20 Royals Who Broke All the Rules and Changed History
Some royals followed tradition, but others stood out by breaking the mold. These powerful figures dared to defy expectations, changing the world around them in bold and lasting ways. Discover how 20 royals went against the rules to shape history forever.
- Tricia Quitales
- 5 min read

Royal families are known for their strict traditions, but not everyone followed the rules. From fighting for freedom to marrying for love, these 20 royals changed what it means to wear a crown. Their choices led to revolutions, reform, and even inspired entire nations. These stories prove that rule-breakers often leave the greatest legacy.
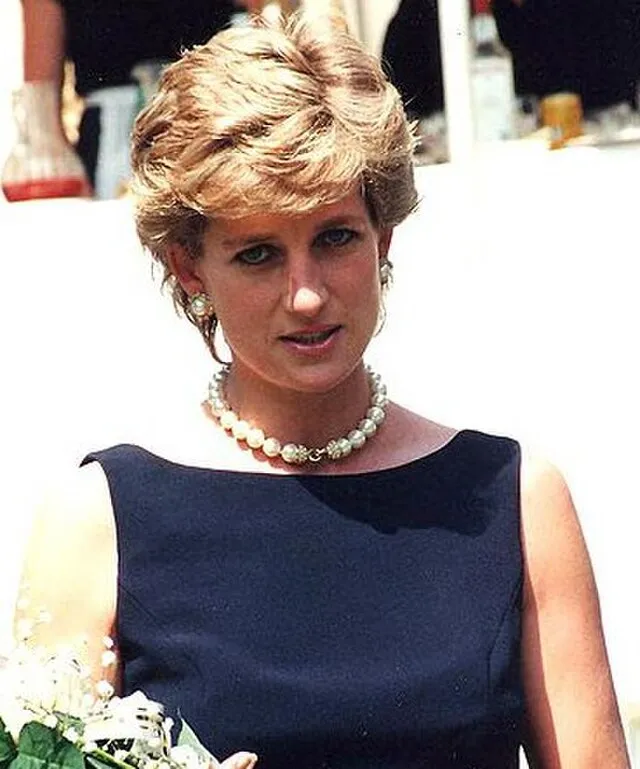
1. Princess Diana (United Kingdom)
 Nick Parfjonov on Wikimedia
Nick Parfjonov on Wikimedia
Diana challenged royal traditions by openly speaking about mental health and personal struggles. She connected with people through charity work, breaking royal protocol by showing public affection. Her honesty and kindness won hearts around the world and modernized the image of the monarchy.
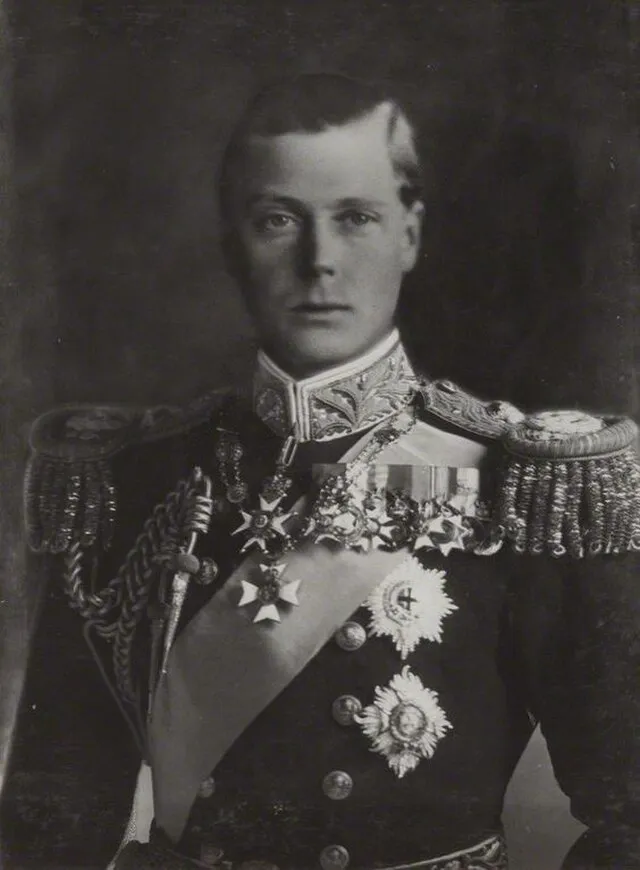
2. King Edward VIII (United Kingdom)
 Lafayette Ltd on Wikimedia
Lafayette Ltd on Wikimedia
Edward gave up the British throne to marry Wallis Simpson, an American divorcée. His decision shocked the world and caused a constitutional crisis. It marked a turning point in how personal love could challenge royal duty.
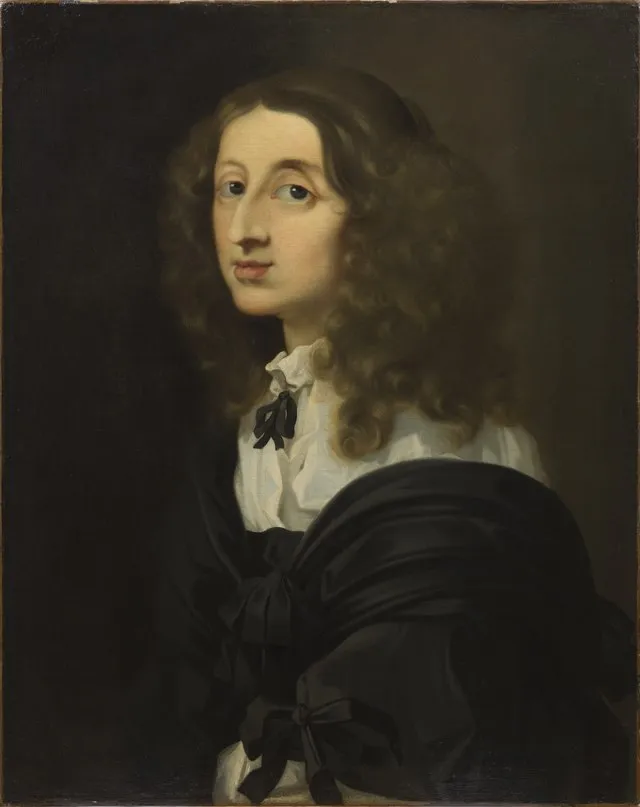
3. Queen Christina (Sweden)
 Sébastien Bourdon on Wikimedia
Sébastien Bourdon on Wikimedia
Christina refused to marry, wore men’s clothes, and gave up her crown. She converted to Catholicism in Protestant Sweden and moved to Rome. Her independent spirit made her one of the most unconventional queens in history.
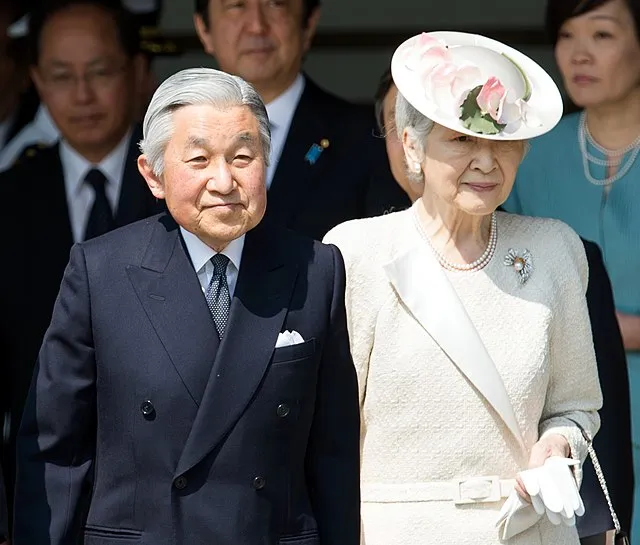
4. Emperor Akihito (Japan)
 East Asia and Pacific Media Hub on Wikimedia
East Asia and Pacific Media Hub on Wikimedia
Akihito married a commoner, Michiko, breaking centuries of royal tradition. He also made efforts to connect with ordinary people and expressed regret for Japan’s wartime actions. His reign brought the monarchy closer to the people.
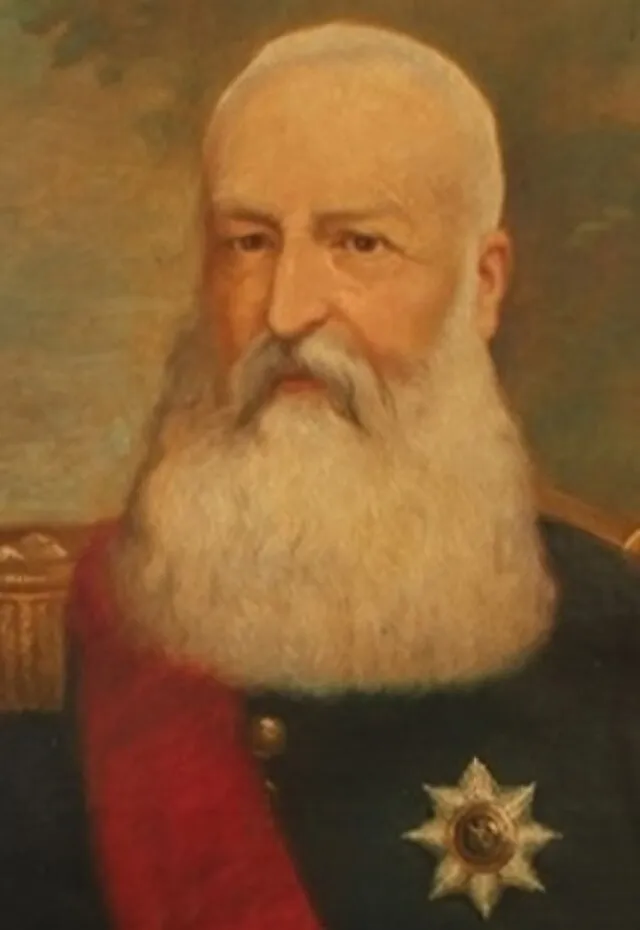
5. King Leopold II (Belgium)
 Albert Dillens on Wikimedia
Albert Dillens on Wikimedia
Though remembered for his brutal rule in Congo, Leopold’s actions broke ethical and political norms of his time. He treated a colony as personal property, sparking international outrage, which led to changes in how colonial powers were held accountable.
6. Marie Antoinette (France)
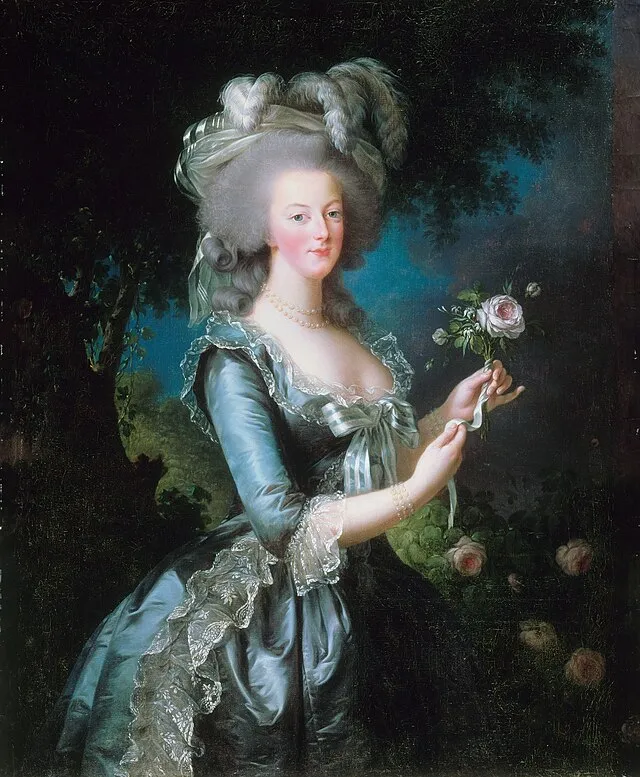 Élisabeth Louise Vigée Le Brun on Wikimedia
Élisabeth Louise Vigée Le Brun on Wikimedia
Often blamed for the French Revolution, Marie Antoinette defied court customs with her lavish lifestyle. She also pushed fashion boundaries and resisted strict court rules. Her rebellion against tradition made her both hated and iconic.
7. King Henry VIII (England)
 Royaltynow on Wikimedia
Royaltynow on Wikimedia
Henry broke from the Catholic Church to divorce his wife and marry Anne Boleyn. He founded the Church of England, which forever changed religion in Britain. His bold move combined personal desire with political revolution.
8. Princess Märtha (Norway)
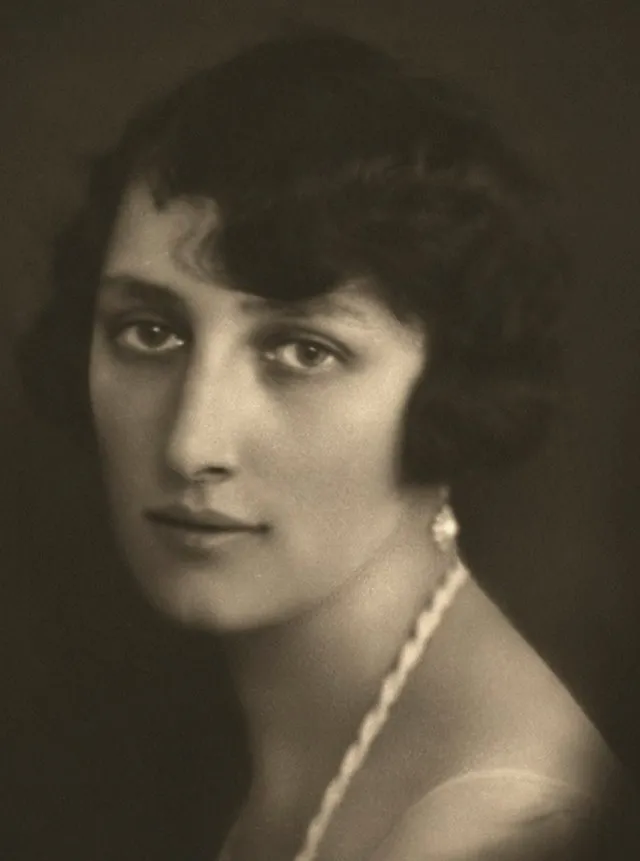 Bernadotte Library on Wikimedia
Bernadotte Library on Wikimedia
Märtha was never crowned queen but played a vital role during WWII. She built strong ties with the U.S. and influenced President Roosevelt’s support for Norway. Her diplomacy helped shape Norway’s future during a critical time.
9. Catherine the Great (Russia)
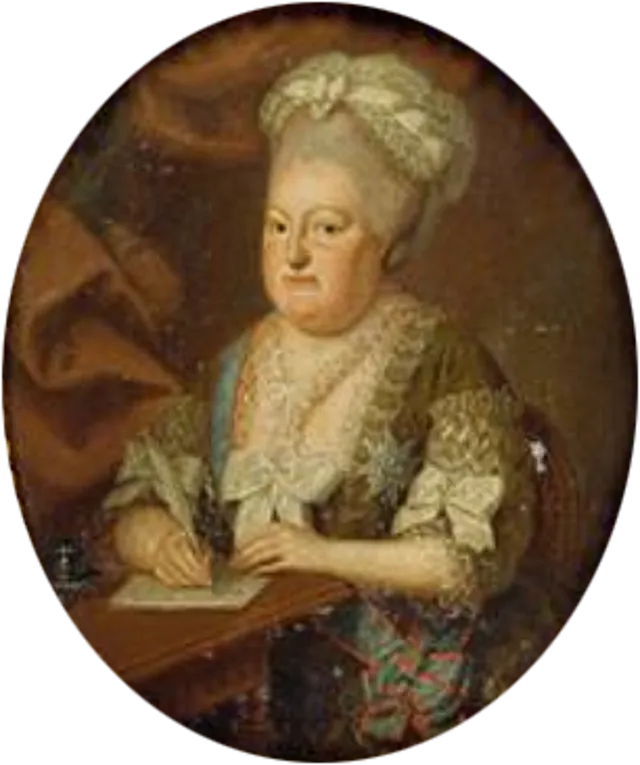 Unidentified painter on Wikimedia
Unidentified painter on Wikimedia
Catherine seized power from her husband in a coup and ruled with strength. She modernized Russia, expanded its territory, and supported the arts. Her reign changed Russia’s future and inspired female rulers.
10. Prince Harry (United Kingdom)
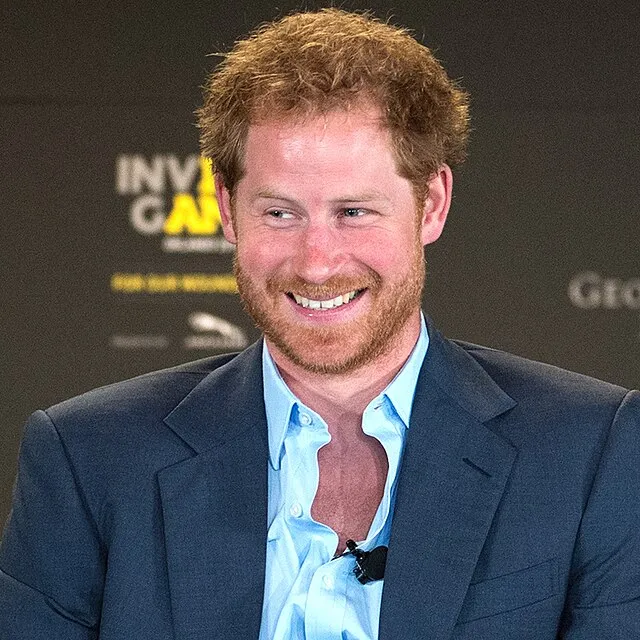 EJ Hersom on Wikimedia
EJ Hersom on Wikimedia
Harry chose to leave royal duties and move to the U.S. with Meghan Markle. His openness about mental health and media pressure broke centuries of royal silence. He showed that personal well-being can outweigh royal expectations.
11. King Ludwig II (Bavaria)
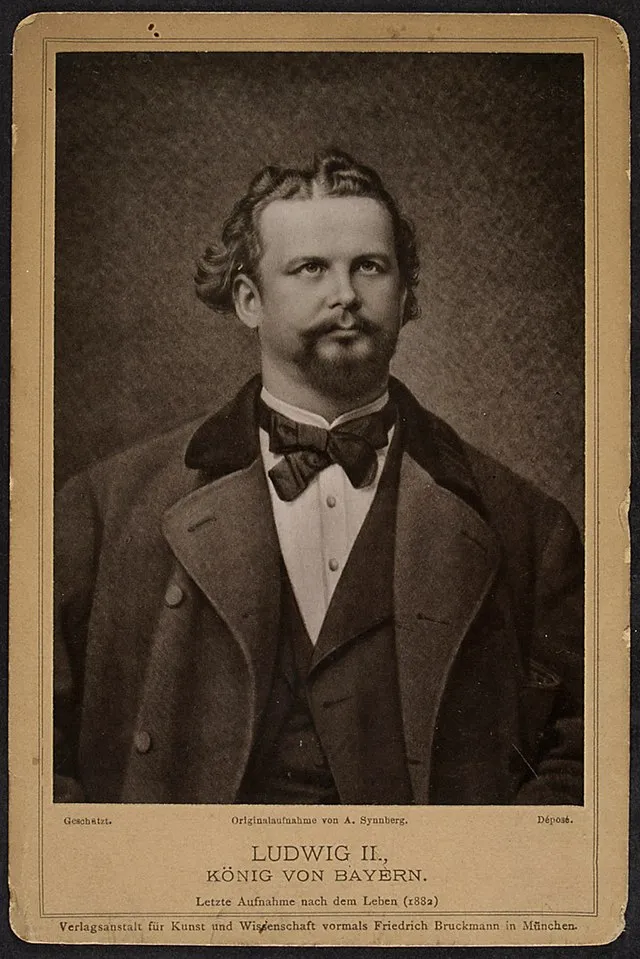 Arthur Synnberg on Wikimedia
Arthur Synnberg on Wikimedia
Ludwig defied political duties to build grand fairytale castles. He focused on art, music, and fantasy over governance. Though seen as eccentric, he left behind iconic landmarks and a legacy of cultural beauty.
12. Queen Rania (Jordan)
 Office of USAID Administrator on Wikimedia
Office of USAID Administrator on Wikimedia
Rania uses her position to promote education, women’s rights, and social justice. She speaks openly about modernizing the Middle East and challenges stereotypes. As a queen, she redefines what royal influence can achieve.
13. King Juan Carlos I (Spain)
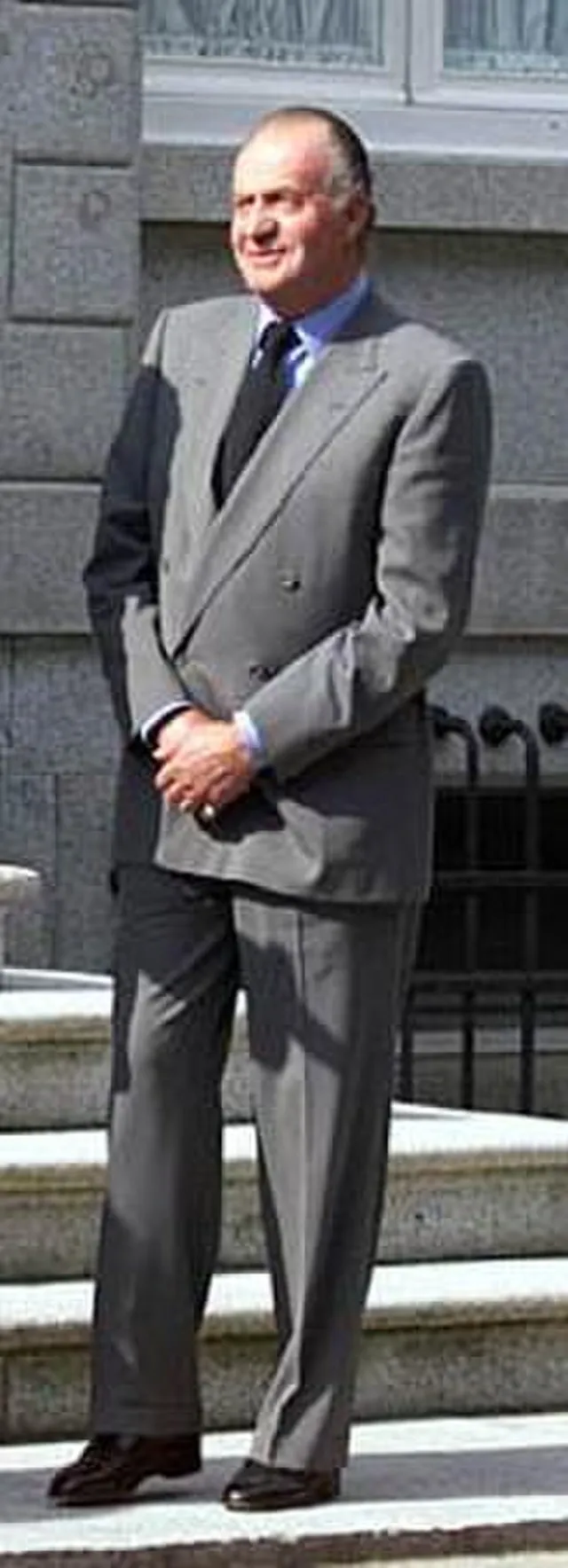 Paul Morse on Wikimedia
Paul Morse on Wikimedia
After Franco’s dictatorship, Juan Carlos led Spain back to democracy. He rejected absolute power and supported a constitutional monarchy. His decision reshaped Spain’s future and brought freedom back to the people.
14. Tsar Nicholas II (Russia)
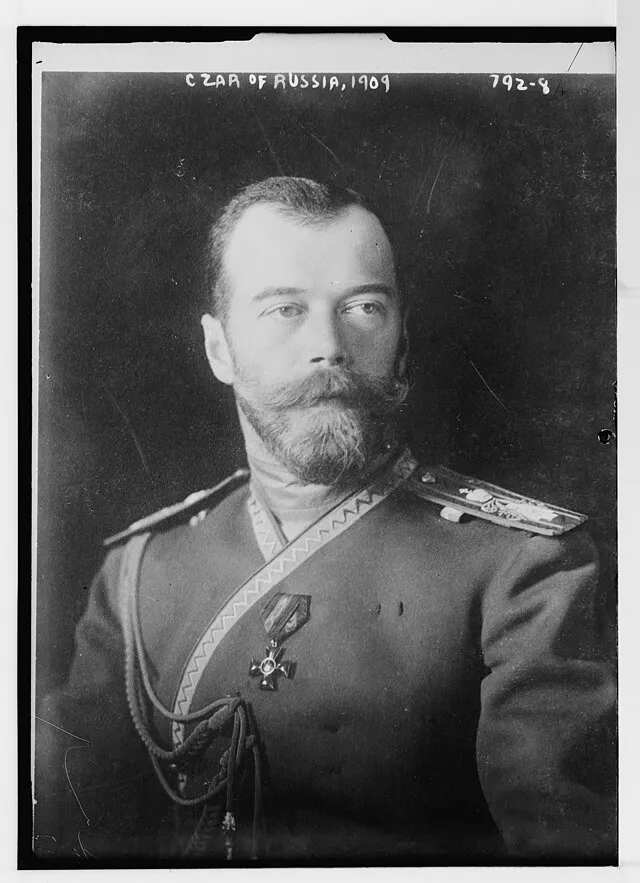 Bain News Service, publisher on Wikimedia
Bain News Service, publisher on Wikimedia
Nicholas ignored rising political unrest and held on to autocratic rule. His refusal to adapt led to the Russian Revolution and the end of the monarchy. His actions serve as a cautionary tale of ignoring change.
15. Princess Stéphanie (Monaco)
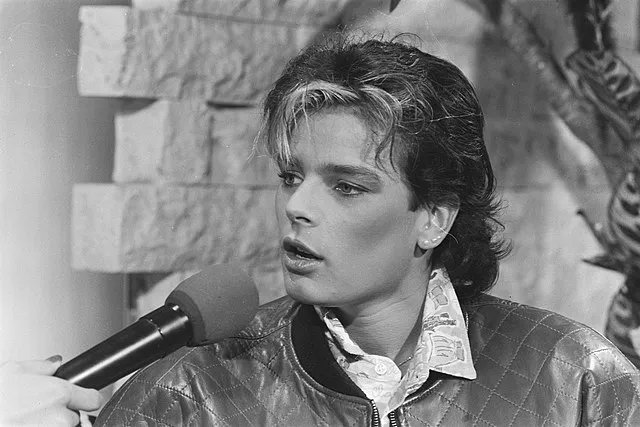 Roland Gerrits / Anefo on Wikimedia
Roland Gerrits / Anefo on Wikimedia
Stéphanie rejected a royal lifestyle and pursued careers in fashion and music. She had public relationships and raised her children outside palace traditions. Her free-spirited choices made headlines and questioned royal roles.
16. King Farouk (Egypt)
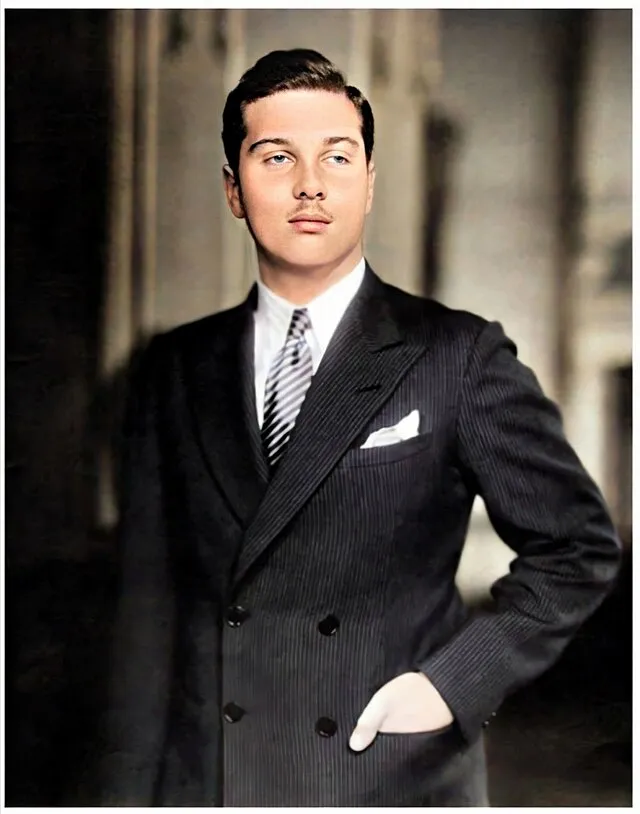 Omario charia on Wikimedia
Omario charia on Wikimedia
Farouk lived extravagantly while his country suffered, breaking moral expectations. His poor leadership led to Egypt abolishing the monarchy. He remains a symbol of how corruption can destroy royal power.
17. Queen Liliʻuokalani (Hawaii)
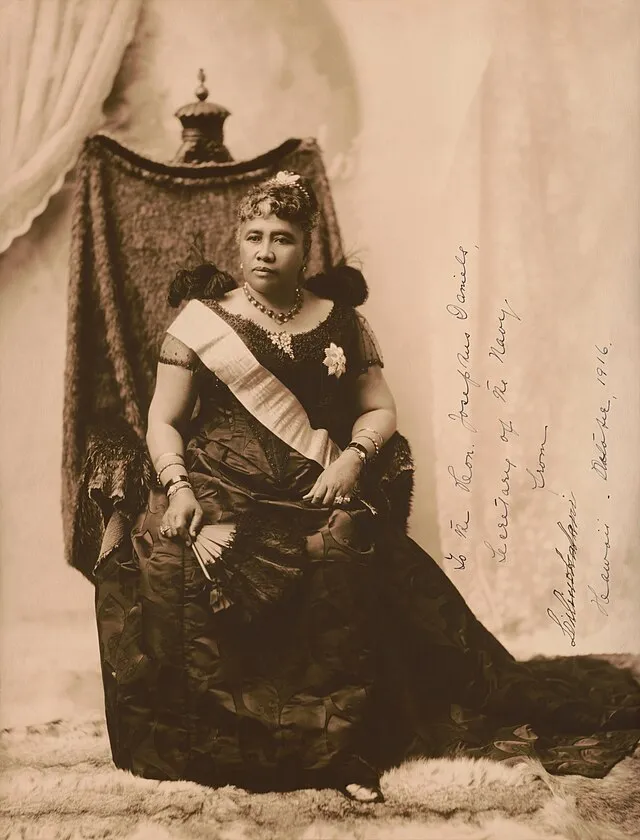 James J. Williams / Adam Cuerden on Wikimedia
James J. Williams / Adam Cuerden on Wikimedia
She tried to protect her people’s rights as foreign powers threatened her kingdom. After being overthrown, she still fought for Hawaiian independence. Her leadership remains a powerful symbol of resistance and identity.
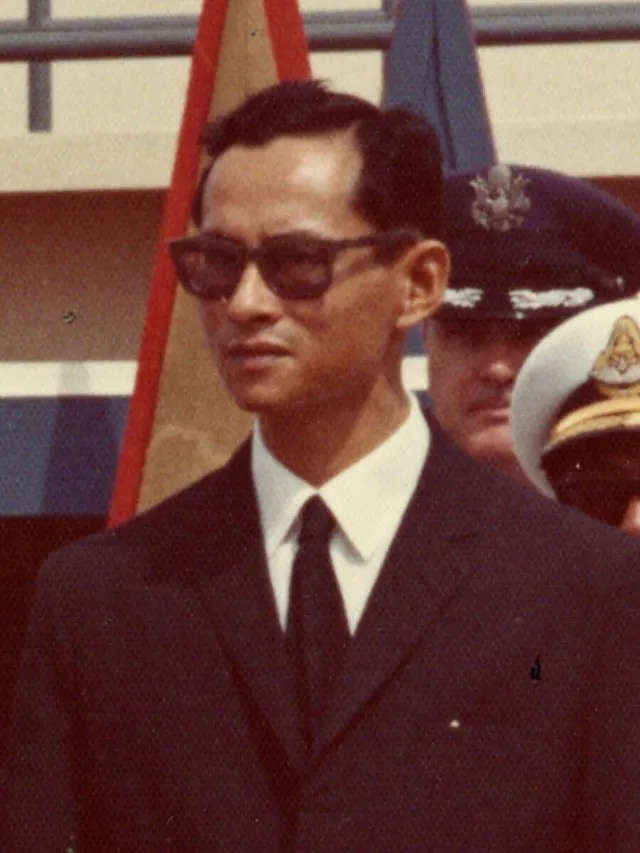
18. King Bhumibol Adulyadej (Thailand)
 Unknown author on Wikimedia
Unknown author on Wikimedia
Bhumibol broke tradition by deeply engaging with his people’s problems. He traveled the countryside and supported grassroots projects. His hands-on leadership style earned him deep respect.
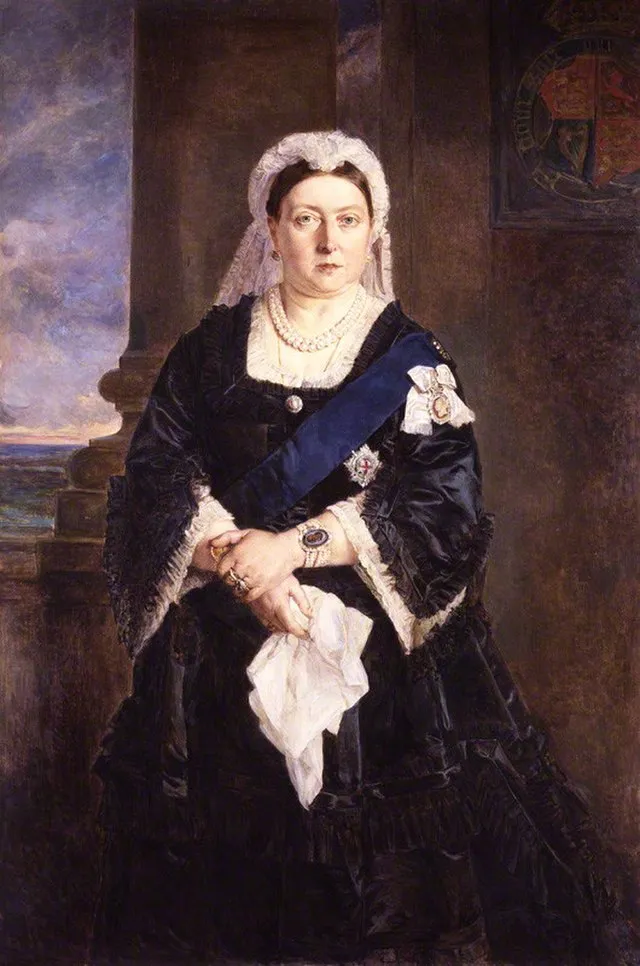
19. Queen Victoria (United Kingdom)
 Julia Abercromby, Baroness Abercromby on Wikimedia
Julia Abercromby, Baroness Abercromby on Wikimedia
Victoria ruled during a time of huge change and expanded the empire. She influenced everything from fashion to politics. Her long reign shaped an entire era and shifted how monarchs interacted with the world.
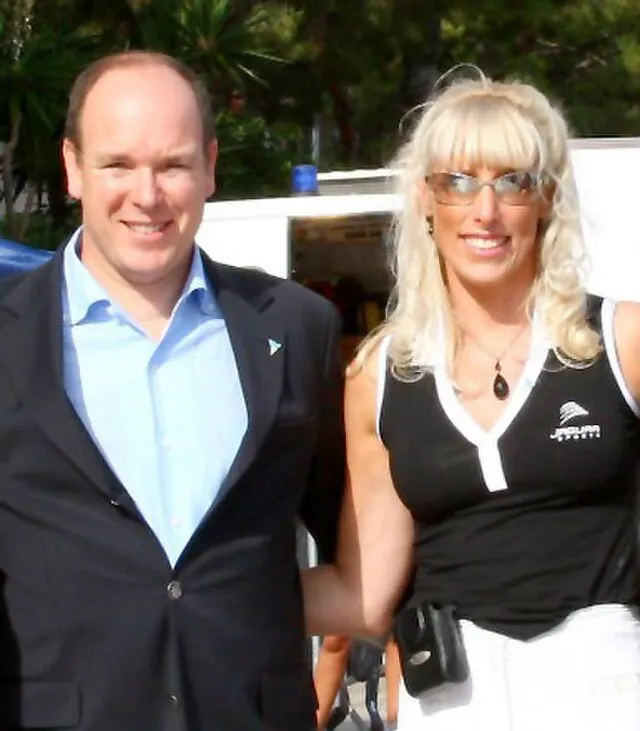
20. Prince Albert II (Monaco)
 SportFiles on Wikimedia
SportFiles on Wikimedia
Albert acknowledged his children, who were born out of wedlock, and married a former Olympic swimmer. He has focused on environmental issues and modern leadership, and his personal and political choices reflect a new royal image.