20 Discoveries That Defied Every Known Scientific Law
Some scientific discoveries challenged established laws, forcing researchers to rethink physics, chemistry, and biology.
- Sophia Zapanta
- 4 min read

Throughout history, certain discoveries seemed impossible according to the scientific knowledge of their time. From unexpected particle behavior to unexplained cosmic phenomena, these findings defied conventional laws. They pushed science forward, often creating new theories and expanding our understanding of the universe.
1. 1. Quantum Entanglement
Farbodk on Wikimedia Commons
Entangled particles affect each other instantly, even across vast distances. This violates classical ideas of locality. Einstein called it “spooky action at a distance.” Experiments confirm entanglement, challenging classical physics.
2. 2. Superconductivity
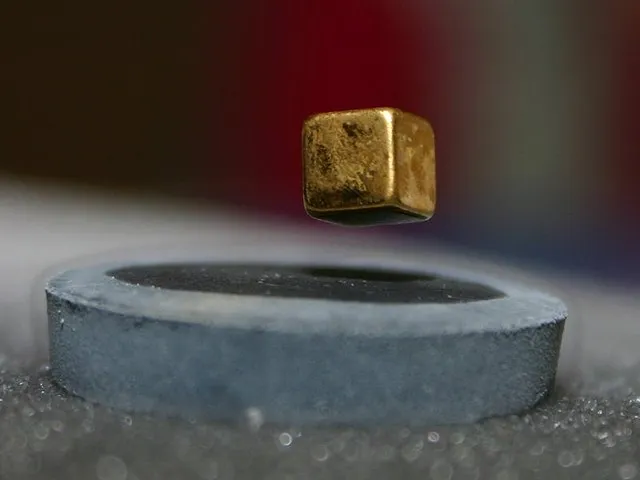

Peter nussbaumer on Wikimedia Commons
Certain materials conduct electricity with zero resistance at very low temperatures. This phenomenon could not be explained by classical physics. It challenges the traditional understanding of electron movement. Superconductors have enabled MRI machines and maglev trains.
3. 3. Superfluidity
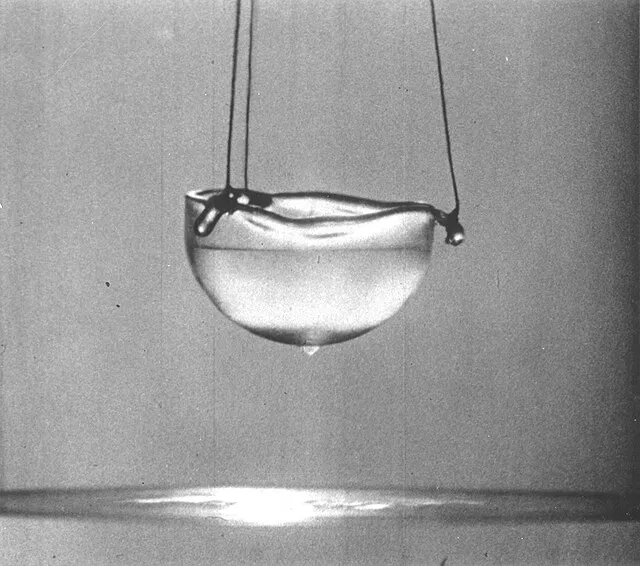
Liquid Helium,Superfluid on Wikimedia Commons
Helium-4 becomes a superfluid at extremely low temperatures, flowing without friction. Its behavior defies classical fluid dynamics. Superfluid can climb walls or flow through tiny pores. It required new quantum mechanical models to explain.
4. 4. Antimatter
NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio on Wikimedia Commons
For every particle, an antiparticle exists that annihilates it upon contact. This challenges simple ideas of matter balance. Antimatter is rare in the universe. Its discovery changed particle physics and cosmology.
5. 5. Neutrino Oscillations
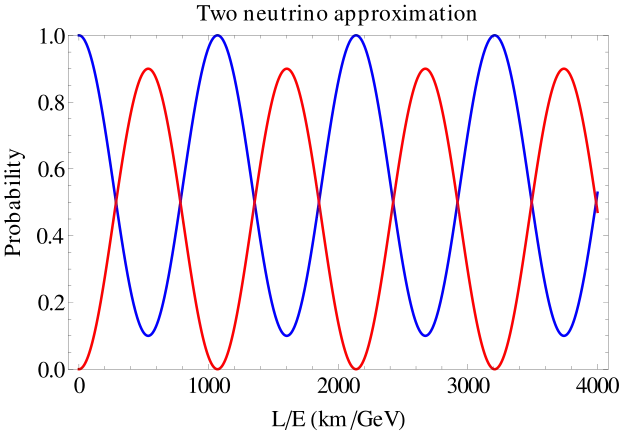
Wikimedia Commons
Neutrinos change type as they travel, implying they have mass. This contradicts the original Standard Model, which assumed massless neutrinos. Experiments in the 1990s confirmed oscillations, reshaping particle physics theories.
6. 6. Dark Matter
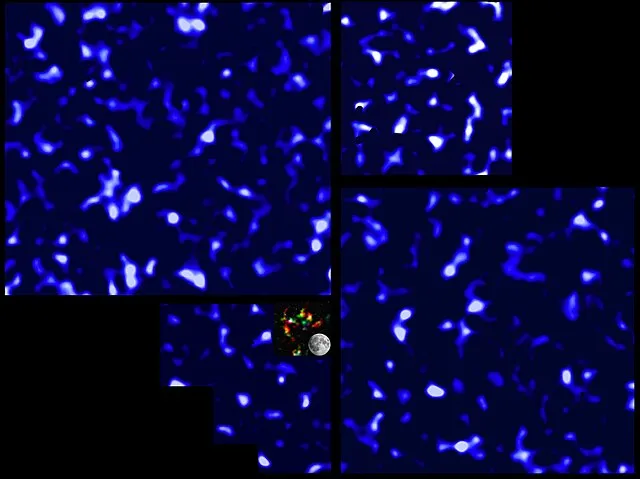
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Lensing Survey on Wikimedia Commons
Galactic rotation curves show more mass than visible matter accounts for. This defies Newtonian physics predictions. Dark matter cannot be seen directly, and its presence is inferred through gravitational effects.
7. 7. Dark Energy
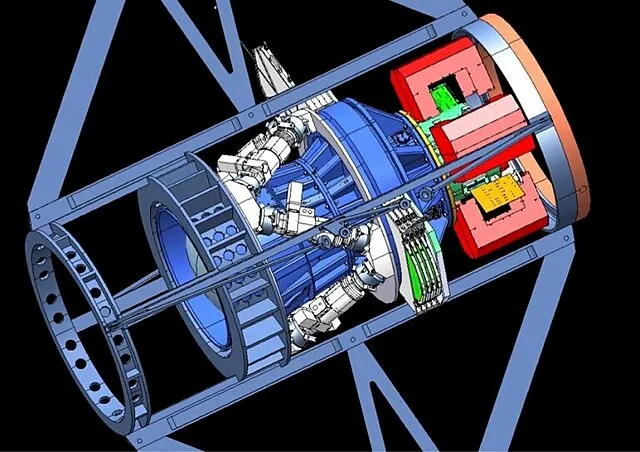
NOIRLab on Wikimedia Commons
The universe’s expansion is accelerating, which violates expectations from gravity alone. This suggests a mysterious form of energy. Dark energy constitutes about 70% of the universe. Its nature remains one of physics’ biggest mysteries.
8. 8. The Casimir Effect
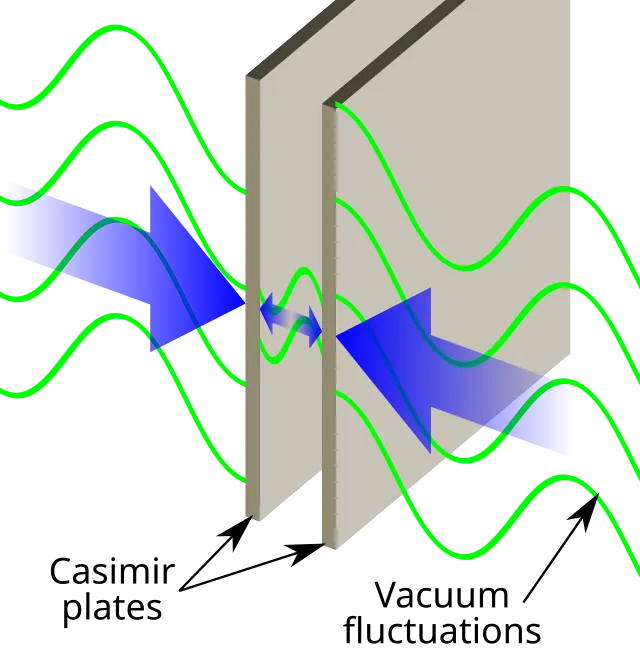
Emok on Wikimedia Commons
Two uncharged metal plates in a vacuum attract due to quantum fluctuations. This seems impossible in classical physics. It demonstrates energy in “empty” space. The effect is relevant in nanotechnology and quantum theory.
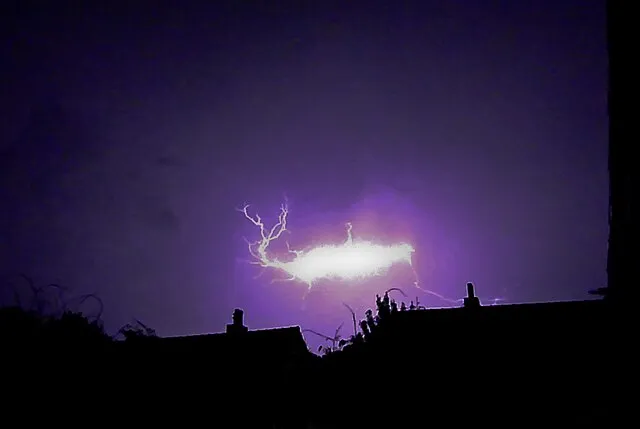
9. 9. Ball Lightning

Joe Thomissen on Wikimedia Commons
Glowing spheres appear during thunderstorms and move unpredictably. Their behavior cannot be explained by standard electromagnetism. Observed for centuries, they remain poorly understood. Some reports suggest they can pass through walls.
10. 10. Muon g-2 Anomaly
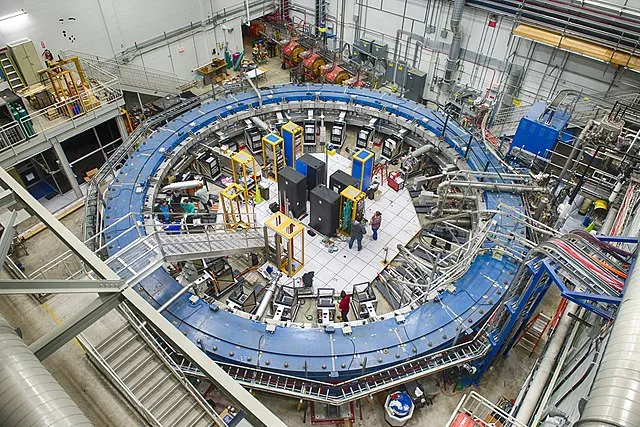
Reidar Hahn on Wikimedia Commons
Muon magnetic properties deviate slightly from predictions. This may indicate unknown particles or forces. It challenges the Standard Model, and experiments at Fermilab continue to explore it.
11. 11. High-Temperature Superconductors

SPat on Wikimedia Commons
Certain ceramics superconduct at unusually high temperatures. This defied prior expectations that only metals at near absolute zero could superconduct. It prompted new theories in condensed matter physics. Applications include power transmission and maglev technology.
12. 12. Quantum Tunneling
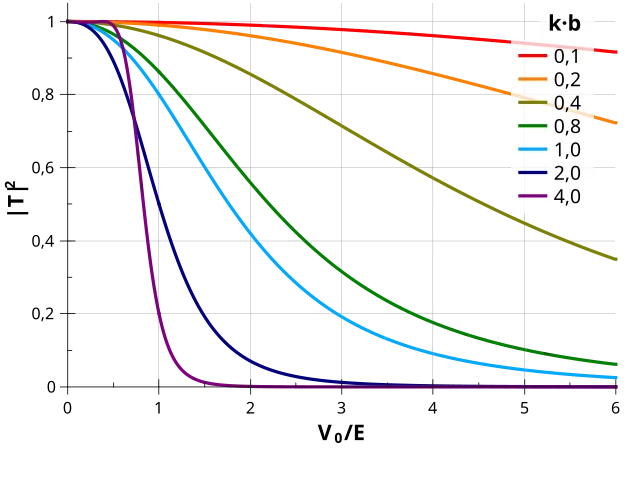
Kondephy on Wikimedia Commons
Particles can pass through barriers that they shouldn’t be able to cross classically. This contradicts Newtonian physics. Quantum tunneling is essential in nuclear fusion and electronics. It illustrates the probabilistic nature of quantum mechanics.
13. 13. The Mpemba Effect
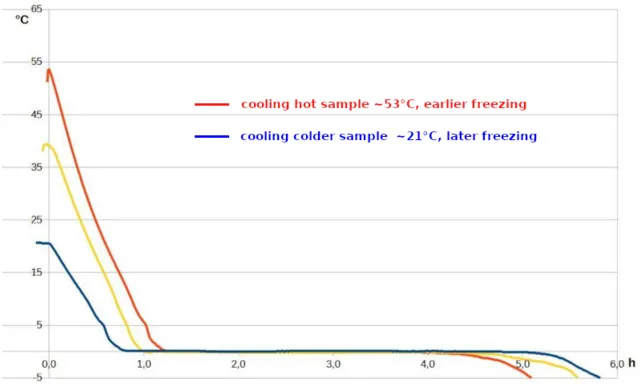
Ren Tier on Wikimedia Commons
Hot water sometimes freezes faster than cold water. This phenomenon defies classical thermodynamics. Scientists still debate why it occurs. Factors may include evaporation, convection, and molecular structure.
14. 14. Time Dilation
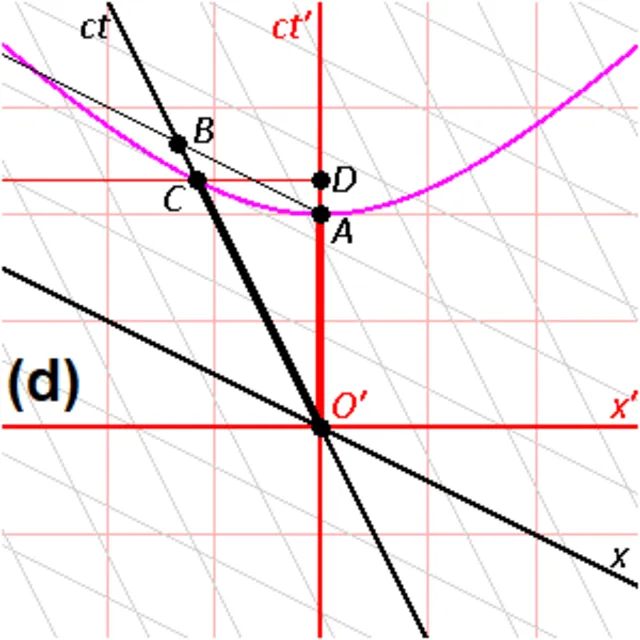
Stigmatella_aurantiaca on Wikimedia Commons
According to relativity, time moves slower for fast-moving objects. This defies classical Newtonian time concepts. Confirmed with atomic clocks on airplanes and satellites. It is crucial for GPS technology.
15. 15. Positron Discovery
Christkannada on Wikimedia Commons
Carl Anderson discovered the first antiparticle, the positron, in 1932. Its existence was predicted theoretically but seemed impossible at the time. This confirmed the antimatter theory. It opened the field of particle physics.
16. 16. Bose-Einstein Condensates
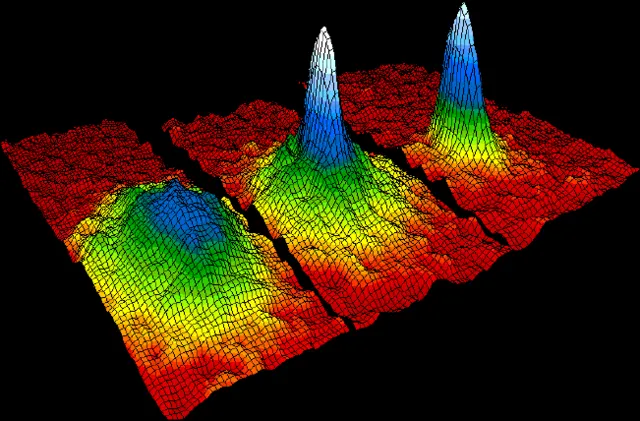
NIST/JILA/CU-Boulder on Wikimedia Commons
At near absolute zero, particles occupy the same quantum state. They behave as a single “super atom.” This violates classical particle expectations. It provides insight into quantum mechanics and superfluidity.
17. 17. Neutron Stars

NASA on Wikimedia Commons
Neutron stars are incredibly dense objects formed from supernovae. Their density and gravity defy classical expectations. One teaspoon of neutron star matter weighs billions of tons. They challenge the understanding of matter under extreme pressure.
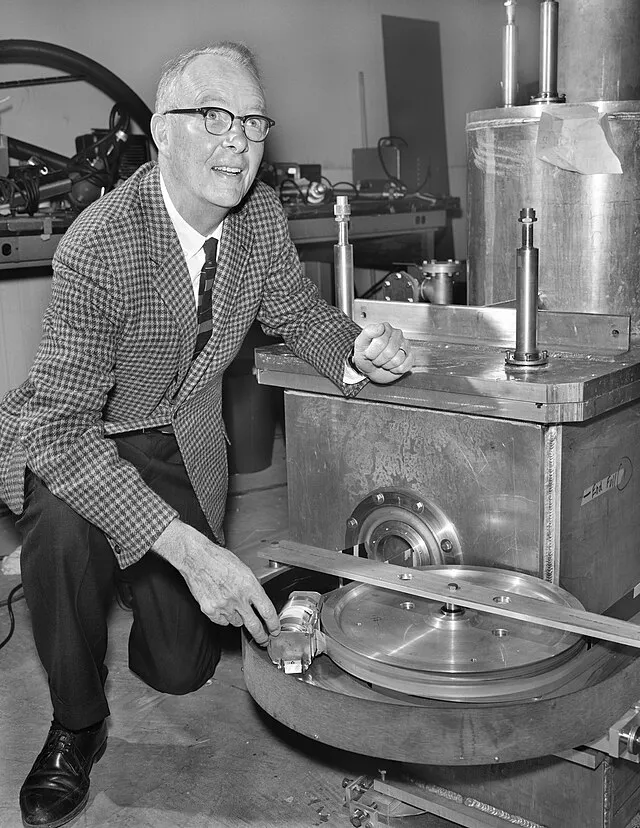
18. 18. Magnetic Monopole (Hypothetical Evidence)

Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory on Wikimedia Commons
Some experiments hint at the existence of isolated magnetic poles. Classical electromagnetism predicts that magnetic poles always exist in pairs. A monopole would revolutionize physics. Conclusive evidence has yet to be found.
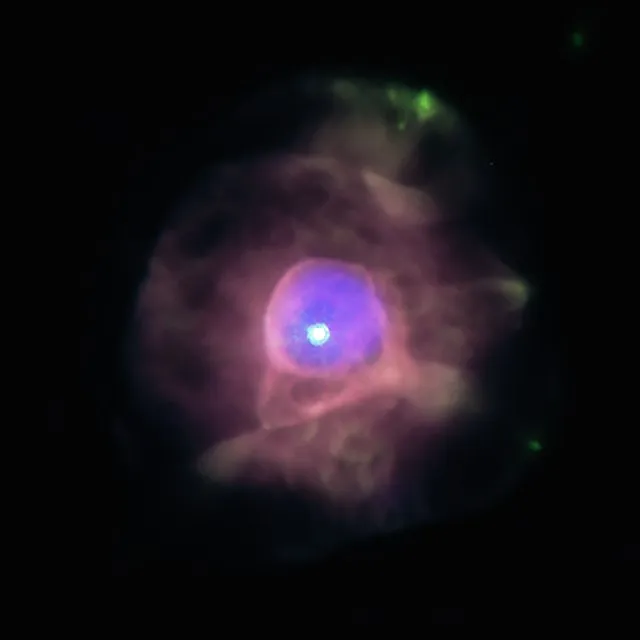
19. 19. Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays

NASA/CXC/UNAM/J. on Wikimedia Commons
Cosmic rays have been detected with energies beyond theoretical limits. This contradicts known astrophysical acceleration processes. Their origin is still unexplained. They challenge our understanding of particle physics in space.
20. 20. The Pioneer Anomaly
Carl Sagan on Wikimedia Commons
Spacecraft Pioneer 10 and 11 deviated from predicted paths. This appeared to violate Newtonian gravity. Later, small thermal forces explained part of the anomaly. The discovery initially challenged gravitational understanding.