20 Discoveries That Could Rewrite Everything We Know About History
A growing collection of scientific breakthroughs is prompting researchers to rethink long-accepted historical narratives. These discoveries hint at civilizations, technologies, and cultures far more complex than previously imagined.
- Tricia Quitales
- 6 min read

New discoveries continue to reshape our understanding of humanity’s past in ways that feel both thrilling and deeply humbling. Fresh evidence from archaeology, genetics, and ancient engineering is revealing chapters of history that seemed impossible only a few years ago. Each finding expands the story of human innovation, migration, belief, and survival. The following exploration dives into twenty breakthroughs that challenge long held assumptions and open surprising new paths of inquiry.
1. 1. The Göbekli Tepe Revelation
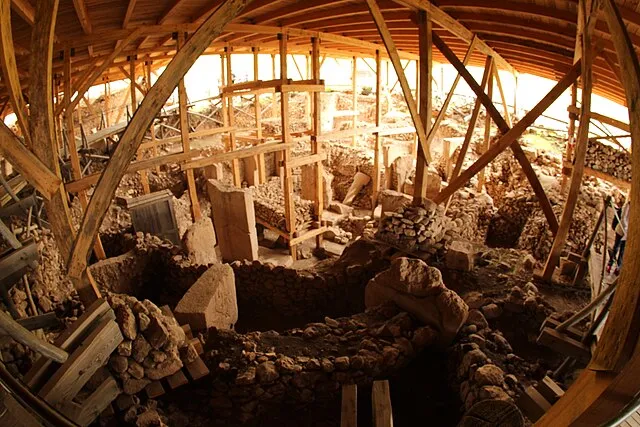

Hamdigumus on wikimedia
Göbekli Tepe in Turkey appears to predate agriculture by several thousand years. Its megalithic pillars suggest a level of organization once thought impossible for hunter-gatherer groups. The site challenges assumptions about the dawn of civilization. It hints that religious or communal gatherings may have inspired farming rather than the reverse. The discovery forces scholars to reconsider how complex societies actually formed.
2. 2. The Denisovan Genome
Joevet on Pixabay
Genetic analysis of Denisovan remains revealed an unknown branch of ancient humans. The discovery transformed ideas about early human migration. Traces of Denisovan DNA in modern populations show that interbreeding was more common than once believed. Their presence in regions across Asia suggests wide-ranging adaptability. Human evolution now appears far more intertwined and diverse.
3. 3. Lost Amazonian Urban Networks
Internet Archive Book Images on wikimedia
Lidar scans uncovered enormous road systems and settlements hidden beneath Amazonian forests. The scale indicates highly organized urban planning. These findings contradict the idea that the Amazon was home only to small tribes. The region may have supported large populations before European contact. The evidence suggests that the rainforest was once engineered and shaped by human hands.
4. 4. The Antikythera Mechanism
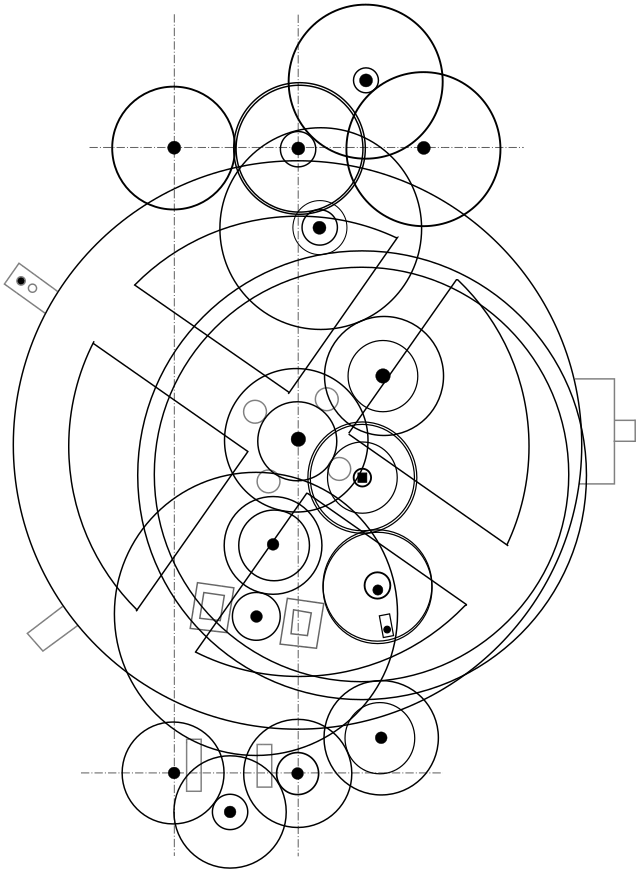
Lead Holder on wikimedia
The Antikythera Mechanism is often called the earliest known analog computer. Its precision reveals sophisticated Greek knowledge of astronomy. Gears and inscriptions point to advanced scientific understanding. The device challenges assumptions about technological limits in the ancient world. It suggests that complex machines were more widespread than surviving artifacts imply.
5. 5. The Younger Dryas Impact Debate

free on Pixabay
Some scientists propose that a cosmic impact triggered abrupt climate change around 12,900 years ago. Evidence includes unusual layers of carbon, platinum, and nanodiamonds. If confirmed, the event might explain sudden cultural shifts in early human societies. It could reveal why some megafauna went extinct. The debate continues, but the implications remain significant.
6. 6. The Tartaria Tablets
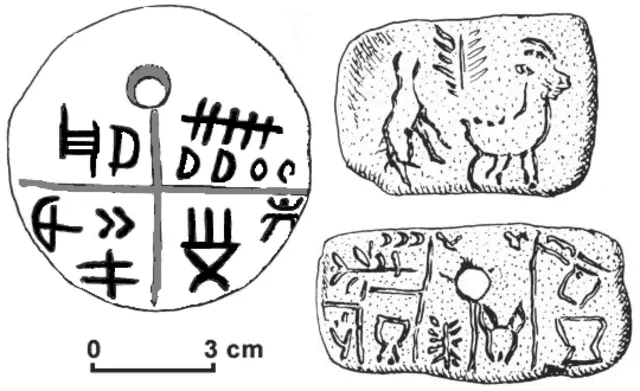
Mazarin07 on wikimedia
The Tartaria Tablets from Romania feature intricate symbols. Some researchers believe they represent early writing. If true, they predate Mesopotamian scripts by centuries. The possibility challenges long-held timelines for the birth of written language. Their meaning remains unknown, yet the potential impact is enormous.
7. 7. The Neolithic Stone Spheres of Costa Rica
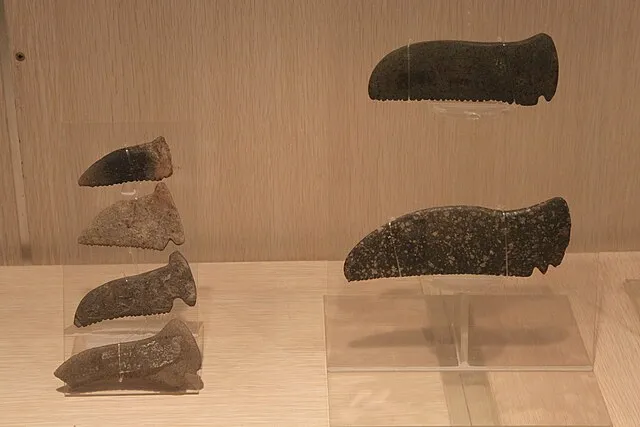

Gary Todd on wikimedia
Massive carved stone spheres dot Costa Rican landscapes. Their precision reflects remarkable craftsmanship. The spheres raise questions about the culture that produced them. Their purpose remains mysterious despite decades of study. They offer a glimpse into symbolic traditions that may never be fully understood.
8. 8. The Indus Valley Water Systems

Unknown author on wikimedia
Archaeologists discovered complex plumbing and drainage in Indus Valley cities. The systems show impressive engineering skill. Their uniformity suggests centralized planning. These features imply sophisticated governance structures. The discoveries indicate that ancient urban life was more advanced than many modern cities assume.
9. 9. The Siberian Permafrost Creatures

Great Sand Dunes National Park and Preserve on wikimedia
Well-preserved Ice Age animals have been uncovered in Siberian permafrost. Their tissues provide genetic insights into extinct species. These remains offer clues about prehistoric ecosystems. Some discoveries show evidence of human interaction with megafauna. The findings continue to reshape our understanding of Ice Age life.
10. 10. The Pyramids Water Pump Theory

Mozmoz31 on wikimedia
Some researchers suggest that specific pyramid corridors reflect hydraulic engineering principles. The theory proposes that ancient builders used water pressure for construction or ceremonial purposes. Such an idea challenges traditional interpretations of pyramid function. Geological markings appear consistent with flowing water. The concept, though debated, broadens discussions about ancient Egyptian science.
11. 11. The Atlit Yam Underwater Settlement
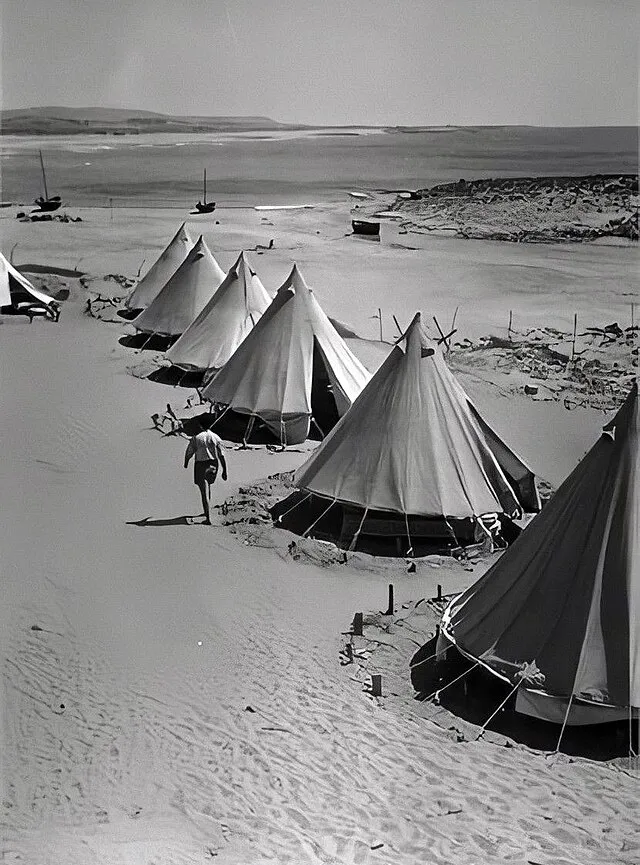

קלצל on wikimedia
Atlit Yam lies submerged off the coast of Israel. The site features homes, wells, and ritual structures. Rising sea levels likely forced its abandonment. Evidence of early disease patterns has been found in its graves. The settlement demonstrates the vulnerability of ancient coastal societies.
12. 12. The Roman Concrete Secret
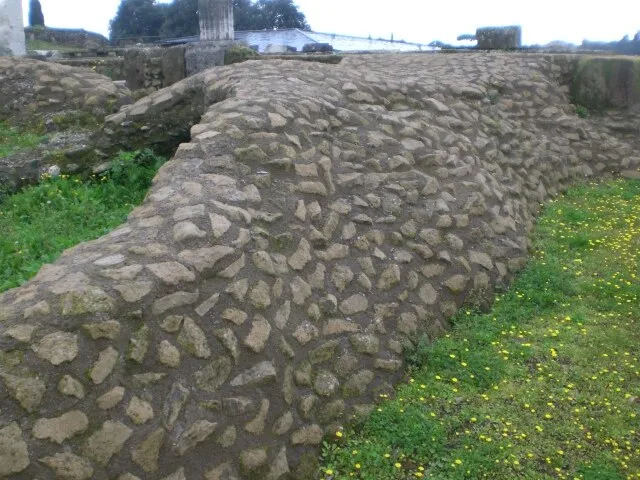

Øyvind on wikimedia
Roman concrete has proven more durable than many modern mixtures. Its resilience stems from volcanic ingredients that self-heal over time. Engineers are studying its composition to develop stronger materials. The discovery shifts perspectives on ancient building science. It shows that past innovations can still outperform current technologies.
13. 13. The Bronze Age Collapse Complexity

Gary Todd on wikimedia
Recent research suggests that multiple factors triggered the Bronze Age collapse. These include climate shifts, trade disruption, and internal conflicts. The event was once attributed mainly to invading groups. New data portrays a more interconnected downfall. Historians now view the collapse as a multifaceted crisis.
14. 14. The Mayan Astronomical Mastery

Unknown author or not provided on wikimedia
Mayan observatories reveal incredible precision in tracking celestial cycles. They predicted events like eclipses with astounding accuracy. Such skills influenced agriculture and ritual life. Their achievements challenge stereotypes of ancient American science. The complexity of their knowledge continues to impress researchers.
15. 15. The Çatalhöyük Social Structure
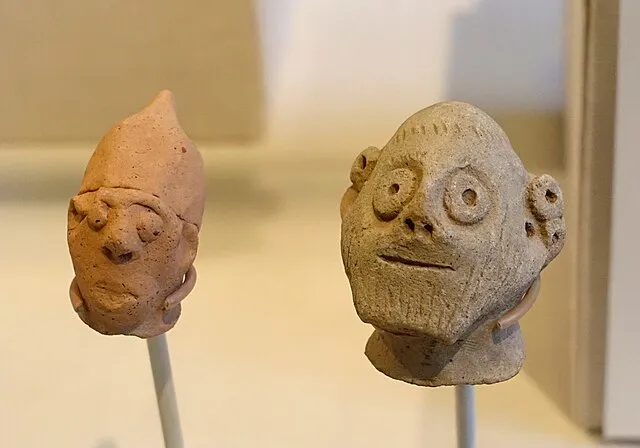

Daderot on wikimedia
Çatalhöyük featured densely packed homes without streets. Residents moved across rooftops and entered homes from above. The layout suggests unique community planning. Artistic finds reveal complex symbolic traditions. The settlement challenges assumptions about early urban life.
16. 16. The Uluburun Shipwreck
Panchamkauns on wikimedia
The Uluburun shipwreck contains artifacts from multiple ancient cultures. Bronze tools, jewelry, and raw materials fill its cargo. The collection showcases vast trade networks in the Late Bronze Age. The ship demonstrates deep connections among early civilizations. The discovery rewrites ideas about ancient global commerce.
17. 17. The Cuneiform Mathematics Tablets

Mason, William Albert, 1855-1923 on wikimedia
Clay tablets from Mesopotamia display advanced mathematical concepts. Some include early forms of trigonometry. The content reveals sophisticated numerical skills. These findings challenge the idea that mathematics developed slowly. Ancient scholars possessed remarkable analytical abilities.
18. 18. The Stonehenge Bluestone Origins
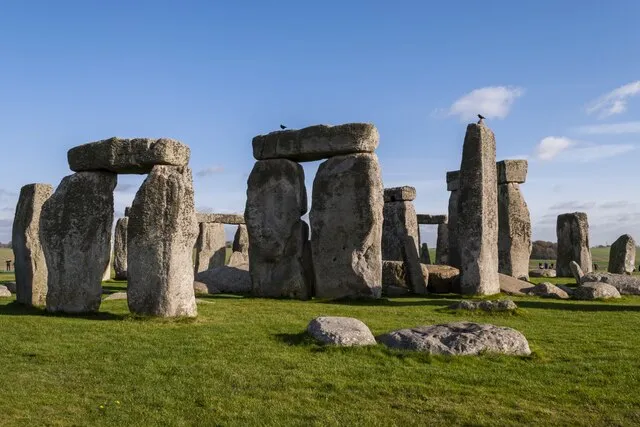

Tristan J. Wilson on wikimedia
Analysis shows that Stonehenge bluestones came from quarries in Wales. Transporting them required immense effort. The process indicates strong cultural or spiritual motivations. The discovery expands understanding of prehistoric logistics. It highlights the determination of early builders.
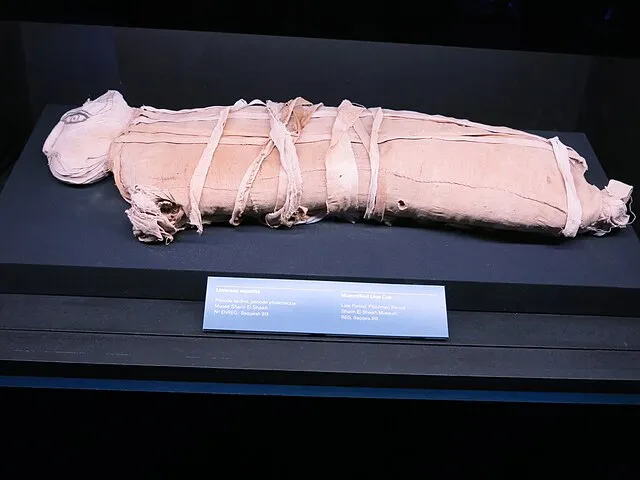
19. 19. The Saqqara Animal Mummies
Tangopaso on wikimedia
Excavations in Saqqara revealed thousands of animal mummies. Many animals played symbolic or religious roles. Their preservation techniques were highly refined. The discoveries illustrate the complexity of ancient Egyptian beliefs. The scale shows how deeply animals influenced cultural identity.
20. 20. The Oldest Known Brewery

Hans on pixabay
Archaeologists identified traces of beer production in caves in Israel. The evidence dates back over thirteen thousand years. Brewing appears to predate agriculture in some regions. This discovery suggests that communal drinking rituals may have shaped early societies. It challenges assumptions about the motivations behind farming.