11 Disasters That Changed Everyday Life Forever
Here's a look at 11 disasters that permanently altered the way people live, work, and interact with the world.
- Alyana Aguja
- 4 min read
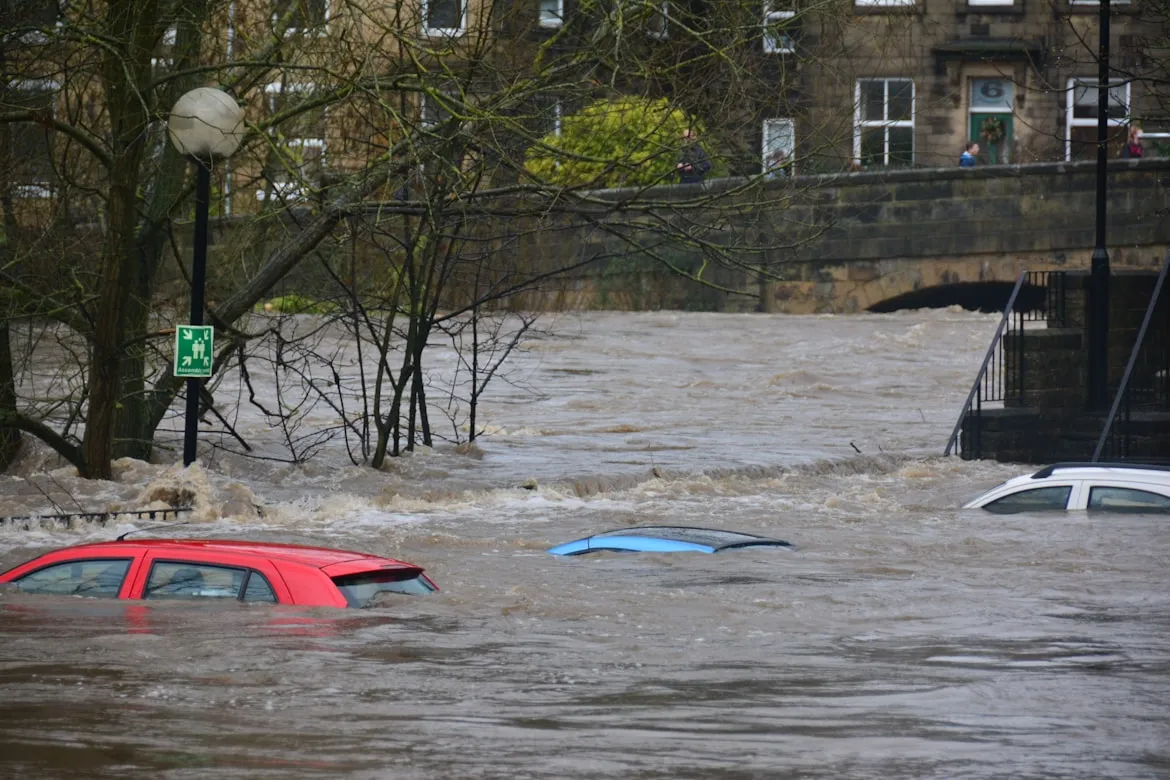

Disasters often leave behind more than destruction; they reshape societies and daily life in lasting ways. From fires and earthquakes to pandemics and financial collapses, these events forced innovations in safety, health, governance, and technology. Each disaster became a turning point that influenced how people build cities, protect workers, travel, and even connect with one another.
1. 1. The Great Fire of London (1666)
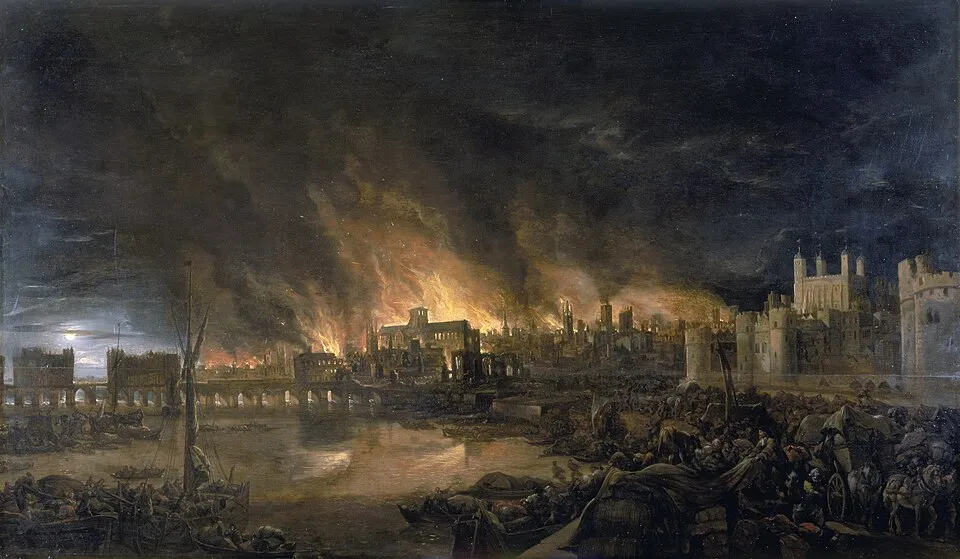

Image from Wikipedia
When the Great Fire swept through London, it destroyed over 13,000 houses and reshaped the way cities were built. Wooden structures gave way to brick and stone, while fire insurance became a new necessity for everyday people. The disaster also led to the creation of organized firefighting services, something we take for granted today.
2. 2. The 1906 San Francisco Earthquake

Image from Wikipedia
The quake and the fires it caused reduced much of San Francisco to rubble, displacing more than half the city’s population. In the aftermath, building codes were strengthened, and urban planning gained new importance. It also pushed advancements in seismology and emergency response systems.
3. 3. The Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire (1911)
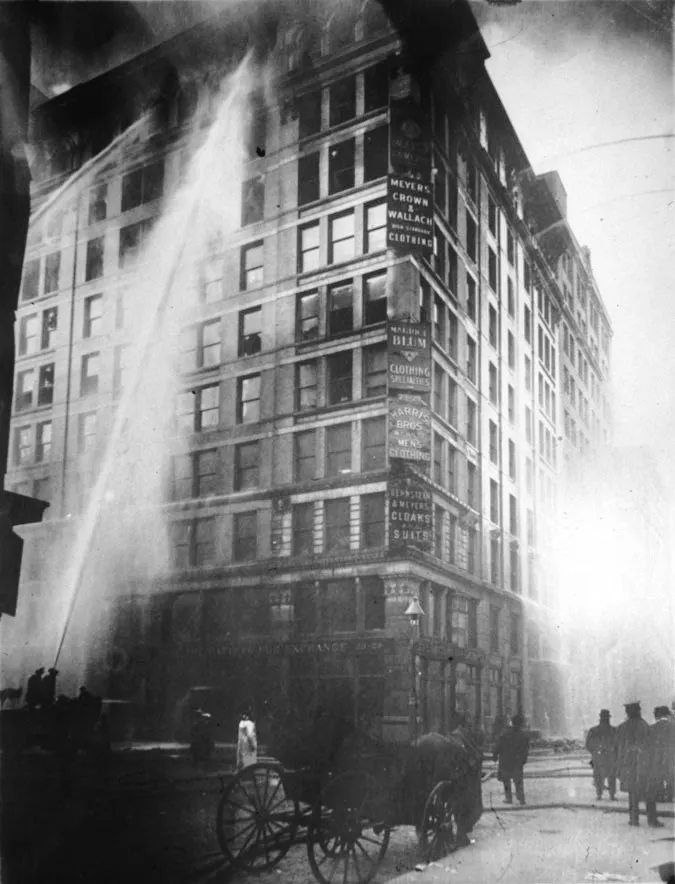

Image from Wikipedia
A fire in a garment factory killed 146 workers, most of them young immigrant women. The tragedy exposed unsafe working conditions and locked doors that trapped victims inside. It spurred major reforms in labor laws, workplace safety standards, and fire regulations.
4. 4. The Spanish Flu Pandemic (1918–1919)
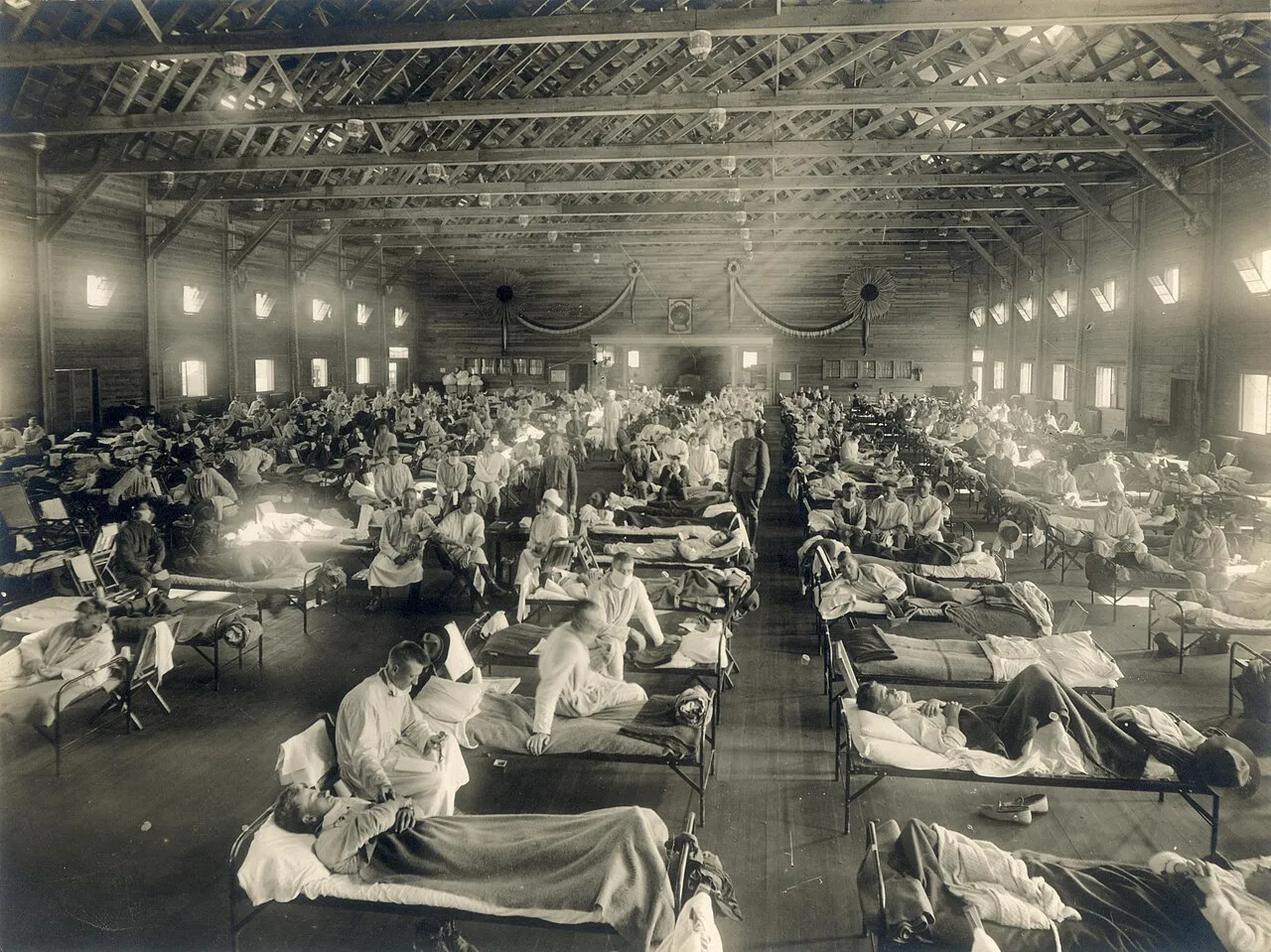
Image from Wikipedia
This influenza outbreak infected a third of the global population and killed millions. The widespread health crisis introduced the use of public mask-wearing and quarantine as community protection measures. It also made governments more proactive in establishing public health systems.
5. 5. The Dust Bowl (1930s)
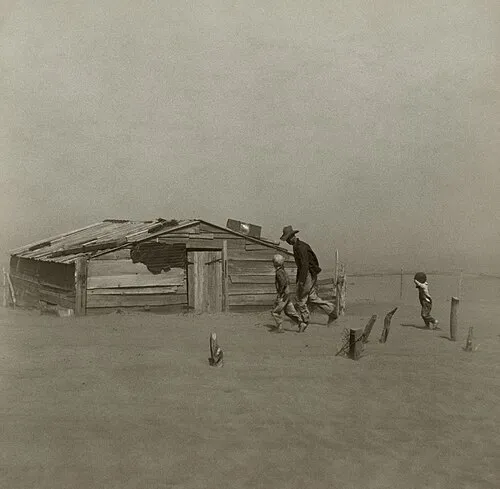

Image from Wikipedia
Severe drought and poor farming practices created massive dust storms across the American Great Plains. Families were forced to migrate, changing the cultural and demographic landscape of the United States. The event led to new agricultural policies, soil conservation programs, and federal disaster relief.
6. 6. The Chernobyl Nuclear Disaster (1986)
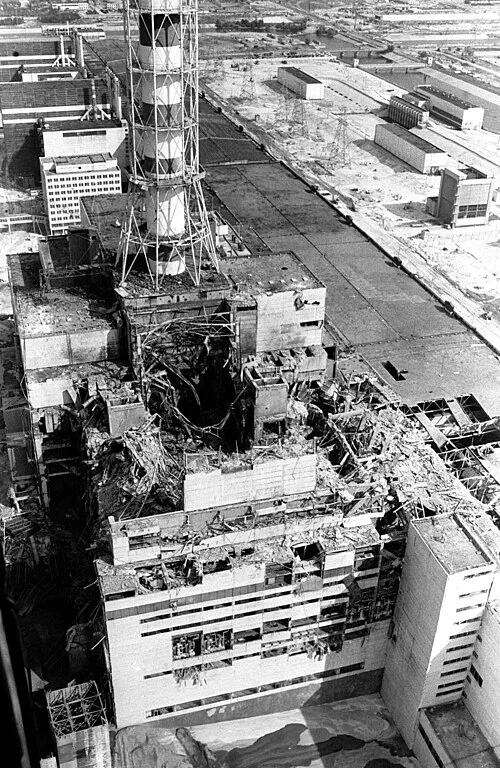

Image from Wikipedia
The explosion at the Chernobyl nuclear plant in Ukraine released radioactive material across Europe. The disaster highlighted the dangers of nuclear power and reshaped global energy policies. It also transformed how governments handled environmental safety, transparency, and emergency preparedness.
7. 7. The Challenger Space Shuttle Explosion (1986)
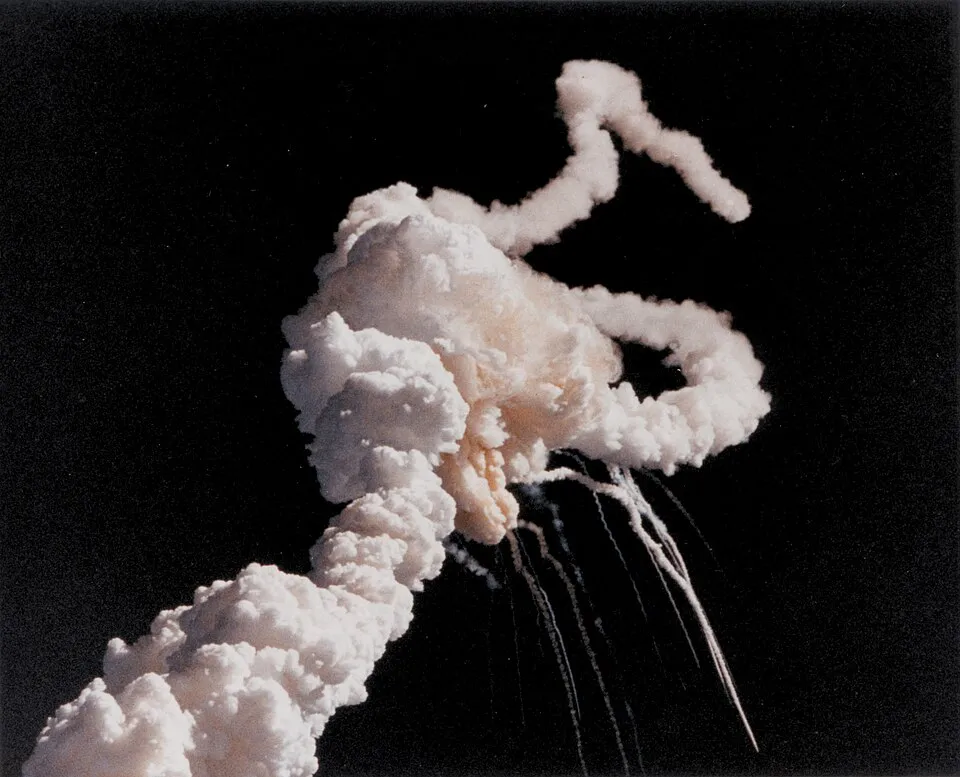

Image from Wikipedia
When the space shuttle Challenger broke apart just after liftoff, it shocked the world. The tragedy revealed flaws in organizational decision-making and engineering oversight at NASA. It reshaped safety procedures in aerospace and reminded the public of the risks of space exploration.
8. 8. The 9/11 Terrorist Attacks (2001)
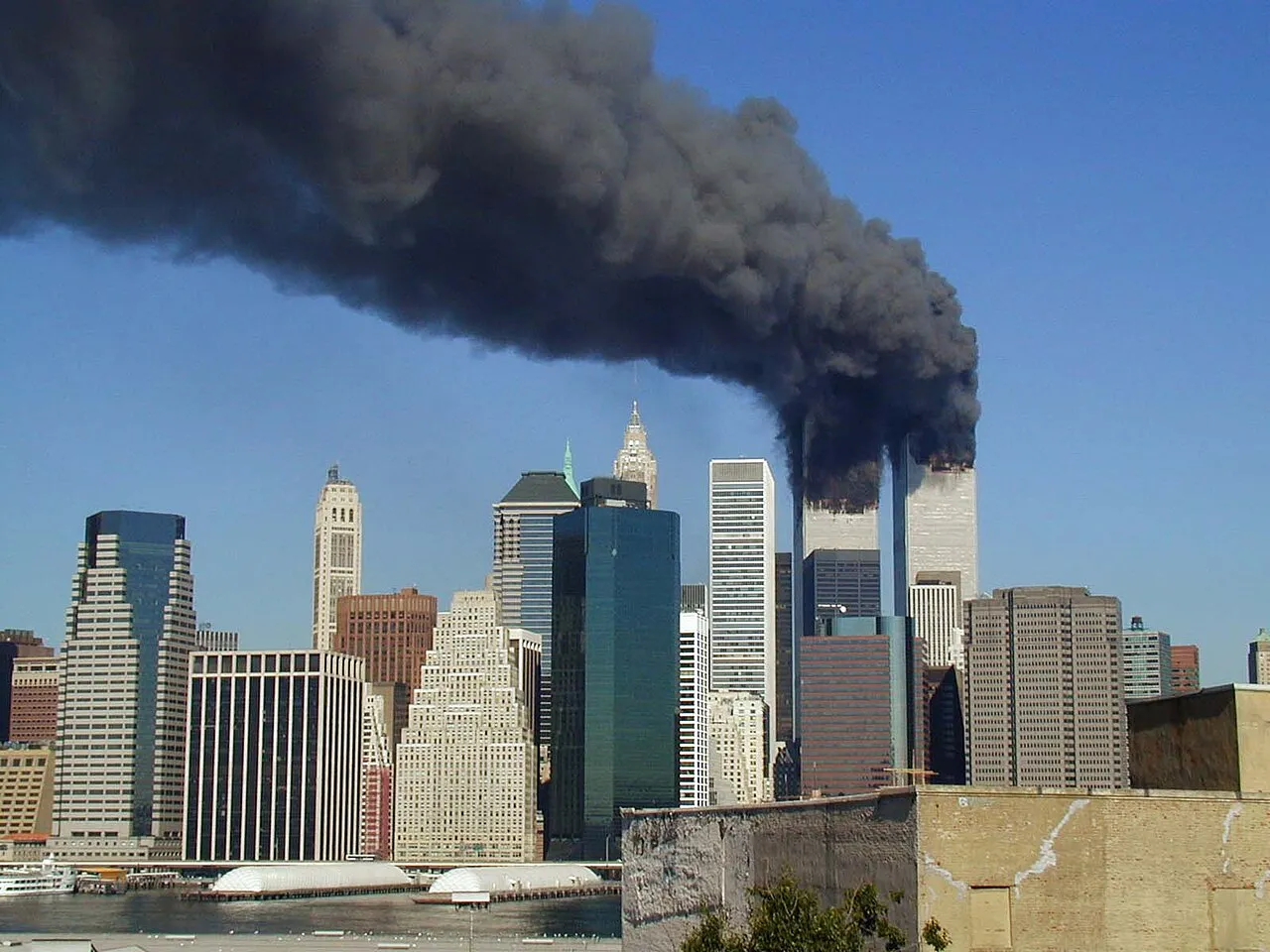

Image from Wikipedia
The September 11 attacks in the United States killed thousands and left a lasting impact on global politics and daily life. Air travel was transformed overnight with new security screenings and restrictions. The disaster also reshaped policies around surveillance, immigration, and counterterrorism worldwide.
9. 9. Hurricane Katrina (2005)
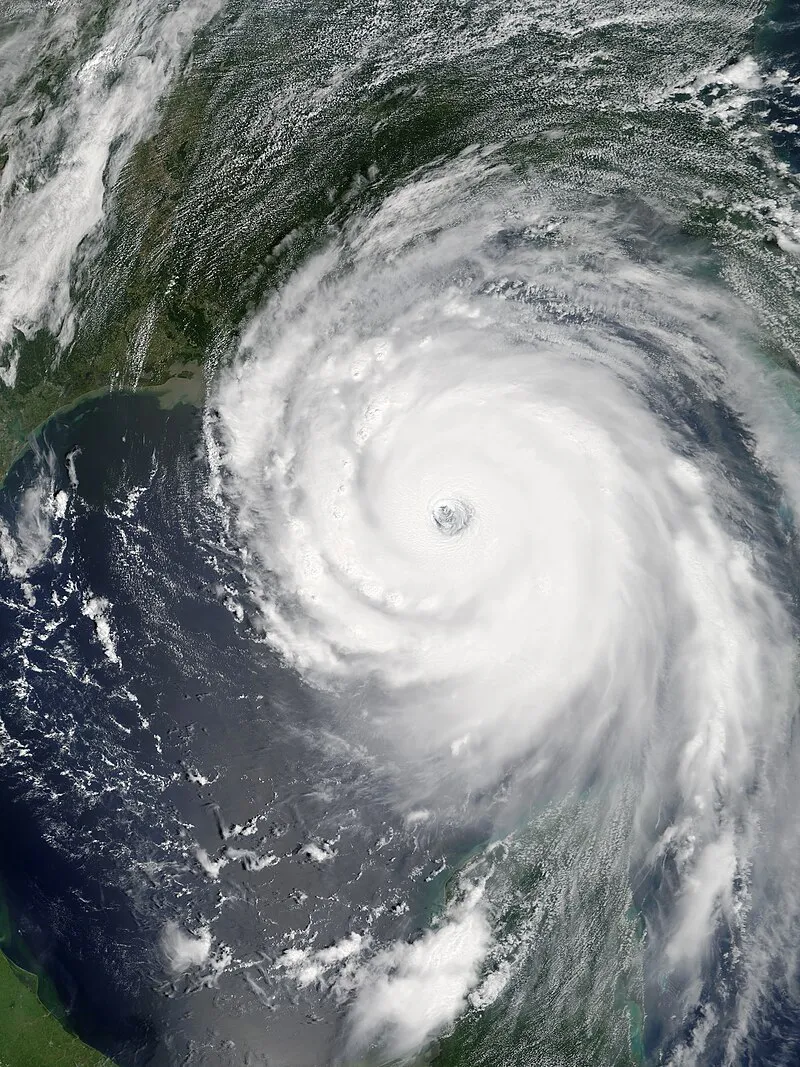

Image from Wikipedia
This powerful storm devastated New Orleans and exposed deep inequalities in disaster response. Flood defenses and emergency management systems came under scrutiny, leading to reforms in how governments prepare for natural disasters. It also brought new awareness to climate change and the vulnerability of coastal cities.
10. 10. The 2008 Global Financial Crisis
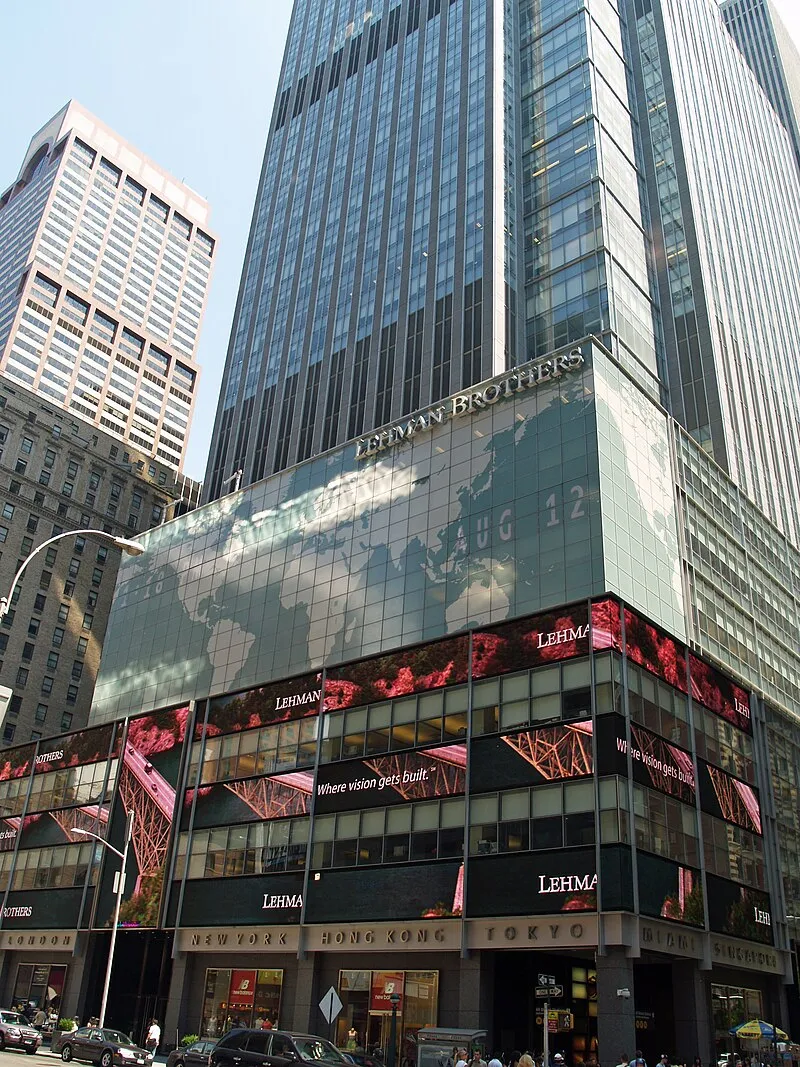

Image from Wikipedia
Triggered by the collapse of housing markets and banking systems, this crisis disrupted economies worldwide. Millions lost jobs and homes, changing attitudes toward debt and financial institutions. It brought about new regulations, stronger consumer protections, and a more cautious approach to personal finance.
11. 11. The COVID-19 Pandemic (2020–2022)
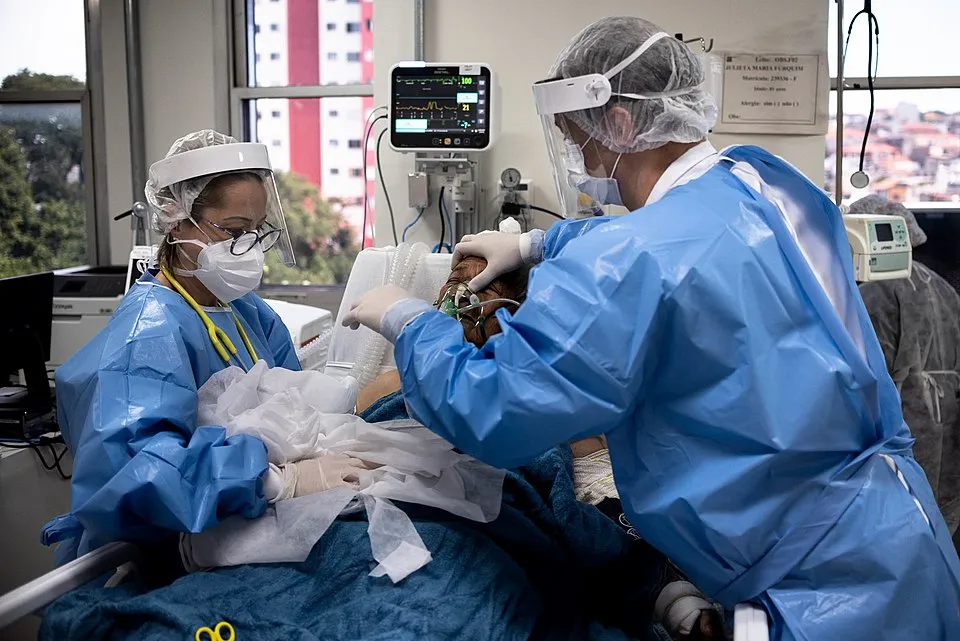
Image from Wikipedia
The pandemic forced lockdowns, remote work, and widespread reliance on digital tools. It reshaped how people learn, shop, and connect, making video calls and online services everyday essentials. The crisis also accelerated medical innovation, including vaccine development and telehealth.