20 Recently Discovered Species in the Natural World
The recent description of these 20 species, ranging from massive anacondas and vibrant fish to tiny frogs and nickel-accumulating plants, illuminates the astonishing depth of undiscovered biodiversity still present in the world's most remote and complex ecosystems.
- Alyana Aguja
- 13 min read

The documentation of 20 recently discovered species dramatically highlights the ongoing process of biological discovery across the globe. These new additions to the tree of life demonstrate that millions of organisms remain unknown to science. The findings often result from applying advanced genetic techniques to previously collected specimens or through dedicated field research in biodiversity hotspots. These discoveries are not merely academic; they often reveal species with restricted distributions. By formally describing and naming these organisms, scientists can draw essential conservation attention to their unique evolutionary value and the pressing need to protect their fragile ecosystems.
1. 1. The Northern Green Anaconda (Eunectes akayima)
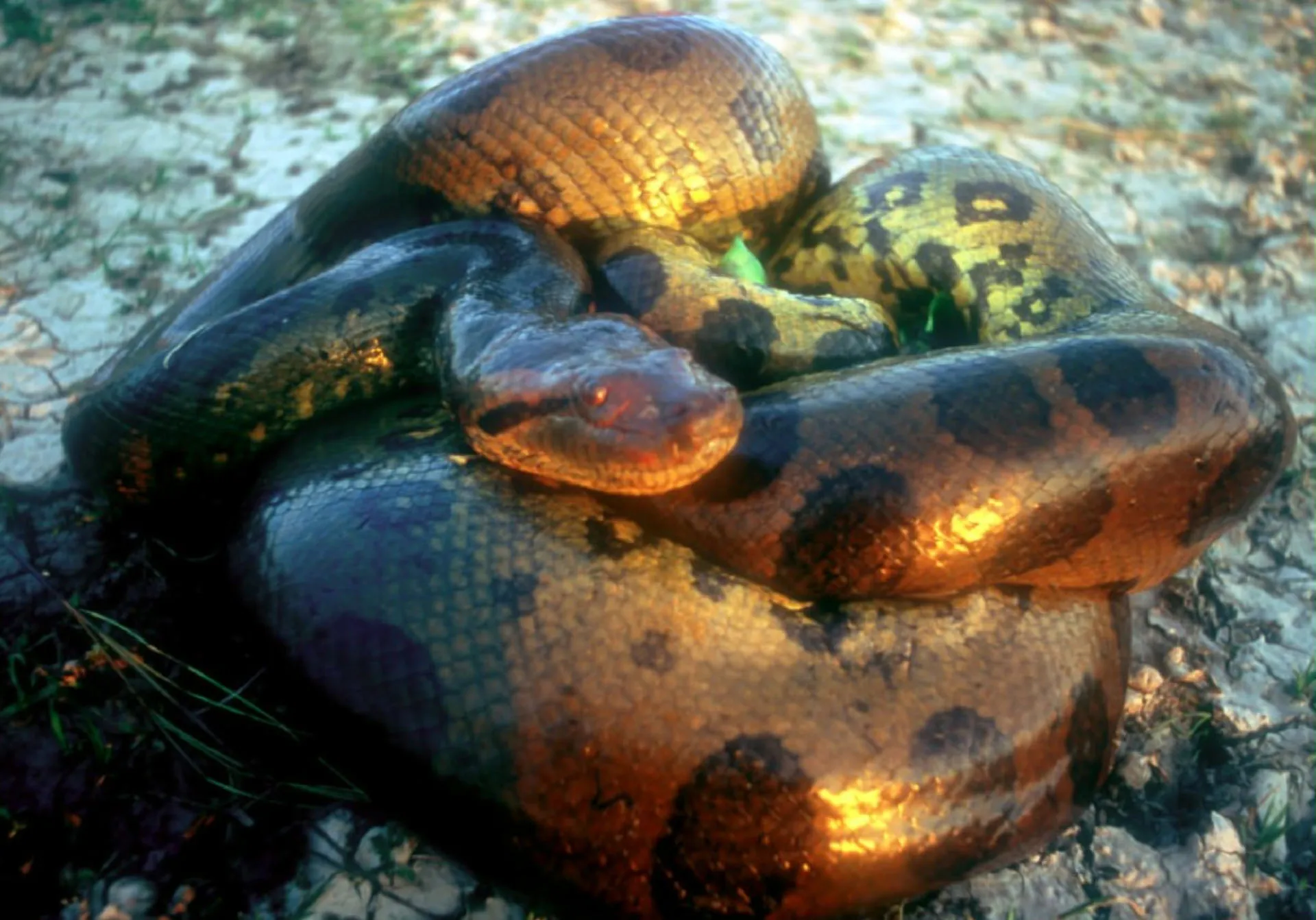

Image from Sci.News
This massive snake species, distinct from the Southern Green Anaconda, was recently confirmed through genetic analysis in the Ecuadorian Amazon. It represents one of the largest and heaviest snakes known, with one individual measured at an astonishing 6.3 meters in length during a scientific expedition. The discovery highlights the deep evolutionary splits that can occur even among seemingly familiar, widespread megafauna.
Eunectes akayima likely separated from its southern relatives approximately 10 million years ago, suggesting a long, independent evolutionary history hidden within the vast Amazonian ecosystem. Its existence underscores the incredible biodiversity still waiting to be formally recognized in the world’s most remote and complex biomes, especially within South America. The formal description emphasizes the critical need for regional conservation efforts to protect this apex predator and its diminishing habitat.
2. 2. The Stream Treefrog (Hyloscirtus tolkieni)

Image from Mongabay
Found in the Andean cloud forests of Ecuador, this vibrant stream treefrog was named in honor of author J.R.R. Tolkien, its fantastical coloring evoking the magnificent creatures of his fantasy worlds. A single individual was enough to confirm it as a new species due to its distinct and unmistakable morphology and coloration, which were unlike any known stream treefrog. The frog’s unique patterns and bright hues, reminiscent of a fantasy tapestry, underscore the biodiversity found within the Río Negro-Sopladora National Park. Researchers believe it only exists in this small, high-elevation area, making it incredibly vulnerable to environmental changes. Its discovery emphasizes the importance of protecting the Andean mountain slopes, which serve as vital reservoirs of unique and endemic amphibian life.
3. 3. The Vampire Hedgehog (Hylomys macarong)

Image from BBC
A truly captivating find from the Greater Mekong region, this small mammal earned its dramatic name from its unusual, elongated, fang-like teeth. Despite its intimidating moniker, the Vampire Hedgehog is actually a type of shrew-like gymnure, a relative of the hedgehog that lacks spines, and is one of two new shrew-like mammals found recently in the area. Its distinctive dental structure is a key morphological feature that sets it apart from closely related species, showcasing the often-subtle but significant differences that separate species. The discovery of the Vampire Hedgehog underscores the fact that even in well-surveyed regions, cryptic diversity among small, ground-dwelling mammals remains a rich area for exploration. Protecting the remaining forests in the Greater Mekong is vital for its survival.
4. 4. The Grumpy Dwarfgoby (Sueviota aethon)

Image from EurekAlert!
This tiny, fiery-red fish was discovered in the coral reefs of the Red Sea and immediately gained attention for its distinctly “pouty” expression. Its lower jaw protrudes slightly, giving it a perpetually irritated look, which inspired the playful common name for the diminutive creature. Measuring only about two centimeters long, it is a fierce predator in its miniature world. Scientific analysis revealed that this species, with its four elongated canines used for catching prey, was previously mistaken for a closely related species, the Fiery Dwarfgoby. The Sueviota aethon’s shorter pelvic fins and unique lack of spots helped distinguish it as an entirely new species. Its discovery highlights the rich and often overlooked diversity thriving within the mesophotic zones of tropical coral reefs globally.
5. 5. The Rosé-Veiled Fairy Wrasse (Cirrhilabrus finifenmaa)

Image from California Academy of Sciences
Hailing from the Maldives, this stunningly colored reef fish is notable for being the first new-to-science species to be formally described by a Maldivian scientist. Its species name, finifenmaa, is the local Dhivehi word for ‘rose’, a tribute to its pink hues and the Maldives’ national flower, perfectly capturing its delicate beauty. The male of the species is particularly striking, exhibiting an array of colors that shift from magenta to peach, a truly dazzling sight among the coral. Found in the mesophotic zone, the so-called “twilight zone” of the ocean, it demonstrates that even well-known dive destinations hold secrets in their deeper waters. The discovery of this wrasse serves as a beautiful reminder of the scientific expertise emerging from local communities.
6. 6. The St. George’s Cross Medusa (New Medusa Jellyfish Species)

Image from Earth.com
Discovered in the depths of the Pacific Ocean, this striking jellyfish is instantly recognizable by a brilliant red cross pattern displayed prominently in the center of its bell. The vibrant cross, contrasting sharply with its translucent body, gives it the common name, evoking the heraldic emblem. This new species is about four inches across, making it a medium-sized gelatinous marvel. The discovery of this mesmerizing creature emphasizes how much of the deep-sea pelagic zone remains unexplored and uncataloged. Beyond its unique visual characteristics, researchers are keen to study its venom, which may hold potential for new therapeutic compounds. The appearance of the distinct cross suggests a warning or an elaborate camouflage, hinting at fascinating ecological interactions yet to be understood.
7. 7. The Nickel Hyperaccumulator Plant (Rinorea niccolifera)

Image from Forest Foundation Philippines
Found on Luzon Island in the Philippines, this unique plant boasts an extraordinary ability to absorb massive amounts of metal, specifically nickel, from the soil. It can accumulate up to 18,000 parts per million of the heavy metal in its tissues without suffering any toxic effects, truly earning its title of “hyperaccumulator.” This remarkable physiological trait gives the plant significant potential in phytoremediation, the use of plants to clean contaminated soils. Its discovery opens new avenues for green technologies that could help reclaim mining sites or areas polluted by industrial waste. The plant’s specialized adaptation showcases a fascinating example of evolutionary response to mineral-rich, serpentine soils, transforming a toxic environment into a niche for survival.
8. 8. The Myloplus sauron (Vegetarian Piranha/Pacu)

Image from CNN
Named after the villain Sauron from The Lord of the Rings, this new species of vegetarian piranha, or pacu, was discovered in the Brazilian Amazon. The fish earned its dramatic name due to its striking appearance: a large, circular black stripe that covers its flank, contrasting with flame-orange fins, which scientists felt resembled the Eye of Sauron. The discovery of Myloplus sauron highlights the rich and often underappreciated diversity of the Amazon’s aquatic life. Although a vegetarian, unlike its famous piranha cousins, its robust teeth are specialized for crushing nuts and fruit. This species’ unique morphology suggests a very specific, isolated evolutionary path, emphasizing how much of the Amazon’s ichthyofauna remains a mystery to science.
9. 9. Webala’s Horseshoe Bat (Rhinolophus webalai)
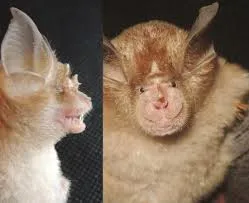
Image from Species New to Science
Hidden among previously collected specimens of horseshoe bats, this distinct species was finally recognized as new through detailed morphological and genetic analysis. Named after Dr. Paul Waswa Webala, a prominent African bat biologist, the species is found in Kenya, adding another crucial piece to the puzzle of African bat diversity. Horseshoe bats are complex to classify due to their subtle physical differences and widespread distribution. This species’ recognition resulted from a careful review of its acoustic calls and cranial features, revealing a separate evolutionary lineage. The formal description highlights the important role of museum collections and modern DNA sequencing in uncovering hidden species diversity even within well-studied animal groups.
10. 10. The ‘Black-Souled’ Aphelandra (Aphelandra almanegra)

Image from Phytotaxa - Magnolia Press
Found in Colombia, this stunning shrub species belongs to a genus popular as houseplants, but this new discovery stands out dramatically. Researchers dubbed it the “black-souled” aphelandra because the center heartwood of the shrub is distinctly black. This unique characteristic is what gives it the species epithet almanegra, which literally translates to black soul. The shrub can reach a height of up to 16 feet and produces spikes covered in hundreds of tiny, delicate pink flowers, creating a magnificent contrast with its dark core. Unfortunately, despite its recent discovery, the species is already considered threatened due to rapid habitat loss from human activities. The finding serves as a poignant reminder that many species may vanish before they are fully understood or even named.
11. 11. The Balete’s Shrew-Like Mouse (Baletemys kampalili)
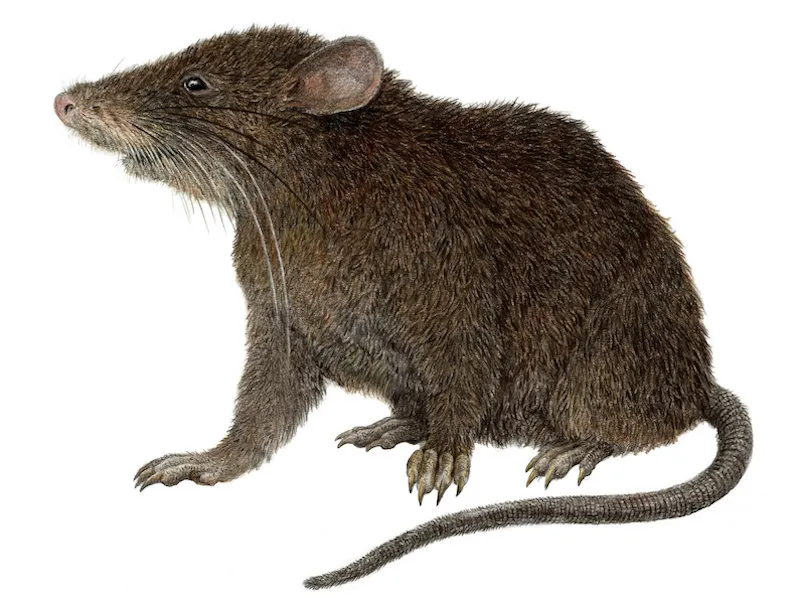

Image from MindaNews
This new genus and species of shrew-like mouse was discovered on Mount Kampalili in Mindanao, Philippines. It was named to honor the late Filipino biologist Danilo Balete, whose extensive field work was instrumental in its discovery. This tiny mammal represents a new lineage, adding significantly to the known mammalian fauna of the Philippines. The discovery of Baletemys kampalili illustrates the importance of the Philippines as a global biodiversity hotspot, particularly for small mammals. Its unique shrew-like features distinguish it from other rodents in the area, suggesting a specialized ecological role within its mountainous habitat. Such discoveries underline the unique evolutionary radiations that occur in isolated island ecosystems.
12. 12. The Anguiculus dicaprioi (Snake)

Image from Down To Earth
A copper-colored snake with a small, domed snout, this species was discovered in the Indian Himalayas and was named after actor and environmentalist Leonardo DiCaprio. This unique naming decision was made to honor his long-standing commitment to global climate change awareness and biodiversity conservation efforts. Living at high elevations, around 6,000 feet above sea level, the small snake is a secretive reptile with a distinct pattern of small brown spots near its head. Its discovery emphasizes the need for increased conservation focus on the often-overlooked serpentine fauna of the Himalayan mountain ranges. By naming it after a prominent figure, the researchers hope to draw more public attention to the threats facing its remote and delicate ecosystem.
13. 13. The Limnonectes cassiopeia (Giant Fanged Frog)
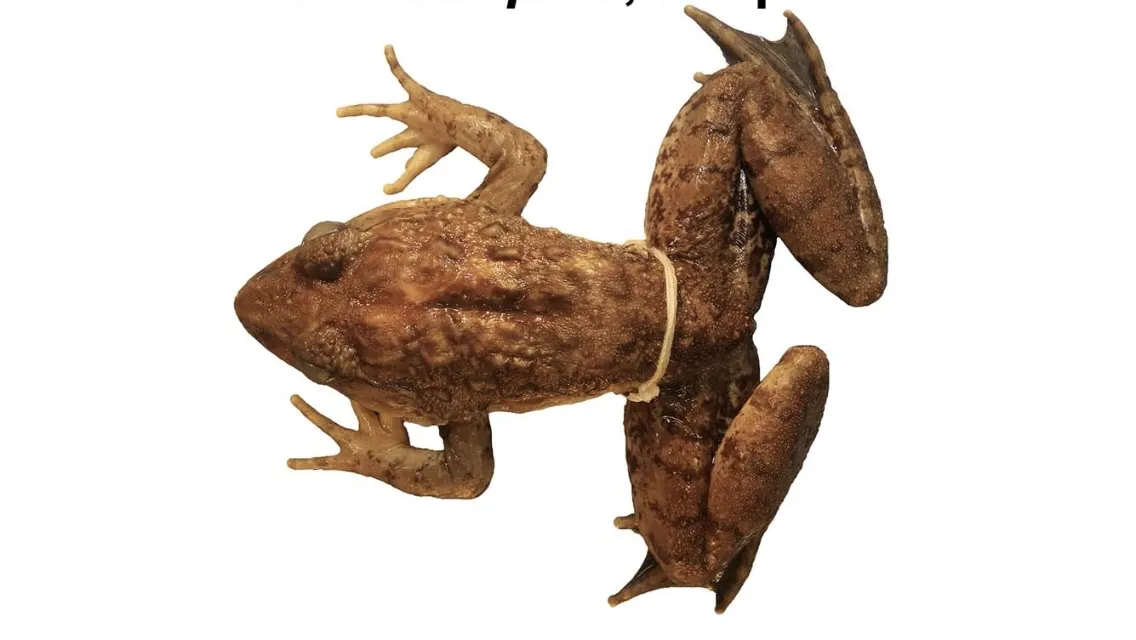

Image from KU News - The University of Kansas
Discovered in the northern Philippines, this giant fanged frog was initially mistaken for a juvenile of a closely related species, the Luzon giant fanged frog. Genetic testing was the key to unlocking its identity, revealing it as a distinct new species, despite its specimens having been collected years ago. A tell-tale feature distinguishing it from its cousin is the color of its toe pads: the newly described species possesses five smaller, distinct white toe pads, a unique trait that inspired its name, reminiscent of the constellation Cassiopeia. This frog species is not considered rare in its local mountain habitat, often living around densely populated towns, showcasing hidden biodiversity literally under human noses.
14. 14. The Tapir Valley Tree Frog (Tlalocohyla celeste)

Image from Magnolia Press
A tiny amphibian, measuring only about two centimeters long, roughly the size of a bottle cap, this vibrant tree frog was discovered in a rewilded reserve in Costa Rica. The small size and bright green coloration make it a jewel of its forest home, but also a difficult species to spot among the dense foliage. This frog’s entire known population is confined to a relatively small area, highlighting the critical role that private nature reserves and rewilding efforts play in safeguarding vulnerable micro-endemics. The discovery of Tlalocohyla celeste demonstrates that even heavily impacted landscapes can quickly begin to recover and reveal their hidden, unique biodiversity when given the chance.
15. 15. The Deep-Sea Isopod (Booralana nickorum)
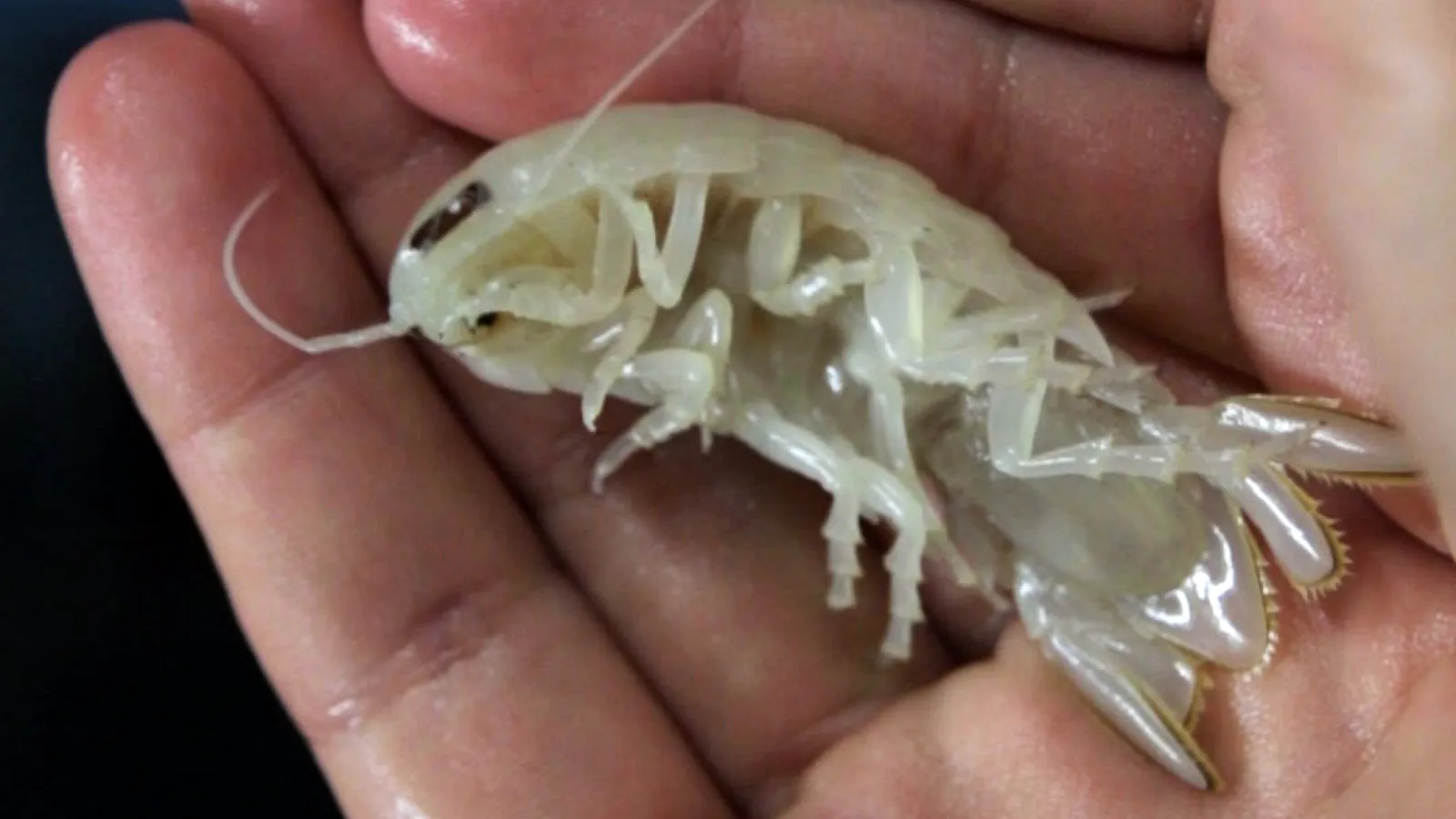
Image from Live Science
This peculiar underwater crustacean, a relative of the terrestrial roly-poly or woodlouse, was recently discovered in the deep waters of the Bahamas. As an isopod, it possesses a segmented body and a scavenging lifestyle, playing an important ecological role in the dark, abyssal plain. The find was part of an extensive survey of the Caribbean’s deep-sea fauna, revealing the staggering biodiversity that exists far beneath the sunlit surface. Booralana nickorum contributes to the increasing list of unique life forms thriving in the deep ocean, often in environments subjected to extreme pressure and low nutrient availability. Its discovery is a testament to the potential for new life in the planet’s vast, unexplored oceanic depths.
16. 16. The Caecilia tesoro (Limbless Amphibian)

Image from AmphibiaWeb
One of two new caecilians described from the Tesoro Escondido Reserve in Ecuador, this species is a limbless, snake-like amphibian that spends most of its life burrowed in the soil. Caecilians are often overlooked due to their subterranean and secretive nature, making their formal description a significant event. Interestingly, this particular species has been observed in at least two distinct color morphs, including a striking yellow variety, which adds to its uniqueness. The discovery emphasizes the rich and unique herpetofauna of the Ecuadorian Andes and highlights how habitat-specific reserves are crucial for protecting these elusive amphibians. Studying its soil-dwelling life cycle can offer new insights into amphibian evolution.
17. 17. The Papillated Redbait (Emmelichthys papillatus)

Image from NOAA Fisheries
Discovered at a fish market in the Philippines, this new species of fish, known locally by its Tagalog name, rebentador pula, was identified not by a researcher at sea but by observing subtle differences in fish being sold. The key distinguishing features were its eye size and fin length. The process of its discovery, starting at a commercial fish auction, highlights how traditional ecological knowledge and careful observation of commercial catches can lead to formal scientific findings. Its presence in the fish market indicates it is part of the local fishery, raising immediate questions about its population status and the need for sustainable management practices.
18. 18. The Nepenthes barcelonae (Pitcher Plant)

Image from A garden’s chronicle
Named in honor of Filipino botanist Julie F. Barcelona, this new species of carnivorous pitcher plant was discovered in the montane tropical rainforests of the Philippines. It possesses a distinctive pitcher shape and mouth, producing red, larger, and stouter pitchers that act as pitfall traps for insects. The plant’s unique morphology sets it apart from other Philippine Nepenthes species, which are already known for their diversity. The discovery of a new carnivorous plant in an established genus underscores the specialized evolutionary niches in island ecosystems. Its presence reinforces the importance of preserving the pristine, high-elevation forests where such highly specialized life forms thrive.
19. 19. The Bent-toed Gecko (Cyrtodactylus santana)

Image from iNaturalist
Discovered in the Lene Hara cave within the Nino Konis Santana National Park in the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, this represents the first bent-toed gecko to be described to the species level in the country. Initially elusive, multiple individuals were eventually caught at night, confirming their nocturnal habits. Genetic and morphological analysis confirmed that this population was a previously undescribed species. This finding is significant for Timor-Leste, a country where biological surveying has been historically limited, suggesting a wealth of undescribed species still exists. The species name is derived from the national park, honoring a local freedom fighter.
20. 20. The Southern Maned Sloth (Bradypus crinitus)

Image from iNaturalist
What was previously thought to be a single species of maned sloth was reclassified into two distinct species following a comprehensive review of DNA, morphology, and behavior. The newly recognized Southern Maned Sloth is distinguished by its flatter skull and a unique head of fur that researchers described as resembling a coconut. Its name, crinitus, meaning ‘hairy,’ perfectly describes its shaggy mane, a feature that distinguishes it from its northern counterpart. This taxonomic split means that the Southern Maned Sloth has a more restricted distribution. The discovery emphasizes how cryptic species, those that look alike but are genetically distinct, can hide in plain sight for decades.