18 Military Blunders That Changed the Outcome of Wars
Here's a list of 18 real military blunders that changed wars, showing how mistakes in planning, strategy, and leadership reshaped history.
- Alyana Aguja
- 5 min read

History is full of wars decided not just by strength, but by costly mistakes that altered outcomes. From Napoleon’s ill-fated march into Russia to Hitler’s disastrous gamble at Stalingrad, these blunders reveal the dangers of miscalculation and arrogance. Each case demonstrates how one error can tip the balance of power and change the course of nations.
1. 1. Napoleon’s Invasion of Russia (1812)
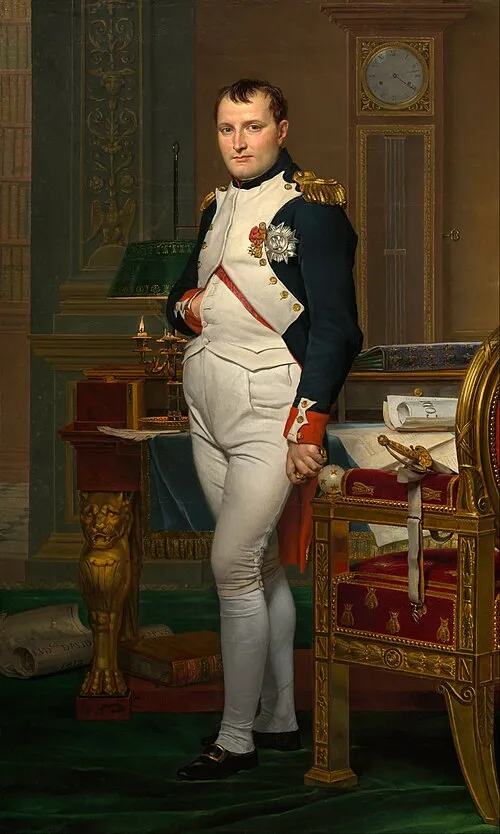

Image from Wikipedia
Napoleon’s decision to invade Russia with over 600,000 troops ended in disaster when the Russian scorched-earth strategy deprived his army of supplies. Harsh winter conditions and disease decimated his forces during the retreat from Moscow. The campaign shattered Napoleon’s reputation for invincibility and weakened his empire permanently.
2. 2. The Charge of the Light Brigade (1854)

Image from Wikipedia
During the Crimean War, miscommunication led British cavalry to charge directly into Russian artillery fire at Balaclava. The result was massive casualties and little strategic gain. The incident became a symbol of bravery mixed with tragic military mismanagement.
3. 3. Hitler Diverting Troops to Stalingrad (1942–1943)
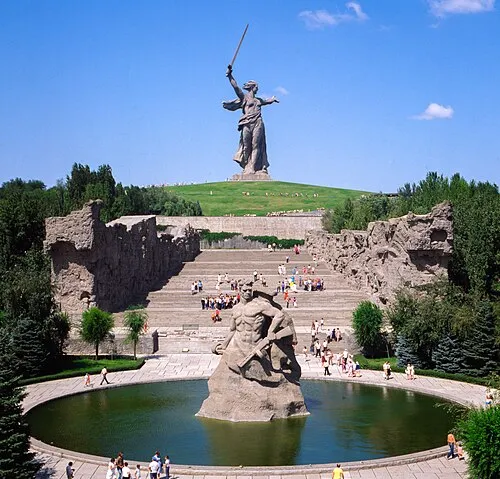

Image from Wikipedia
Instead of focusing on capturing Moscow, Hitler diverted German forces to Stalingrad. The prolonged battle drained resources and ended in Germany’s first major defeat. The loss crippled the Wehrmacht and shifted momentum to the Soviet Union.
4. 4. Confederate Pickett’s Charge at Gettysburg (1863)

Image from Wikipedia
General Robert E. Lee ordered a direct assault on Union lines at Gettysburg, despite strong defensive positions. The attack led to devastating Confederate losses. It marked the turning point of the American Civil War in favor of the Union.
5. 5. The Gallipoli Campaign (1915–1916)

Image from Wikipedia
The Allies underestimated Ottoman resistance during the Gallipoli landings. Poor planning and logistical failures caused heavy losses and eventual withdrawal. The failed campaign boosted Turkish morale and hurt Allied credibility.
6. 6. The Spanish Armada (1588)
Image from Wikipedia
Spain’s attempt to invade England was thwarted by poor planning, bad weather, and effective English naval tactics. Ships were scattered and forced to retreat in disarray. The defeat secured England’s naval dominance and began Spain’s decline.
7. 7. France’s Maginot Line Strategy (1940)

Image from Wikipedia
France built the Maginot Line to block a German invasion, but the Germans bypassed it through Belgium. The reliance on outdated defenses left France vulnerable. The blunder led to a swift German occupation of France.
8. 8. Japan Attacking Pearl Harbor (1941)

Image from Wikipedia
apan’s attack on Pearl Harbor crippled the U.S. Pacific Fleet temporarily but provoked American entry into World War II. Instead of weakening the U.S., it galvanized the nation. The decision ensured Japan would face a much stronger enemy.
9. 9. The Battle of Little Bighorn (1876)

Image from Wikipedia
General George Custer underestimated Native American forces under Sitting Bull and Crazy Horse. His men were surrounded and annihilated. While a temporary victory for the Sioux, it led to overwhelming U.S. retaliation.
10. 10. The Fall of Singapore (1942)

Image from Wikipedia
British forces in Singapore underestimated Japanese capabilities and focused defenses seaward, leaving landward approaches weak. The Japanese advanced swiftly and captured the city in one week. The surrender of 80,000 British troops was one of the worst defeats in British military history.
11. 11. Athens’ Sicilian Expedition (415–413 BC)

Image from Wikipedia
Athens attempted to conquer Sicily during the Peloponnesian War, but poor planning and leadership doomed the mission. The fleet was destroyed, and thousands of soldiers were lost. The defeat accelerated Athens’ decline and eventual loss to Sparta.
12. 12. The Battle of Tannenberg (1914)

Image from Wikipedia
Russian commanders failed to coordinate during the invasion of East Prussia. German forces under Hindenburg and Ludendorff encircled and destroyed a Russian army. The defeat weakened Russian morale early in World War I.
13. 13. Italy’s Invasion of Greece (1940)

Image from Wikipedia
Mussolini’s ill-prepared invasion of Greece ended in failure, with Italian forces pushed back into Albania. Germany had to divert resources to assist, delaying its invasion of the Soviet Union. The blunder cost the Axis precious time and momentum.
14. 14. The Battle of Dien Bien Phu (1954)

Image from Wikipedia
French forces set up a fortified base in a valley in Vietnam, believing it was defensible. Viet Minh forces surrounded the valley and used artillery from the hills to crush the French. The defeat ended French colonial rule in Indochina.
15. 15. Operation Market Garden (1944)

Image from Wikipedia
The Allies attempted a bold airborne operation to seize bridges in the Netherlands. Poor intelligence and underestimated German resistance led to failure. The setback prolonged the war in Europe.
16. 16. The Battle of Karansebes (1788)

Image from Wikipedia
During the Austro-Turkish War, Austrian troops mistook each other for the enemy after a drunken quarrel. Panic spread, and soldiers fired on their own side. The blunder cost thousands of lives and left them vulnerable to Ottoman attack.
17. 17. The Siege of Vienna by the Ottomans (1683)
Image from Wikipedia
The Ottomans underestimated the resilience of Vienna and the speed of European reinforcements. Delays in breaching the city walls allowed a relief army to arrive. The defeat marked the decline of Ottoman expansion into Europe.
18. 18. The Fall of Constantinople’s Weak Gate Defense (1453)
Image from Wikipedia
During the Ottoman siege of Constantinople, a small gate known as the Kerkoporta was left unsecured. Ottoman troops exploited the mistake and entered the city. The oversight sealed the Byzantine Empire’s fate and shifted global power.