18 Discovered Substances With Unknown Properties
Across laboratories and natural environments, scientists continue to stumble upon strange substances that defy known chemical laws. Their unpredictable reactions and unknown origins inspire both curiosity and cautious fascination within the scientific community.
- Tricia Quitales
- 6 min read

Science has uncovered countless materials, yet some remain mysteries that defy full explanation. These substances intrigue researchers with behaviors that cannot be easily categorized or replicated. Whether found in deep space, laboratory experiments, or ancient artifacts, their compositions continue to puzzle modern science.
1. 1. Red Rain Cells of Kerala, India

Łukasz Martenka on pexels
In 2001, Kerala experienced rain tinted deep red, containing microscopic cells of unknown origin. These particles resisted DNA detection and extreme temperatures. Some scientists suggested extraterrestrial origins, while others considered unusual algae. Despite years of study, their composition remains uncertain. The “red rain” continues to fascinate researchers around the world.
2. 2. Metallic Hydrogen

Unknown author or not provided on wikimedia
Created under immense pressure, metallic hydrogen was first observed in controlled laboratory conditions. It exhibits properties of both a metal and a superconductor. Scientists believe it could revolutionize energy storage and propulsion systems. However, the material often disappears when pressure is released, making the study difficult. Its stability and potential remain largely unknown.
3. 3. Element 126 (Unbihexium)

Karola G on pexels
Theoretical and possibly synthesized in trace amounts, element 126 is part of the hypothesized “island of stability.” Predictions suggest it might exhibit extraordinary nuclear properties. However, it has yet to be fully confirmed or isolated. The few potential traces detected vanished almost instantly. Its existence challenges our understanding of atomic limits.
4. 4. The Black Goo of Iraq

Teona Swift on pexels
Discovered in ancient archaeological sites, a strange black substance was found coating artifacts and chambers. Chemical analysis failed to identify its exact composition. It resists decay, corrosion, and heat beyond known organic materials. Some believe it served a ritualistic or preservative purpose. The material’s durability has yet to be explained scientifically.
5. 5. Dark Matter

J. Bahcall, Institute for Advance Study, Princeton and NASA/ESA on wikimedia
Although it makes up most of the universe’s mass, dark matter remains invisible and undetectable by conventional instruments. Its gravitational effects are observed across galaxies, but its structure is unknown. Scientists theorize it may consist of exotic particles. Decades of experiments have failed to capture it directly. Understanding dark matter could redefine physics entirely.
6. 6. Quasicrystals
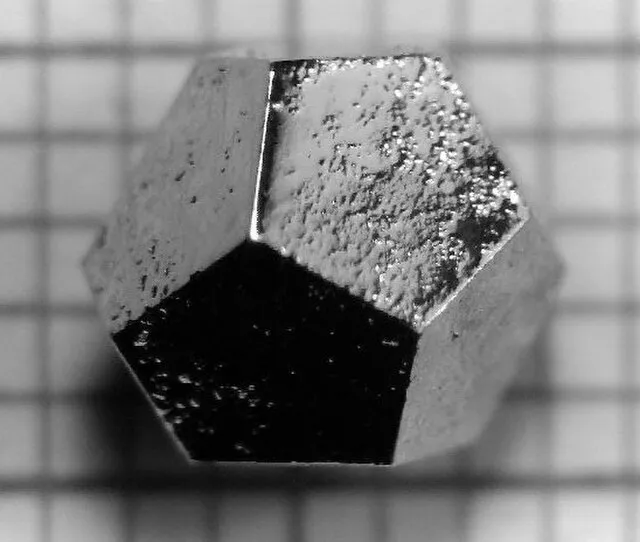
AMES lab on wikimedia
Quasicrystals were first discovered in a meteorite, defying traditional crystal symmetry. Their atomic arrangement follows mathematical patterns that do not repeat. These structures display unique strength and thermal stability. Despite replication in labs, their natural formation process remains unclear. They blur the boundary between natural and artificial materials.
7. 7. Ormus (White Powder Gold)

Karola G on pexels
Referred to in alchemical texts, Ormus is believed to contain altered states of matter. Modern enthusiasts claim it possesses unusual electromagnetic and healing properties. Scientific tests have yet to confirm its molecular identity. Some samples behave inconsistently under controlled analysis. It remains a mysterious blend of myth and material science.
8. 8. Bose-Einstein Condensate
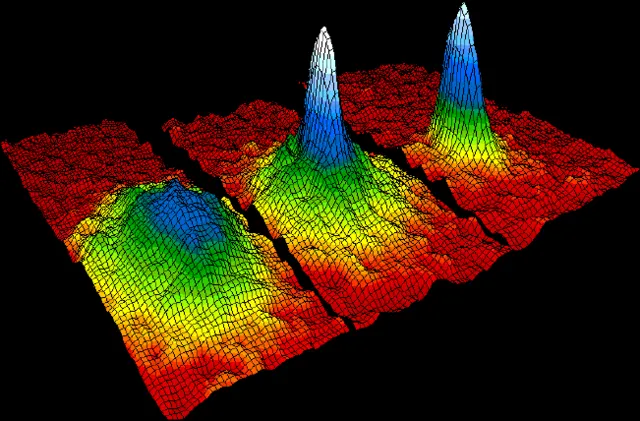
NIST/JILA/CU-Boulder on wikimedia
This rare state of matter forms when atoms are cooled near absolute zero. Under such conditions, particles behave as one unified quantum entity. Albert Einstein and Satyendra Bose first predicted it. Despite its creation in laboratories, its potential applications are still speculative. Scientists are only beginning to explore its unknown behaviors.
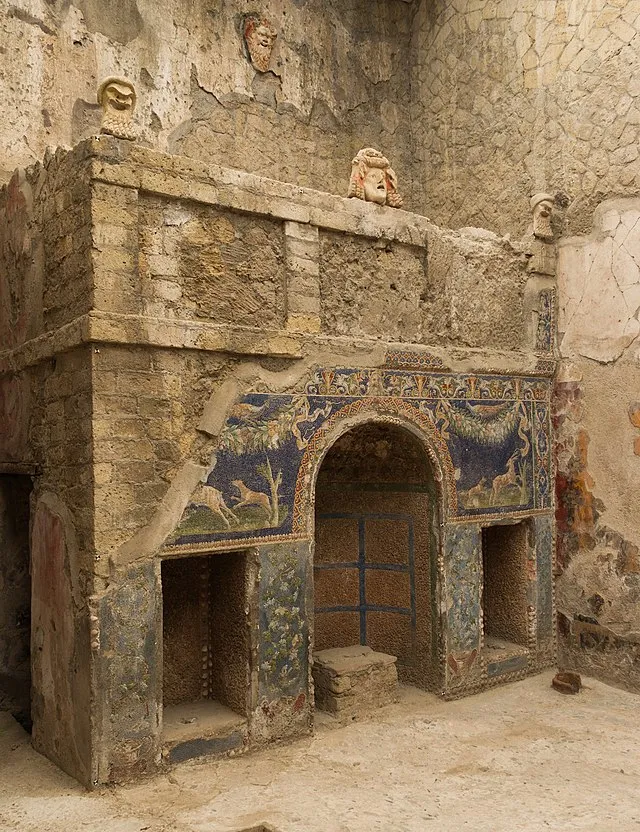
9. 9. Herculaneum Preservation Compound

Jebulon on wikimedia
In the ruins of Herculaneum, some organic materials, such as wood and food, were carbonized yet preserved. The chemical environment that caused this remains unreplicated. Researchers found traces of mineral interaction unlike anything known. The combination produced stability at extreme heat. Its protective chemistry continues to puzzle archaeologists and chemists alike.
10. 10. Transparent Aluminum
Pixabay on pexels
Initially fictional, transparent aluminum was later synthesized in laboratory conditions. It combines the clarity of glass with the strength of metal. However, its creation requires massive energy input and remains unstable at room temperature. Scientists do not fully understand how its atomic bonds maintain transparency. It could redefine modern construction materials once perfected.
11. 11. Ferrofluid Variants

Groupe Borra on wikimedia
Ferrofluids are magnetic liquids, but newly discovered variants behave unpredictably. Some maintain magnetic properties even when the external field is removed. Their viscosity and movement defy standard magnetism theories. Researchers cannot fully explain their stability under variable conditions. These strange liquids continue to reveal unexplored magnetodynamic effects.
12. 12. Substance Found in Tunguska Soil, Siberia

Aldoparisi on wikimedia
After the Tunguska explosion in 1908, fragments of a glass-like material were discovered in the area. They contained chemical structures not matching any known terrestrial mineral. Theories range from cometary origin to high-energy reactions in the atmosphere. Its exact molecular configuration remains unsolved. The material may hold clues about cosmic impact events.
13. 13. Black Stone of Kaaba, Saudi Arabia
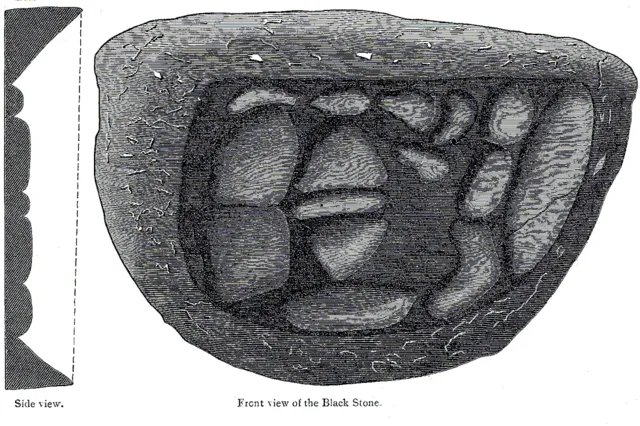
Public domain on wikimedia
The Black Stone embedded in the Kaaba has puzzled scientists and historians for centuries. It is thought to be of meteoritic origin, but its composition does not match known meteorites. The surface shows unique fusion patterns resistant to erosion. Studies have been limited due to its sacred status. Its true material nature remains an enduring mystery.
14. 14. Vitreous Desert Glass, Egypt

Vassil on wikimedia
Scattered across the Sahara, this yellow-green glass formed thousands of years ago. It possesses extreme purity and hardness, surpassing modern glassmaking techniques. The cause of its formation remains debated, possibly linked to a cosmic explosion or lightning storm. Chemical analysis has not pinpointed its source. Its creation defies both natural and artificial explanation.
15. 15. Superionic Ice

cottonbro studio on pexels
Found deep within planetary interiors, superionic ice behaves neither like a solid nor a liquid. Its oxygen atoms form a lattice while hydrogen ions move freely within it. Scientists recreated it under extreme pressure, revealing electrical conductivity beyond expectations. However, its natural stability remains poorly understood. It challenges the conventional definition of ice.
16. 16. Unknown Polymer in Ancient Roman Paints
Elcap on wikimedia
Roman frescoes and paintings often retain color despite centuries of exposure. Researchers found trace polymers within pigments that resist oxidation. These compounds have no modern chemical equivalent. Their synthesis process remains unidentified. The discovery demonstrates that ancient artisans possessed advanced material knowledge.
17. 17. Metallic Spheres from Klerksdorp, South Africa

ambientCG / Lennart Demes on wikimedia
Small metallic spheres discovered in rock layers estimated to be billions of years old baffle scientists. They exhibit precise grooves and symmetry rarely found in natural formations. Their composition includes nickel and other metals in unusual ratios. Some believe they are geological oddities, others suspect ancient manufacturing. Their exact origin and purpose remain unresolved.
18. 18. Alien-like Material in Interstellar Dust

NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Ariz. on wikimedia
Collected by NASA’s Stardust mission, interstellar dust samples revealed complex organic compounds. Some of these molecules exhibit reactions unknown to chemistry on Earth. Their stability under radiation contradicts known organic behavior. Researchers continue to study their atomic structures with great caution. These materials may hold the key to understanding extraterrestrial chemistry.