16 Tech Gadgets from the Past That Were Doomed from the Start
This list highlights 16 tech gadgets that were introduced with high hopes but never caught on.
- Daisy Montero
- 4 min read

Not every gadget becomes a success. This list looks at 16 tech devices that failed, even though they seemed exciting at first. Some were too expensive, others had confusing features, and a few just did not work well. They may be gone now, but people still remember them for all the wrong reasons.
1. Amazon Fire Phone (2014)
 Chris F on Wikimedia Commons
Chris F on Wikimedia Commons
Amazon’s venture into smartphones with the Fire Phone was short-lived. Despite its unique 3D interface, the device suffered from limited app support and unclear market positioning, leading to its discontinuation within a year.
2. Microsoft Kin (2010)
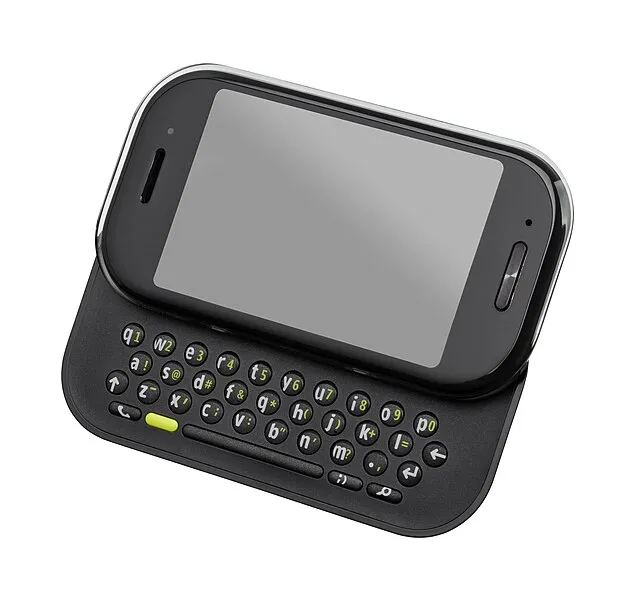 Evan-Amos on Wikimedia Commons
Evan-Amos on Wikimedia Commons
Targeting the teen market, the Microsoft Kin emphasized social media integration. However, its lack of essential features and high price point led to poor sales, resulting in its discontinuation just 48 days after launch.
3. HTC First (2013)
 Tuxinaut on Wikimedia Commons
Tuxinaut on Wikimedia Commons
Dubbed the “Facebook Phone,” the HTC First featured deep Facebook integration. However, users found the interface intrusive, and the device failed to gain traction, resulting in its rapid exit from the market.
4. Google Glass (2013)
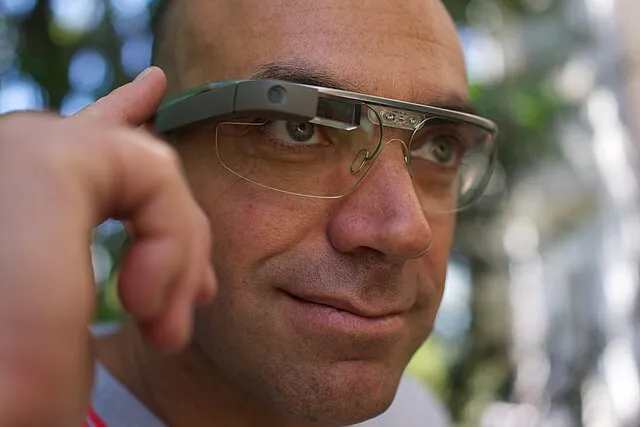 Loïc Le Meur on Wikimedia Commons
Loïc Le Meur on Wikimedia Commons
Google Glass introduced the concept of smart eyewear, offering augmented reality features. Despite its innovation, concerns over privacy, limited functionality, and high cost led to its commercial failure.
5. Nintendo Virtual Boy (1995)
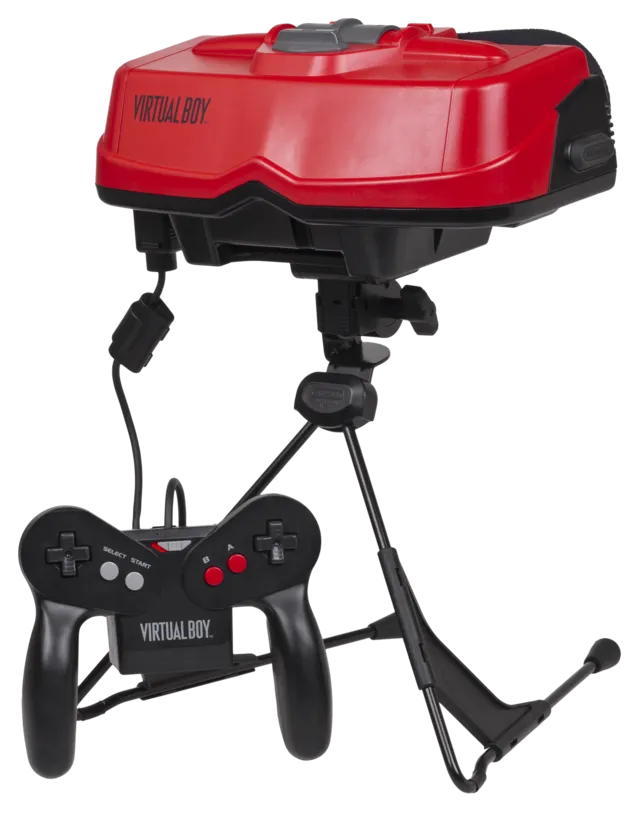 Evan-Amos on Wikimedia Commons
Evan-Amos on Wikimedia Commons
Nintendo’s attempt at 3D gaming with the Virtual Boy was ahead of its time. However, its monochromatic display, discomfort during use, and lack of compelling games resulted in poor sales and a short lifespan.
6. CueCat (2000)
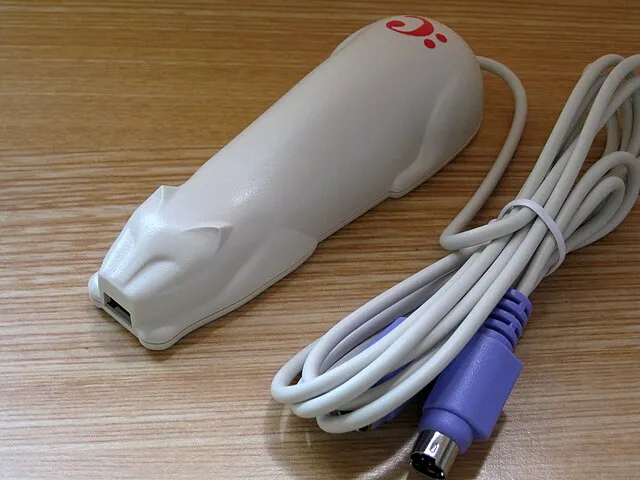 Jerry Whiting on Wikimedia Commons
Jerry Whiting on Wikimedia Commons
The CueCat aimed to bridge the gap between print media and the internet by scanning barcodes to access websites. However, it was deemed unnecessary and raised privacy concerns, leading to its quick demise.
7. Juicero Press (2016)
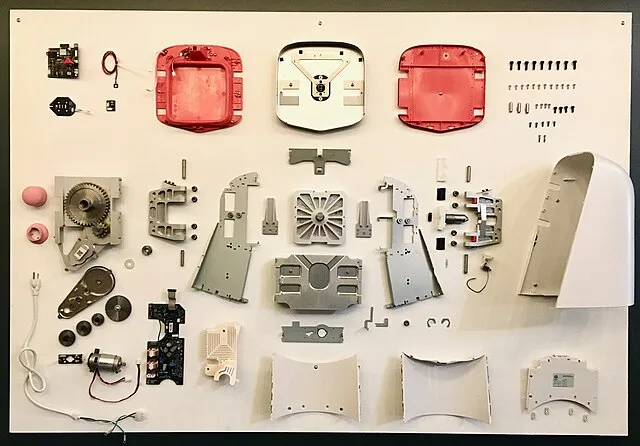 Steve Jurvetson from Menlo Park, USA on Wikimedia Commons
Steve Jurvetson from Menlo Park, USA on Wikimedia Commons
Juicero’s high-tech juicer required proprietary juice packs and an internet connection to function. When it was revealed that the packs could be squeezed by hand, the product faced ridicule and was discontinued.
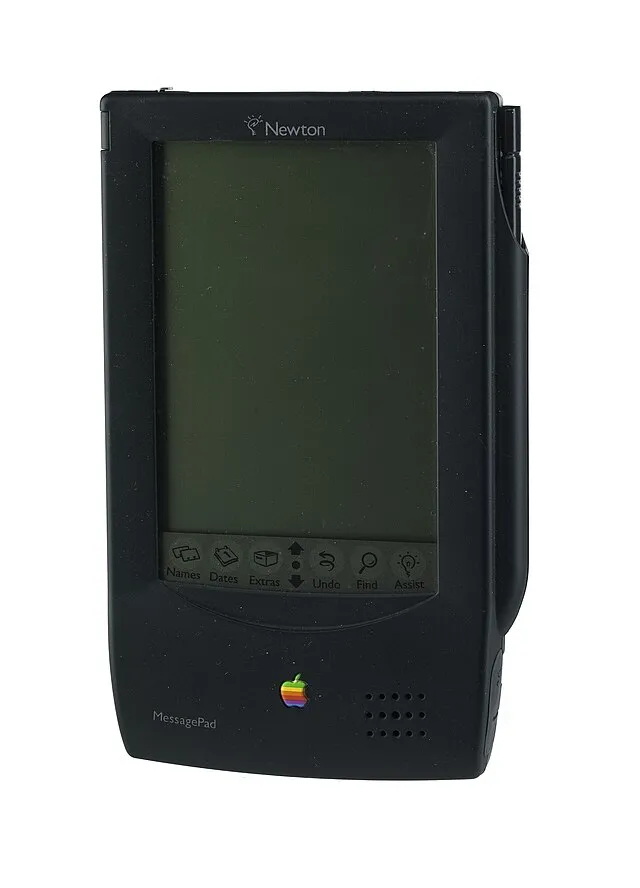
8. Apple Newton (1993)
 National Museum of American History on Wikimedia Commons
National Museum of American History on Wikimedia Commons
Apple’s Newton was an early attempt at a personal digital assistant. Its ambitious handwriting recognition was unreliable, leading to poor reviews and eventual discontinuation.
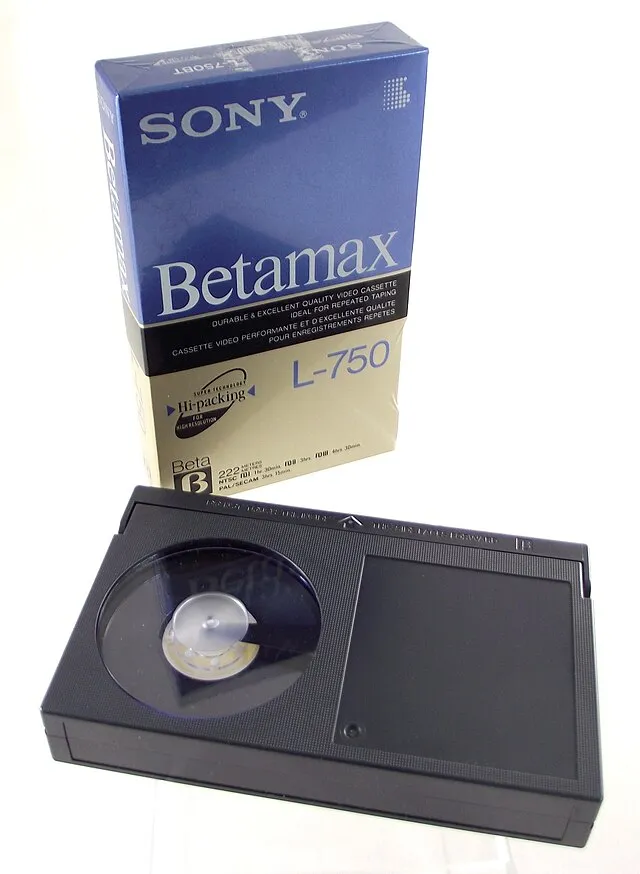
9. Sony Betamax (1975)
 Museum of Obsolete Media on Wikimedia Commons
Museum of Obsolete Media on Wikimedia Commons
Betamax offered superior video quality compared to VHS. However, its shorter recording time and higher cost led consumers to favor VHS, resulting in Betamax’s market failure.
10. BlackBerry PlayBook (2011)
 Luca Viscardi on Wikimedia Commons
Luca Viscardi on Wikimedia Commons
BlackBerry’s entry into the tablet market lacked essential features like native email and calendar apps. Combined with a limited app ecosystem, the PlayBook failed to compete with established tablets.
11. Samsung Galaxy Fold (2019)
 Kengurukroshka on Wikimedia Commons
Kengurukroshka on Wikimedia Commons
The Galaxy Fold introduced foldable screen technology. However, early units suffered from screen durability issues, leading to a delayed launch and tarnished reputation.
12. Google Nexus Q (2012)
 Unknown Google employee or contractor on Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Google employee or contractor on Wikimedia Commons
Google’s Nexus Q was a media streaming device with a unique design. However, its high price and limited functionality compared to competitors led to its quick withdrawal from the market.
13. Palm Foleo (2007)
 Thom Cochrane from Auckland, New Zealand on Wikimedia Commons
Thom Cochrane from Auckland, New Zealand on Wikimedia Commons
The Foleo was designed as a companion device for smartphones. However, its redundancy and lack of clear purpose led to its cancellation shortly after announcement.
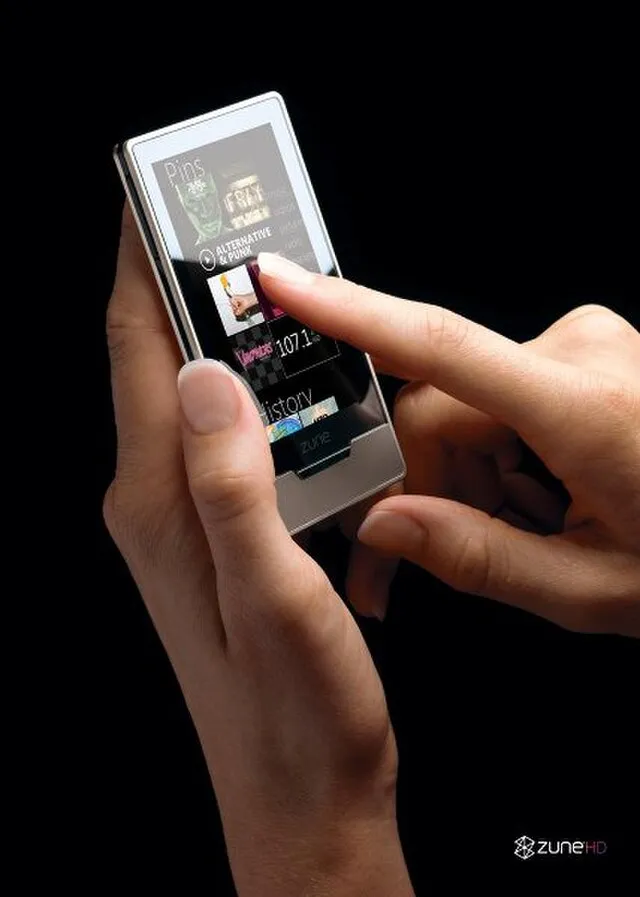
14. Microsoft Zune (2006)
 Microsoft Sweden on Wikimedia Commons
Microsoft Sweden on Wikimedia Commons
Microsoft’s attempt to rival the iPod with the Zune fell short due to late market entry, lack of innovation, and insufficient marketing. Despite decent hardware, it couldn’t overcome Apple’s dominance in the portable music player market.
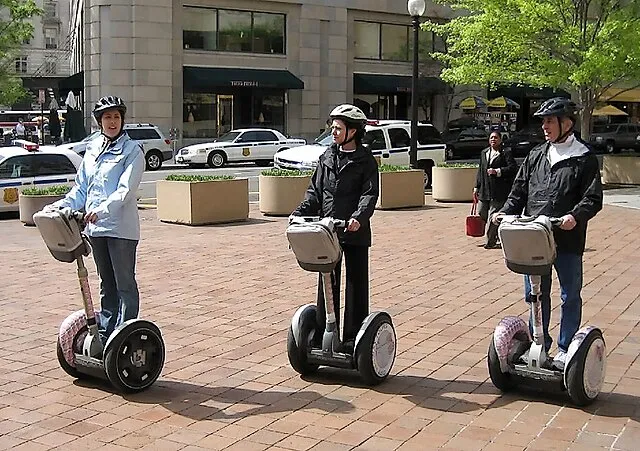
15. Segway PT (2001)
 Richard from DC, US on Wikimedia Commons
Richard from DC, US on Wikimedia Commons
Touted as a revolution in personal transportation, the Segway PT failed to gain widespread adoption due to high cost, bulky design, and regulatory hurdles. Its niche appeal couldn’t justify the initial hype.
16. Pebble Smartwatch (2013)
 Reensen on Wikimedia Commons
Reensen on Wikimedia Commons
As a pioneer in the smartwatch industry, Pebble gained early success through crowdfunding. However, it couldn’t compete with tech giants like Apple and Samsung, leading to its acquisition and discontinuation.