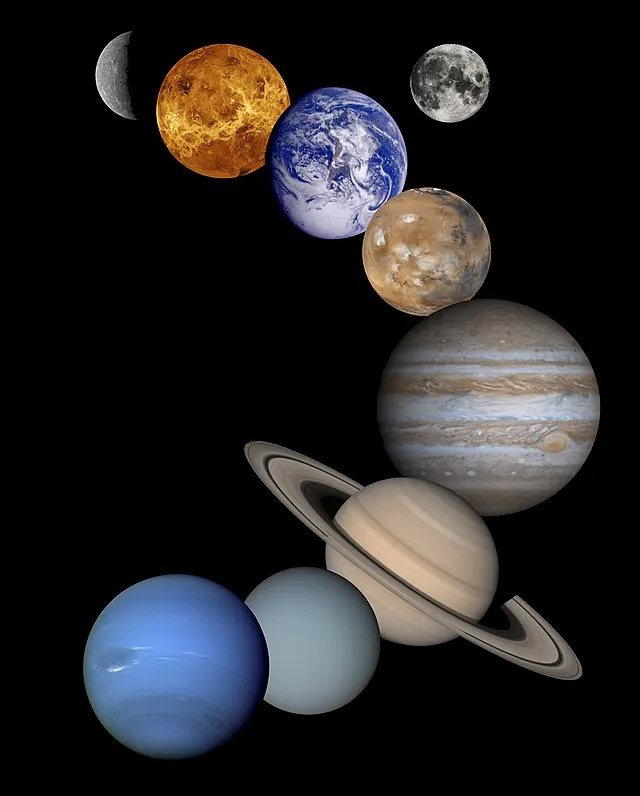
10. The Formation of the Solar System
 NASA/JPL on Wikimedia
NASA/JPL on Wikimedia
Scientists grew more aware of how our solar system evolved in the 20th century. Through meteorite and distant star analysis, they discovered that our solar system sprung from a large molecular cloud. Known as solar nebula theory, this mechanism clarified the formation of the Sun, planets, and other solar system bodies.
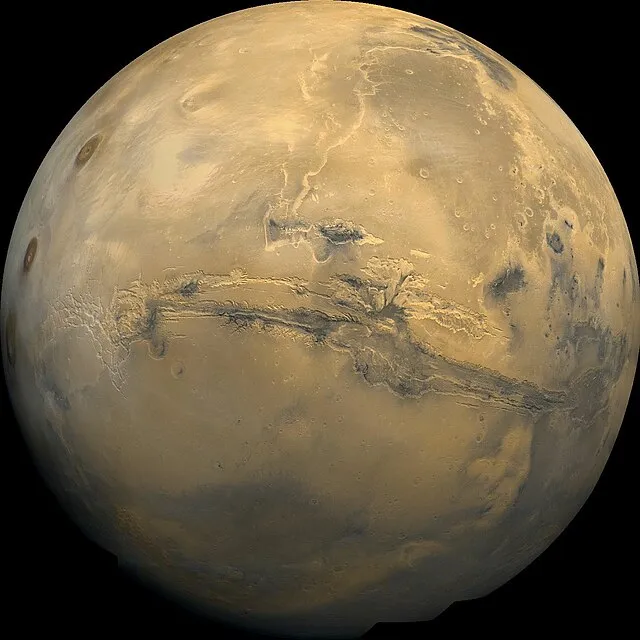
11. The Discovery of Water on Mars
 NASA / USGS on Wikimedia
NASA / USGS on Wikimedia
Whether in the past or present, water on Mars was found in the 2000s. The rovers of NASA discovered evidence of ancient riverbeds and minerals formed in the water. The prospect of life on Mars was much enhanced by this discovery.
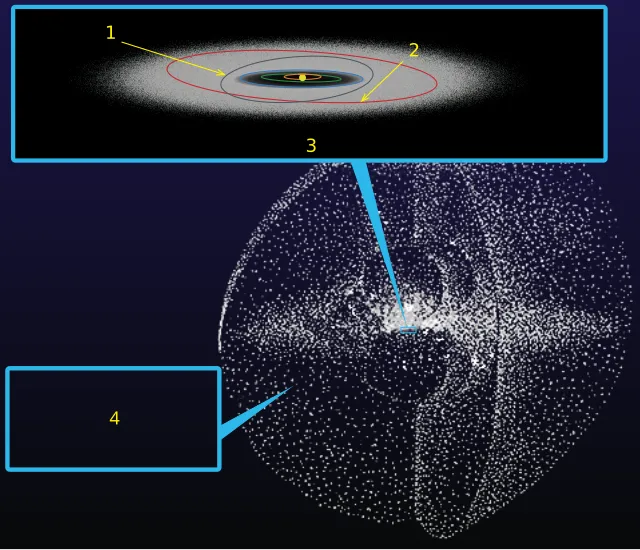
12. The Discovery of the Kuiper Belt (1992)
 NASA on Wikimedia
NASA on Wikimedia
Astronomers found the icy body-filled Kuiper Belt beyond Neptune in 1992. Pluto and another minor planet reside in this region. The finding of the Kuiper Belt provided advanced knowledge of the outer solar system.
13. The Search for Dark Energy
 Yihan Wang on Pexels
Yihan Wang on Pexels
About 68% of the cosmos is dark energy, which was initially proposed in the late 1990s to account for the universe’s fast expansion. Observations of far-off supernovae pointed to an accelerating rather than slowing down universe expansion. This enigmatic acceleration is ascribed to dark energy.
14. The Discovery of the Higgs Boson (2012)
 Emre Bilgiç on Pexels
Emre Bilgiç on Pexels
Scientists at CERN verified the Higgs boson’s existence in 2012; this particle provides mass for other particles. Its discovery was a major victory for particle physics’ Standard Model. Though theorized for decades, the Higgs boson remained elusive until the Large Hadron Collider tests.
15. Voyager’s Golden Record and the Message to the Stars
 Agnieszka Taggart on Pexels
Agnieszka Taggart on Pexels
NASA launched the Voyager probes in 1977. These probes carried a golden record, including photos and sounds depicting Earth. The logs were meant to be a message to any extraterrestrial society the spacecraft encountered. The Voyager project has enlarged our perspective on our role in the universe.